Tutorial Sensor Amplifier
This tutorial provides information related to sensor amplifiers, schematics, and noise. It presents a discussion around sensors and their outputs.
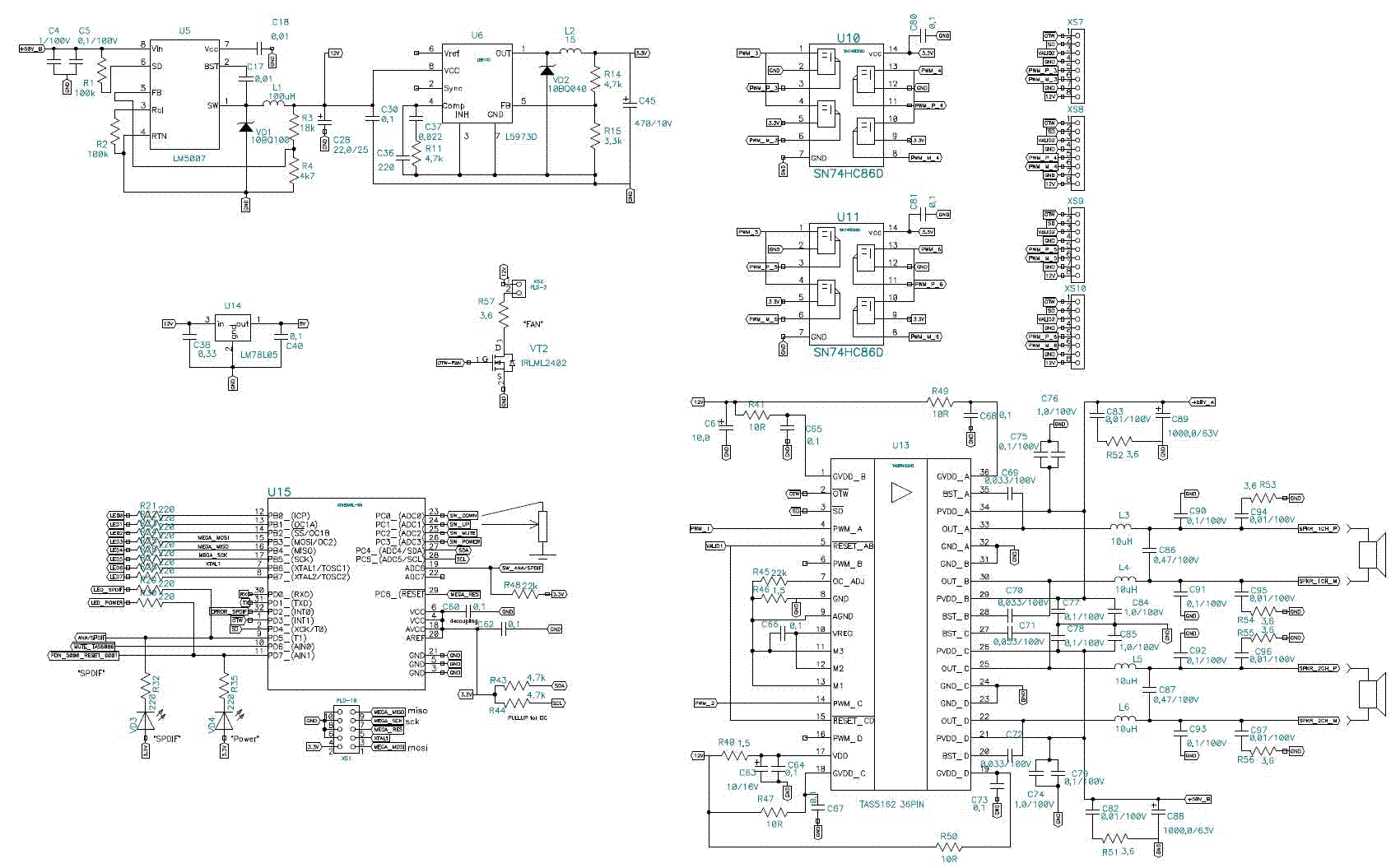
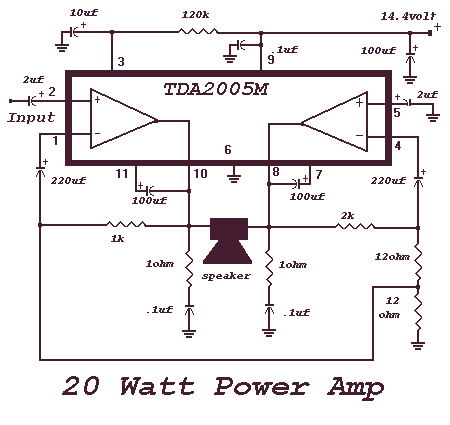
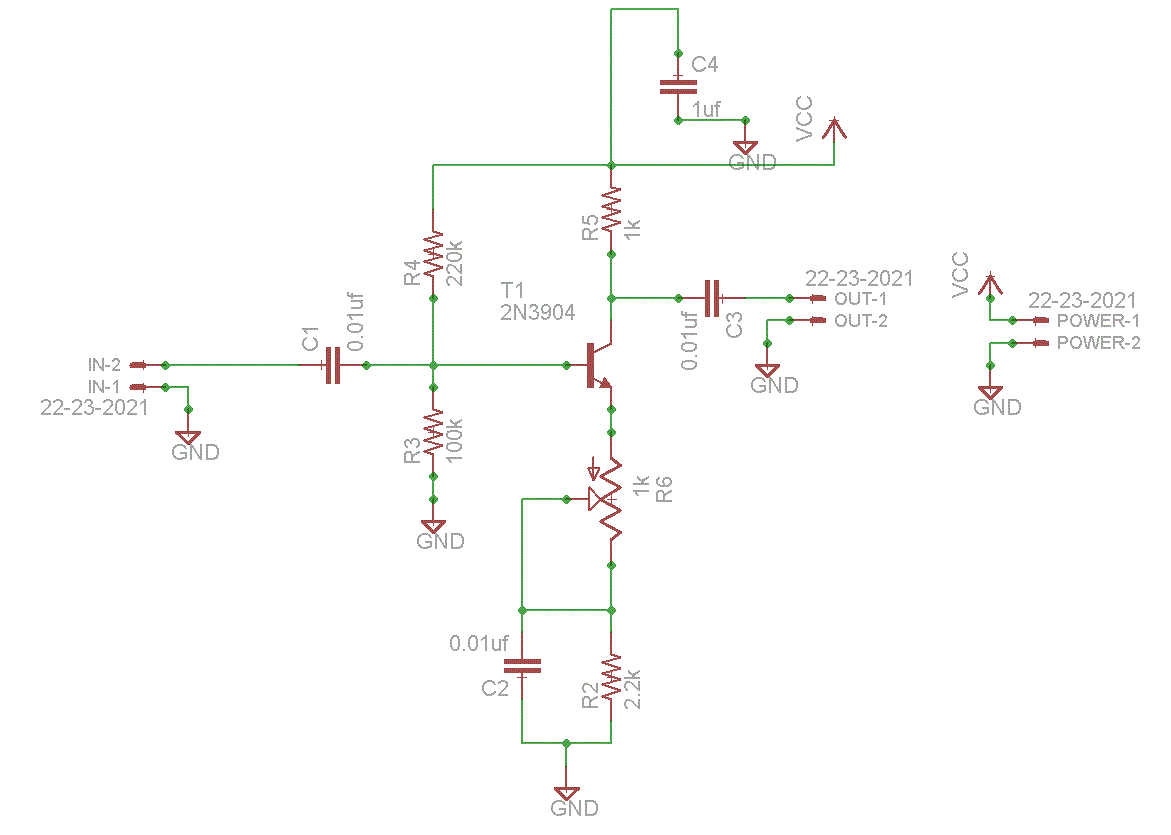
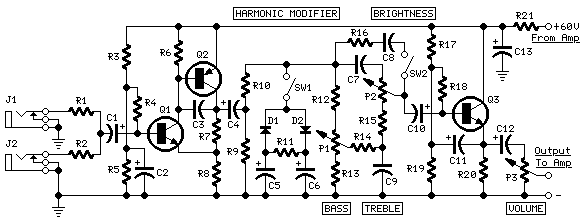
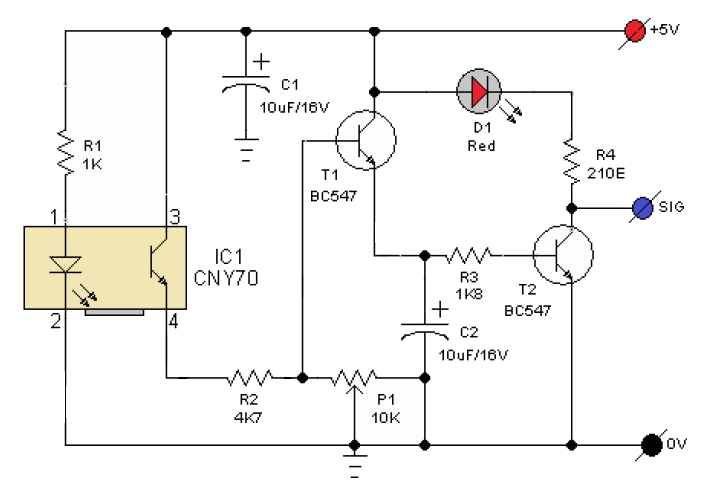
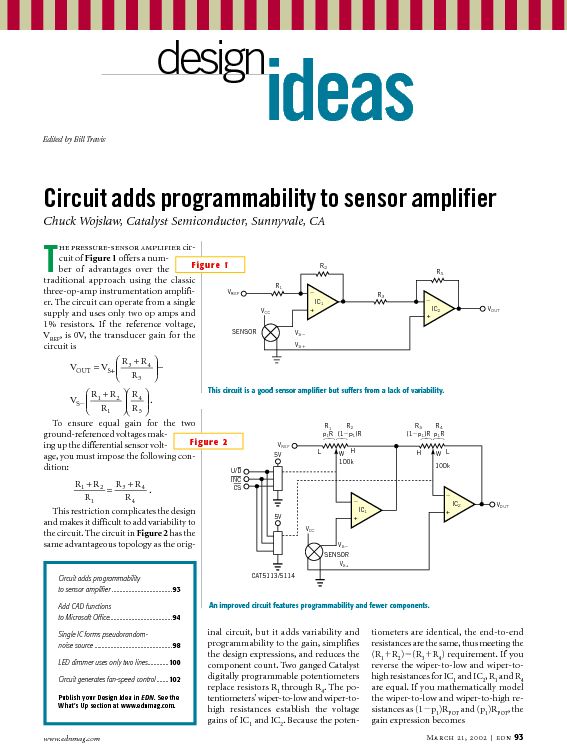
Sensor amplifiers are critical components in various electronic systems, especially in applications where signals from sensors need to be conditioned before further processing. A sensor amplifier typically amplifies the small signals generated by sensors, which can be affected by various forms of noise. The schematic of a sensor amplifier circuit generally includes the sensor itself, an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors for gain setting, and capacitors for noise filtering.
In a typical configuration, the sensor generates a voltage signal proportional to the physical quantity being measured, such as temperature, light, or pressure. This signal is often too weak to be processed directly by subsequent circuitry, necessitating amplification. The op-amp is used to increase the signal level while maintaining linearity. Feedback resistors are utilized to set the gain of the amplifier, allowing for customization based on the sensor's output characteristics and the requirements of the following stages.
