Tilt Sensor via Accelerometer Circuit
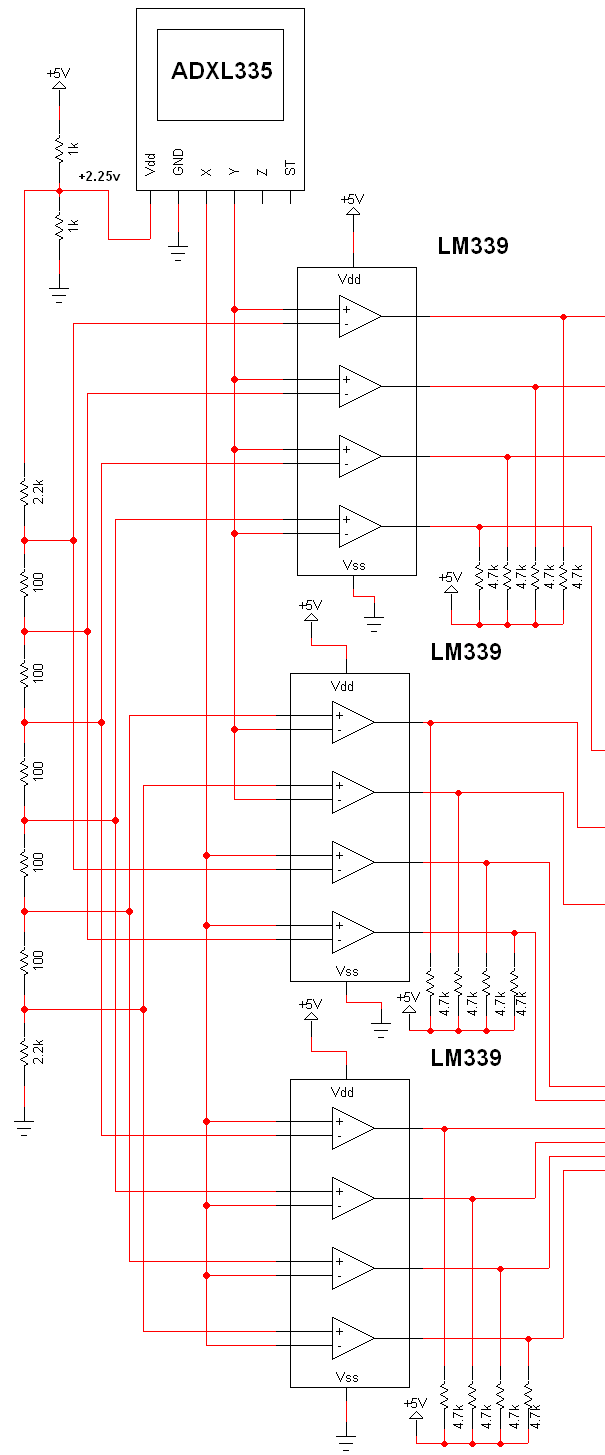
The schematic for this project is extensive, and the complete schematic is displayed below. It is divided into two sections: the analog and digital sections. The schematic illustrates the analog-to-digital conversion circuit, which includes 12 comparators—6 for the X-axis and 6 for the Y-axis. These comparators output a logic '1' when active (as previously described in the theory section), and a logic '0' otherwise. The output from the comparators is sent to the digital circuit for parsing. The comparator utilized in this circuit is the LM339, which contains four comparators in a single package and operates from a single power supply. To meet the requirement of 12 comparators, three LM339 ICs are employed. Additionally, two voltage dividers are implemented. The first voltage divider consists of two 1kΩ resistors, which reduce the initial +5V to +2.25V, and this voltage is also used to power the accelerometer. Although this part of the design could be simplified, a more complex approach was chosen.
