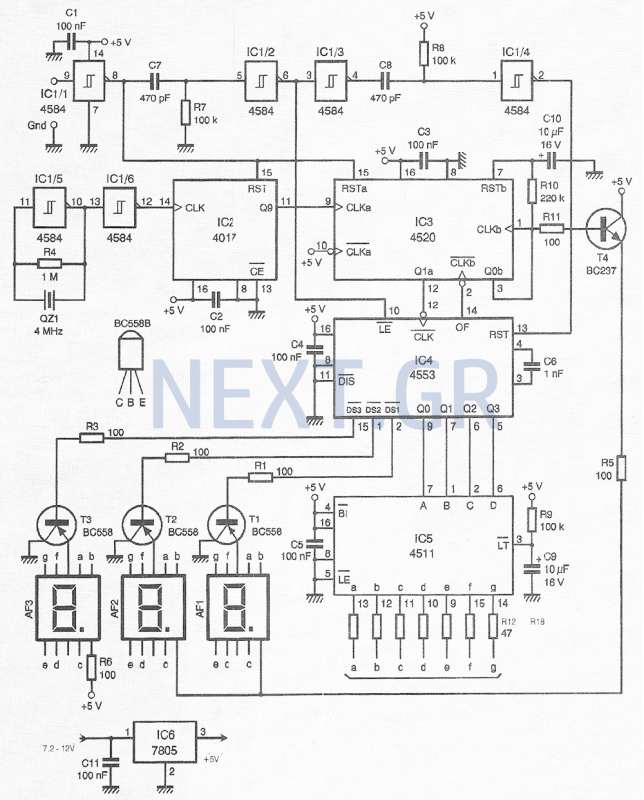
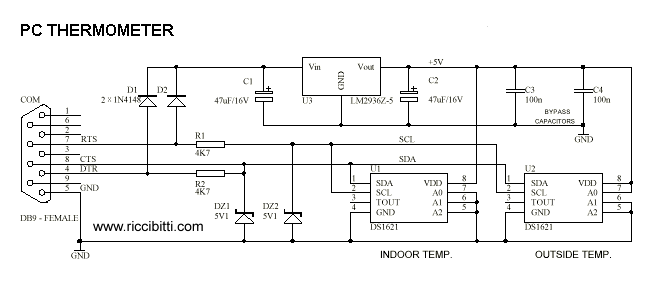
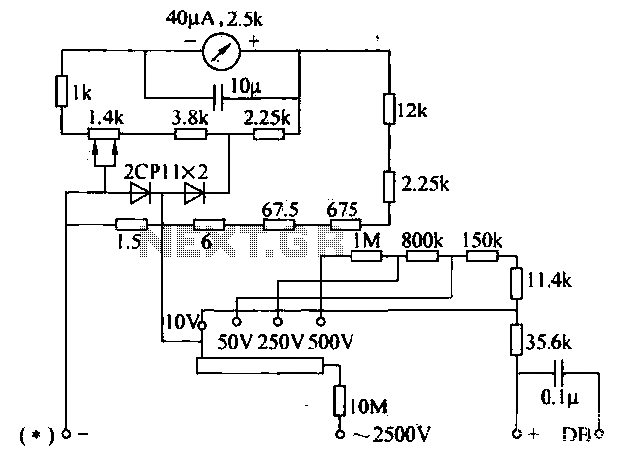
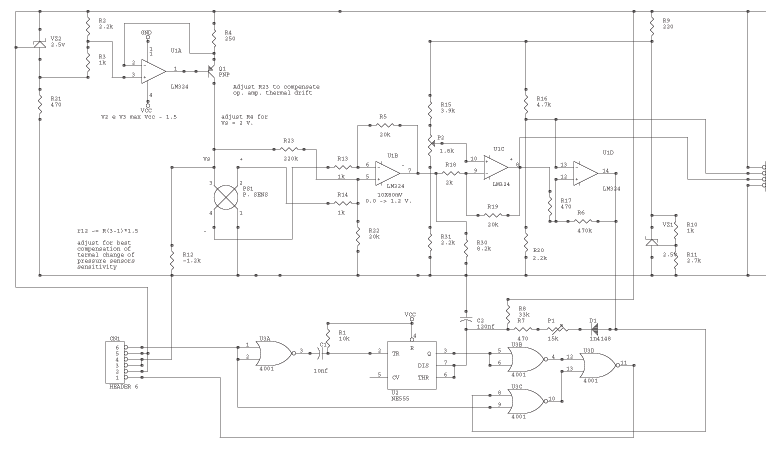
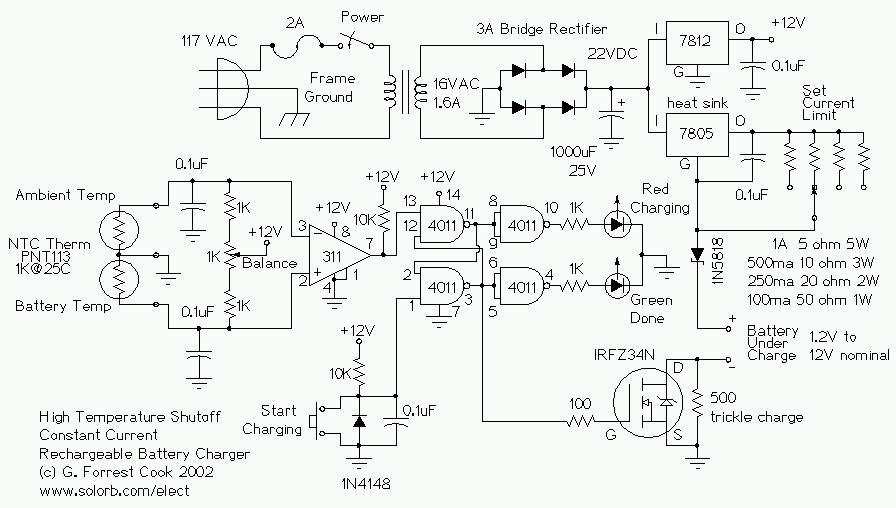
Temperature meter
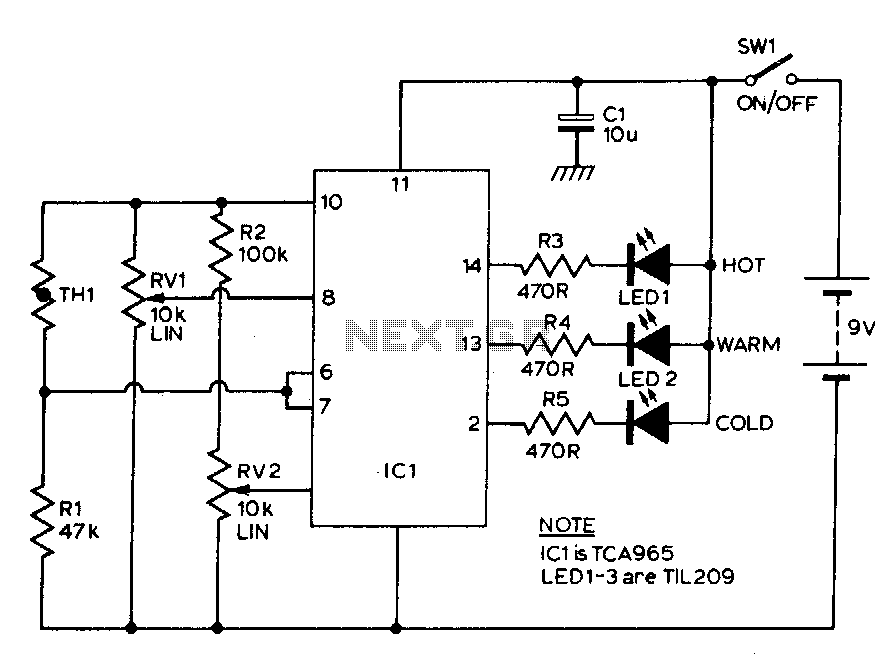
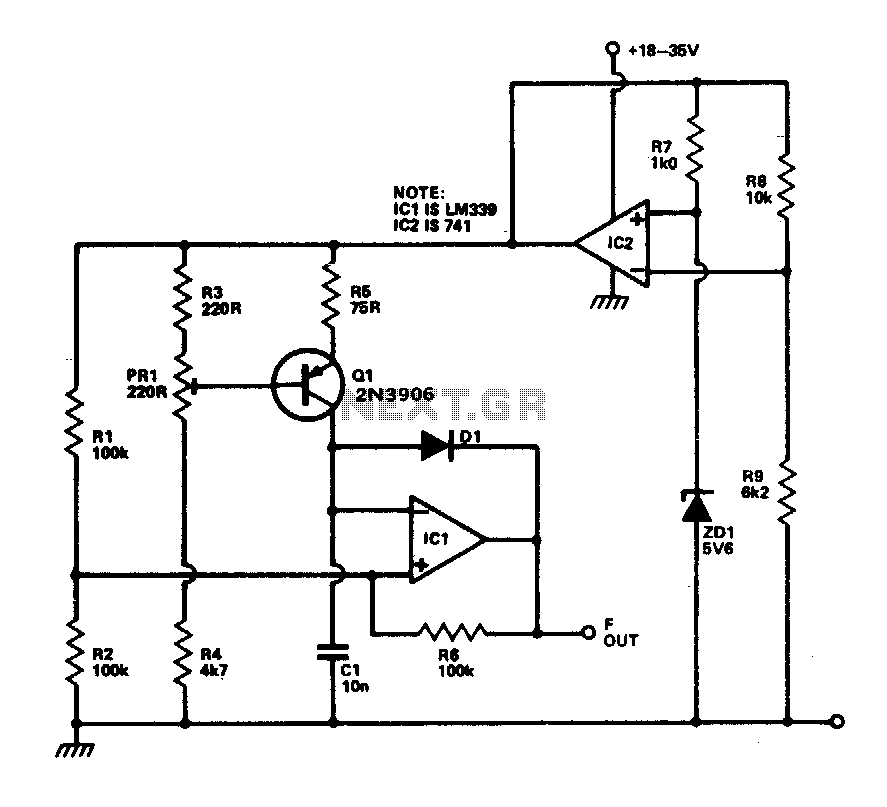
The TCA965 window discriminator IC enables the use of potentiometers RV1 and RV2 to configure the window height and window width, respectively. Resistor R1 and thermistor TH1 form a potential divider connected across the supply lines. Resistor R1 is selected so that at ambient temperature, the voltage at the junction of these components is approximately half of the supply voltage. As the temperature of the sensor varies, the voltage will also change. Potentiometer RV1 adjusts the point corresponding to the center voltage of a window, the width of which is determined by RV2. The switching points of the IC feature a Schmitt trigger characteristic with low hysteresis. The outputs of the IC indicate whether the input voltage is within the designated window or outside of it, based on whether the voltage is too high or too low. The outputs drive LEDs through a current-limiting resistor.
