Touch Activated Alarm System
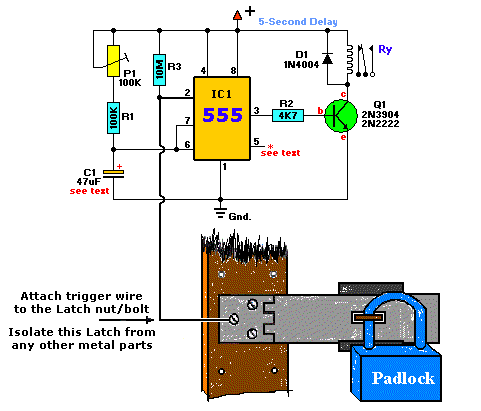
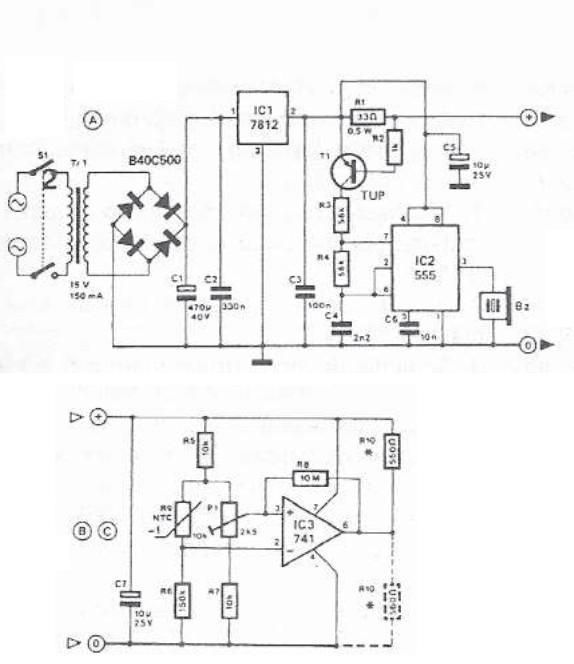
The 555 timer IC can be of various types, all of which are pin-compatible. However, some CMOS variants may lack sufficient power to drive a transistor, in which case a standard 555 timer should be used. If a 12V power supply is chosen, the working voltage of capacitor C1 should be increased to 25V. The value of C1 must be adjusted to achieve the desired output pulse duration. The timing can be calculated using the equation: T = 1.1 * (R1 + P1) * C1, assuming R1 + P1 equals 150K. For a 1-second pulse width, C1 should be set to 6 µF. For a 5-second pulse width, C1 should be 30 µF or the nearest available value, such as 22 or 33 µF. Additionally, P1 can be used to fine-tune the timing. A general guideline is that the working voltage of capacitors should be at least double the supply voltage; for example, if the power source is 9V, the capacitor(s) should have a voltage rating of at least 18V. Transistor T1 can be replaced with a suitable alternative. Any appropriate relay can be used for the project, and if space is not a constraint, any size can be selected. This circuit was designed to prevent students from tampering with security cameras in computer labs. It is important to ensure that the metal casing is not grounded, although the schematic indicates that it can be connected to any metal surface. A 12V DC power source is recommended. A normally closed RESET switch can be connected between the positive supply and the designated point in the schematic. The trigger wire, which connects to pin 2 of the 555 timer, will activate the relay by utilizing body resistance when touched. The contact point must be clean and make good contact with the trigger wire. This circuit may not be suitable for all applications. It is noteworthy that pin 5 is not included in the schematic as it is not necessary; however, in noisy environments, a small 0.01 µF ceramic capacitor can be added between pin 5 and ground without causing harm. Importantly, there is an approximate 5-second delay built into the circuit before the relay is activated to prevent false triggering. Care must be taken to ensure that pin 2 does not touch any ground points, as this would cause the circuit to continuously reset and fail to operate. The circuit functions correctly when installed in wooden doors. If the circuit does not work, it is advisable to check the trigger input, verify that there is a signal from output pin 3, and experiment with the values of R3 and C1.
The 555 timer circuit operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a trigger input. The circuit consists of the 555 timer IC, a resistor (R1), a potentiometer (P1), and a capacitor (C1). The pulse width (T) is determined by the values of R1, P1, and C1, with the formula T = 1.1 * (R1 + P1) * C1 guiding the selection of component values.
For the capacitor C1, it is essential to select a capacitor with a voltage rating that exceeds the supply voltage. This ensures reliability and longevity under normal operating conditions. The choice of a 12V power source necessitates a capacitor with a minimum rating of 25V to provide a safety margin.
The relay, which serves as the output device, can be any suitable type, such as an electromechanical relay or a solid-state relay, depending on the application requirements. The relay is activated when the circuit is triggered by a touch on the trigger wire connected to pin 2 of the 555 timer. This design allows for a simple user interface while maintaining security.
In terms of layout, it is crucial to ensure that all connections are secure and that the circuit is housed in a non-conductive enclosure to prevent accidental grounding. The inclusion of a RESET switch allows for manual resetting of the circuit, enhancing control over the operation.
The circuit's design also includes a delay feature to mitigate false triggering, which is particularly useful in environments where inadvertent touches may occur. The use of a ceramic capacitor at pin 5, while optional, can improve stability in electrically noisy environments.