The analog-to-digital conversion circuit is a critical component of the overall project, facilitating the translation of analog signals from sensors into digital data for further processing. The use of LM339 comparators is advantageous due to their reliability and ease of integration into various applications. Each LM339 IC contains four comparators, allowing for efficient utilization of space and resources. In this design, three LM339 ICs are connected in parallel to achieve the required 12 comparator outputs.
The voltage dividers play an essential role in establishing reference voltages for the comparators. The first voltage divider, composed of two equal-value 1kΩ resistors, effectively halves the input voltage from +5V to +2.5V. This reference voltage is crucial for determining the threshold at which the comparators will switch their outputs from logic '0' to logic '1'. The divided voltage is also used to power the accelerometer, ensuring that the entire system operates within the correct voltage range.
The design can potentially be simplified by using fewer components or alternative configurations, which may reduce complexity and improve efficiency. However, the current design prioritizes reliability and ease of troubleshooting, which may justify the additional complexity. Overall, this schematic provides a robust framework for analog-to-digital conversion, enabling accurate data acquisition from the sensors involved in the project.The schematic for this project is fairly large and you can see the complete schematic below. To explain what is happening here I will split it into two sections which I will call the analog and digital sections. The schemtic below (click to enlarge it) is the analog to digital conversion circuit. It has 12 comparators, 6 for the X axis and 6 for the Y axis. These comparators will output a logic `1` when in an active state (previously described in the theory section) otherwise they output a logic `0`. This output is then passed onto the digital circuit where it is parsed. The comparator used for this part of the circuit is the tried and true LM339. It has 4 comparators inside of it and runs off of a single power supply. Since we need 12 comparators in total, 3 LM339 IC`s will be used. Two voltage dividers are used. The first voltage divider is made up of two 1k © resistors which divides the intial +5v down and is then fed to the reference resistor voltage divider.
The divided input voltage turns out to be +2. 25v and it is also used to power the accelerometer. This part of the design could be simplified but I got a little lazy, sorry! 🔗 External reference
The analog-to-digital conversion circuit is a critical component of the overall project, facilitating the translation of analog signals from sensors into digital data for further processing. The use of LM339 comparators is advantageous due to their reliability and ease of integration into various applications. Each LM339 IC contains four comparators, allowing for efficient utilization of space and resources. In this design, three LM339 ICs are connected in parallel to achieve the required 12 comparator outputs.
The voltage dividers play an essential role in establishing reference voltages for the comparators. The first voltage divider, composed of two equal-value 1kΩ resistors, effectively halves the input voltage from +5V to +2.5V. This reference voltage is crucial for determining the threshold at which the comparators will switch their outputs from logic '0' to logic '1'. The divided voltage is also used to power the accelerometer, ensuring that the entire system operates within the correct voltage range.
The design can potentially be simplified by using fewer components or alternative configurations, which may reduce complexity and improve efficiency. However, the current design prioritizes reliability and ease of troubleshooting, which may justify the additional complexity. Overall, this schematic provides a robust framework for analog-to-digital conversion, enabling accurate data acquisition from the sensors involved in the project.The schematic for this project is fairly large and you can see the complete schematic below. To explain what is happening here I will split it into two sections which I will call the analog and digital sections. The schemtic below (click to enlarge it) is the analog to digital conversion circuit. It has 12 comparators, 6 for the X axis and 6 for the Y axis. These comparators will output a logic `1` when in an active state (previously described in the theory section) otherwise they output a logic `0`. This output is then passed onto the digital circuit where it is parsed. The comparator used for this part of the circuit is the tried and true LM339. It has 4 comparators inside of it and runs off of a single power supply. Since we need 12 comparators in total, 3 LM339 IC`s will be used. Two voltage dividers are used. The first voltage divider is made up of two 1k © resistors which divides the intial +5v down and is then fed to the reference resistor voltage divider.
The divided input voltage turns out to be +2. 25v and it is also used to power the accelerometer. This part of the design could be simplified but I got a little lazy, sorry! 🔗 External reference