Noise is an important consideration in the design of sensor amplifier circuits. Various types of noise, such as thermal noise, flicker noise, and electromagnetic interference, can adversely affect the signal integrity. To mitigate these effects, careful layout design, proper grounding techniques, and the use of filtering capacitors are essential. The placement of components in the schematic should minimize the length of signal paths and reduce the potential for noise pickup.
In summary, the design of a sensor amplifier circuit involves a thorough understanding of the sensor characteristics, op-amp configurations, gain setting, and noise management strategies to ensure accurate and reliable signal processing.In this tutorial we can get information related to sensor amplifier, schematic, and noise. This tutorial presents discussion around sensor, output, and.. 🔗 External reference
Sensor amplifiers are critical components in various electronic systems, especially in applications where signals from sensors need to be conditioned before further processing. A sensor amplifier typically amplifies the small signals generated by sensors, which can be affected by various forms of noise. The schematic of a sensor amplifier circuit generally includes the sensor itself, an operational amplifier (op-amp), resistors for gain setting, and capacitors for noise filtering.
In a typical configuration, the sensor generates a voltage signal proportional to the physical quantity being measured, such as temperature, light, or pressure. This signal is often too weak to be processed directly by subsequent circuitry, necessitating amplification. The op-amp is used to increase the signal level while maintaining linearity. Feedback resistors are utilized to set the gain of the amplifier, allowing for customization based on the sensor's output characteristics and the requirements of the following stages.
Noise is an important consideration in the design of sensor amplifier circuits. Various types of noise, such as thermal noise, flicker noise, and electromagnetic interference, can adversely affect the signal integrity. To mitigate these effects, careful layout design, proper grounding techniques, and the use of filtering capacitors are essential. The placement of components in the schematic should minimize the length of signal paths and reduce the potential for noise pickup.
In summary, the design of a sensor amplifier circuit involves a thorough understanding of the sensor characteristics, op-amp configurations, gain setting, and noise management strategies to ensure accurate and reliable signal processing.In this tutorial we can get information related to sensor amplifier, schematic, and noise. This tutorial presents discussion around sensor, output, and.. 🔗 External reference