Overall, this 555 timer-based circuit provides an effective solution for applications requiring controlled timing and relay activation, with considerations for safety, reliability, and user interaction.The 555 can be almost any type, they are all pin-compatible. Although some CMOS types may not have enough power to drive the transistor, in that case use an ordinary 555. C1`s working voltage should be increased to 25V if you decide to go with a 12V power source. Change the value of C1 for the desired output pulse. For the timing use this equation: T=1. 1*(R1+P1)*C1 assuming R1 + P1 = 150K, then select C1 as follows: C1 = 6 µF for each 1-second pulse width. For example, if you want the pulse width to be 5 seconds, C1 should be 30uf or nearest value like 22 or 33 µF.
Additionally, P1 can adjust the rest. Rule of thumb: the working voltage of capacitors are at least double the supplied voltage, in other words, if the power source is 9Volt, your capacitor(s) is at least 18V. Transistor T1 can be any approximate substitute. Use any suitable relay for your project and if you`re not tight on space, use any size. I`ve build this particular circuit to prevent students from fiddling with the security cameras in computer labs at the University I am employed.
I made sure the metal casing was not grounded. But as the schematic shows you can basically hook it up to any type of metal surface. I used a 12-vdc power source. Use any suitable relay to handle your requirements. A `RESET` switch (Normally Closed) can be added between the positive and the `arrow-with-the-+`. The trigger (touch) wire is connected to pin 2 of the 555 and will trigger the relay, using your body resistance, when touched. It is obvious that the `touching` part has to be clean and makes good contact with the trigger wire. This particular circuit may not be suitable for all applications. Just in case you wonder why pin 5 is not listed in the schematic diagram; it is not really needed. In certain noisy conditions a small 0. 01µF; ceramic capacitor is placed between pin 5 and ground. It does no harm to add one or leave it out. NOTE: For those of you who did not notice, there is an approximate 5-second delay build-in before activation of the relay to avoid false triggering, or a `would-be` thief, etc.
AGAIN, make sure the latch (pin 2) is not touching anything `ground` or the circuit just keeps resetting itself and so will not work. My shed has wooden doors so works fine. If you can`t get yours to work, check the trigger input, verify there is some sort of signal coming from output pin 3, play with the value of R3/C1, etc.
🔗 External reference
The 555 timer circuit operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a trigger input. The circuit consists of the 555 timer IC, a resistor (R1), a potentiometer (P1), and a capacitor (C1). The pulse width (T) is determined by the values of R1, P1, and C1, with the formula T = 1.1 * (R1 + P1) * C1 guiding the selection of component values.
For the capacitor C1, it is essential to select a capacitor with a voltage rating that exceeds the supply voltage. This ensures reliability and longevity under normal operating conditions. The choice of a 12V power source necessitates a capacitor with a minimum rating of 25V to provide a safety margin.
The relay, which serves as the output device, can be any suitable type, such as an electromechanical relay or a solid-state relay, depending on the application requirements. The relay is activated when the circuit is triggered by a touch on the trigger wire connected to pin 2 of the 555 timer. This design allows for a simple user interface while maintaining security.
In terms of layout, it is crucial to ensure that all connections are secure and that the circuit is housed in a non-conductive enclosure to prevent accidental grounding. The inclusion of a RESET switch allows for manual resetting of the circuit, enhancing control over the operation.
The circuit's design also includes a delay feature to mitigate false triggering, which is particularly useful in environments where inadvertent touches may occur. The use of a ceramic capacitor at pin 5, while optional, can improve stability in electrically noisy environments.
Overall, this 555 timer-based circuit provides an effective solution for applications requiring controlled timing and relay activation, with considerations for safety, reliability, and user interaction.The 555 can be almost any type, they are all pin-compatible. Although some CMOS types may not have enough power to drive the transistor, in that case use an ordinary 555. C1`s working voltage should be increased to 25V if you decide to go with a 12V power source. Change the value of C1 for the desired output pulse. For the timing use this equation: T=1. 1*(R1+P1)*C1 assuming R1 + P1 = 150K, then select C1 as follows: C1 = 6 µF for each 1-second pulse width. For example, if you want the pulse width to be 5 seconds, C1 should be 30uf or nearest value like 22 or 33 µF.
Additionally, P1 can adjust the rest. Rule of thumb: the working voltage of capacitors are at least double the supplied voltage, in other words, if the power source is 9Volt, your capacitor(s) is at least 18V. Transistor T1 can be any approximate substitute. Use any suitable relay for your project and if you`re not tight on space, use any size. I`ve build this particular circuit to prevent students from fiddling with the security cameras in computer labs at the University I am employed.
I made sure the metal casing was not grounded. But as the schematic shows you can basically hook it up to any type of metal surface. I used a 12-vdc power source. Use any suitable relay to handle your requirements. A `RESET` switch (Normally Closed) can be added between the positive and the `arrow-with-the-+`. The trigger (touch) wire is connected to pin 2 of the 555 and will trigger the relay, using your body resistance, when touched. It is obvious that the `touching` part has to be clean and makes good contact with the trigger wire. This particular circuit may not be suitable for all applications. Just in case you wonder why pin 5 is not listed in the schematic diagram; it is not really needed. In certain noisy conditions a small 0. 01µF; ceramic capacitor is placed between pin 5 and ground. It does no harm to add one or leave it out. NOTE: For those of you who did not notice, there is an approximate 5-second delay build-in before activation of the relay to avoid false triggering, or a `would-be` thief, etc.
AGAIN, make sure the latch (pin 2) is not touching anything `ground` or the circuit just keeps resetting itself and so will not work. My shed has wooden doors so works fine. If you can`t get yours to work, check the trigger input, verify there is some sort of signal coming from output pin 3, play with the value of R3/C1, etc.
🔗 External reference