The TCA965 window discriminator integrated circuit is designed for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring and control through a defined voltage window. The configuration begins with the use of two potentiometers: RV1 and RV2. RV1 is crucial for setting the reference voltage at the center of the window, while RV2 determines the width of the voltage window. This allows the system to effectively respond to temperature fluctuations detected by the thermistor TH1.
The potential divider formed by resistor R1 and thermistor TH1 is essential for establishing a voltage level that reflects the ambient temperature. The choice of R1 is critical; it is selected to ensure that under standard conditions, the output voltage at the divider's junction is half of the supply voltage. This midpoint serves as a reference for the window discriminator's operation. As the temperature changes, the resistance of TH1 varies, leading to a corresponding change in the voltage at the junction. This dynamic input is what the TCA965 monitors to determine if the temperature remains within acceptable limits.
The Schmitt trigger configuration within the IC incorporates a low hysteresis characteristic, which is advantageous for minimizing noise and ensuring stable switching behavior. The output state of the IC will indicate whether the input voltage—derived from the potential divider—is within the defined window or outside of it. If the voltage exceeds the upper threshold or falls below the lower threshold, the IC will activate its output signals.
These output signals are then utilized to drive LEDs, providing a visual indication of the operational state. A current-limiting resistor is included in series with the LEDs to prevent excessive current flow, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the indicator lights. This design not only enhances user interaction through visual feedback but also serves as a critical component in the overall temperature monitoring system, allowing for real-time assessment of environmental conditions.TCA965 window discriminator IC allows the potentiometers RVl and RV2 to set up a window height and window width respectively. Rl and thermistor THl for a potential divider connected across the supply lines. Rl is chosen such that at ambient temperature the voltage at the junction of these two components will be approximately half supply.
As the temperature of the sensor changes, the voltage will change. RVl will set the point which corresponds to the center voltage of a window the width of which is set by RV2 The switching points of the JC feature a Schmitt characteristic with low hysteresis. The outputs of ICl indicate whether the input voltage is within the window or outside by virtue of being either too high or too low. The outputs of ICl drive the LEDs via a current limiting resistor.
The TCA965 window discriminator integrated circuit is designed for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring and control through a defined voltage window. The configuration begins with the use of two potentiometers: RV1 and RV2. RV1 is crucial for setting the reference voltage at the center of the window, while RV2 determines the width of the voltage window. This allows the system to effectively respond to temperature fluctuations detected by the thermistor TH1.
The potential divider formed by resistor R1 and thermistor TH1 is essential for establishing a voltage level that reflects the ambient temperature. The choice of R1 is critical; it is selected to ensure that under standard conditions, the output voltage at the divider's junction is half of the supply voltage. This midpoint serves as a reference for the window discriminator's operation. As the temperature changes, the resistance of TH1 varies, leading to a corresponding change in the voltage at the junction. This dynamic input is what the TCA965 monitors to determine if the temperature remains within acceptable limits.
The Schmitt trigger configuration within the IC incorporates a low hysteresis characteristic, which is advantageous for minimizing noise and ensuring stable switching behavior. The output state of the IC will indicate whether the input voltage—derived from the potential divider—is within the defined window or outside of it. If the voltage exceeds the upper threshold or falls below the lower threshold, the IC will activate its output signals.
These output signals are then utilized to drive LEDs, providing a visual indication of the operational state. A current-limiting resistor is included in series with the LEDs to prevent excessive current flow, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the indicator lights. This design not only enhances user interaction through visual feedback but also serves as a critical component in the overall temperature monitoring system, allowing for real-time assessment of environmental conditions.TCA965 window discriminator IC allows the potentiometers RVl and RV2 to set up a window height and window width respectively. Rl and thermistor THl for a potential divider connected across the supply lines. Rl is chosen such that at ambient temperature the voltage at the junction of these two components will be approximately half supply.
As the temperature of the sensor changes, the voltage will change. RVl will set the point which corresponds to the center voltage of a window the width of which is set by RV2 The switching points of the JC feature a Schmitt characteristic with low hysteresis. The outputs of ICl indicate whether the input voltage is within the window or outside by virtue of being either too high or too low. The outputs of ICl drive the LEDs via a current limiting resistor.