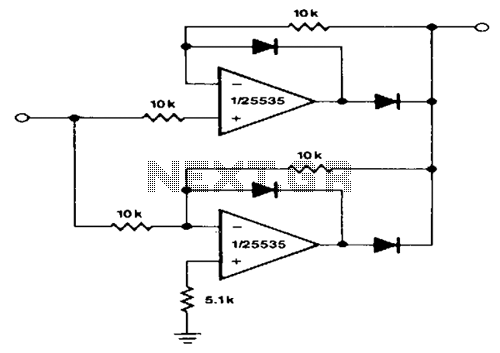
ULTRA PURE 125KHz SINE WAVE SIGNAL SOURCE
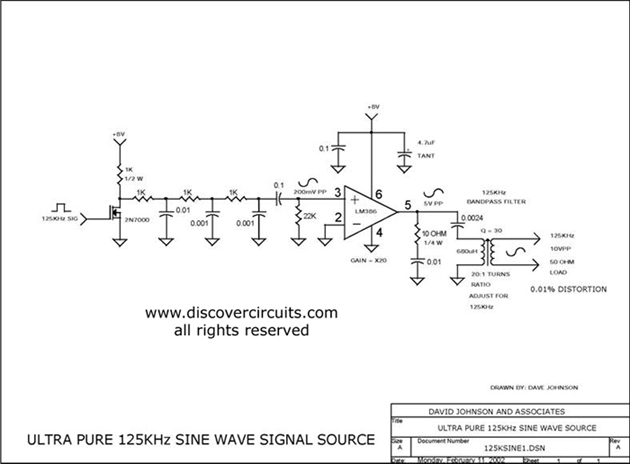
Ultra pure 125 kHz sine wave signal source. For certain RFID systems operating at 125 kHz, a very low distortion signal source is essential. The circuit presented here produces a 10-volt peak-to-peak signal.
The ultra pure 125 kHz sine wave signal source is designed to meet the stringent requirements of RFID systems that operate at this frequency. The circuit utilizes precision components to ensure minimal distortion, which is critical for reliable communication in RFID applications. The output of the circuit is a 10-volt peak-to-peak sine wave, suitable for driving various RFID transponders and readers.
The circuit typically includes a waveform generator, which can be based on a precision oscillator or a microcontroller with a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). The oscillator is configured to generate a 125 kHz sine wave, and additional filtering stages may be employed to smooth the waveform and eliminate unwanted harmonics.
To achieve the desired output voltage, the circuit may incorporate an amplifier stage. This amplifier is designed to maintain linearity and low distortion while providing the necessary gain to achieve the 10-volt peak-to-peak output. Feedback mechanisms can be implemented to further enhance the stability and fidelity of the output signal.
Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the circuit must operate reliably under varying load conditions. A regulated power supply is often used to ensure that the oscillator and amplifier stages receive consistent voltage levels, thereby minimizing variations in signal output.
Overall, the design of the ultra pure 125 kHz sine wave signal source emphasizes precision, low distortion, and stability, making it an ideal choice for applications in RFID technology where signal integrity is paramount.ULTRA PURE 125KHz SINE WAVE SIGNAL SOURCE . For some RFID systems, which is at 125KHz, a very low distortion signal source is required. The circuit on this page results in a 10-volt peak-peak signal into. 🔗 External reference
The ultra pure 125 kHz sine wave signal source is designed to meet the stringent requirements of RFID systems that operate at this frequency. The circuit utilizes precision components to ensure minimal distortion, which is critical for reliable communication in RFID applications. The output of the circuit is a 10-volt peak-to-peak sine wave, suitable for driving various RFID transponders and readers.
The circuit typically includes a waveform generator, which can be based on a precision oscillator or a microcontroller with a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). The oscillator is configured to generate a 125 kHz sine wave, and additional filtering stages may be employed to smooth the waveform and eliminate unwanted harmonics.
To achieve the desired output voltage, the circuit may incorporate an amplifier stage. This amplifier is designed to maintain linearity and low distortion while providing the necessary gain to achieve the 10-volt peak-to-peak output. Feedback mechanisms can be implemented to further enhance the stability and fidelity of the output signal.
Power supply considerations are also crucial, as the circuit must operate reliably under varying load conditions. A regulated power supply is often used to ensure that the oscillator and amplifier stages receive consistent voltage levels, thereby minimizing variations in signal output.
Overall, the design of the ultra pure 125 kHz sine wave signal source emphasizes precision, low distortion, and stability, making it an ideal choice for applications in RFID technology where signal integrity is paramount.ULTRA PURE 125KHz SINE WAVE SIGNAL SOURCE . For some RFID systems, which is at 125KHz, a very low distortion signal source is required. The circuit on this page results in a 10-volt peak-peak signal into. 🔗 External reference