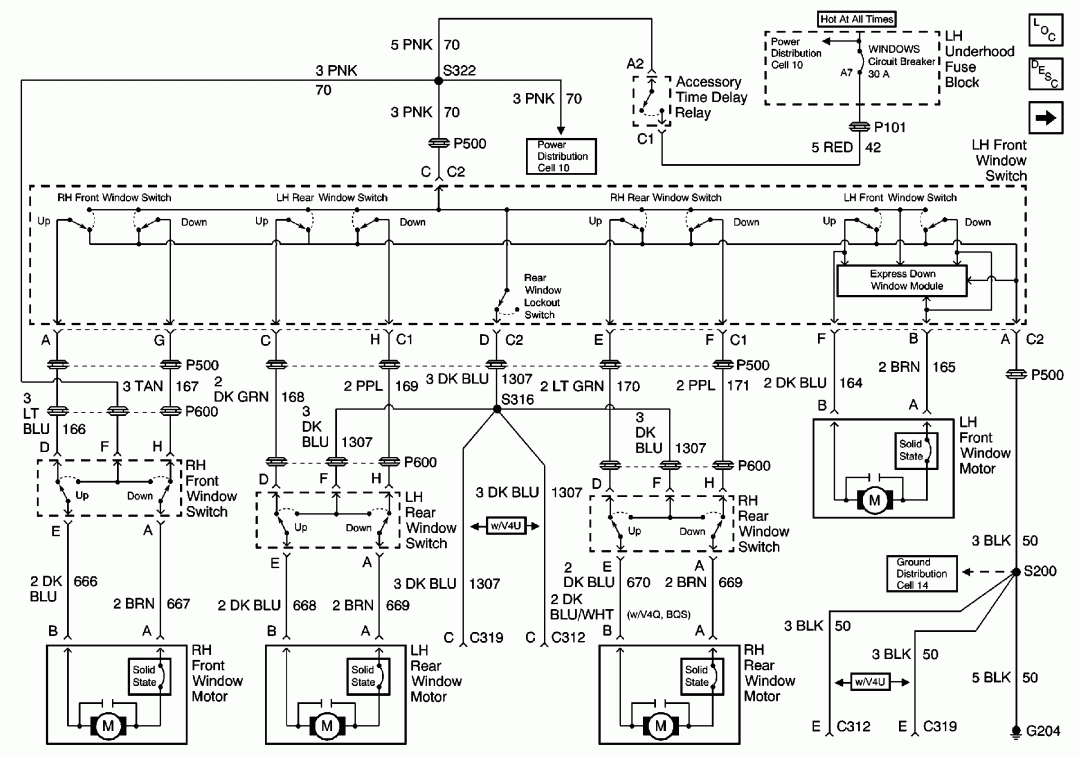
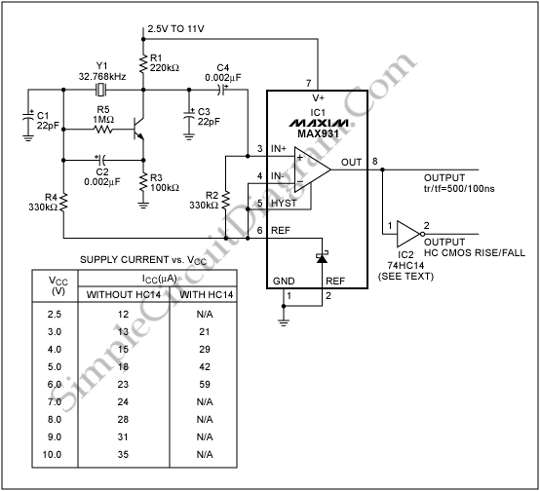
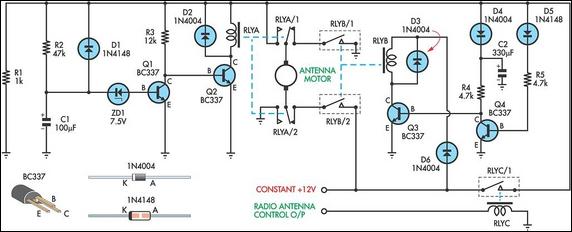
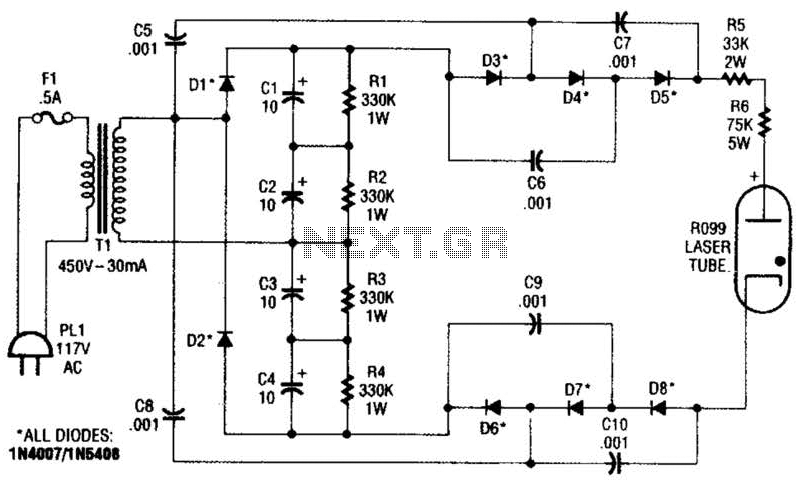
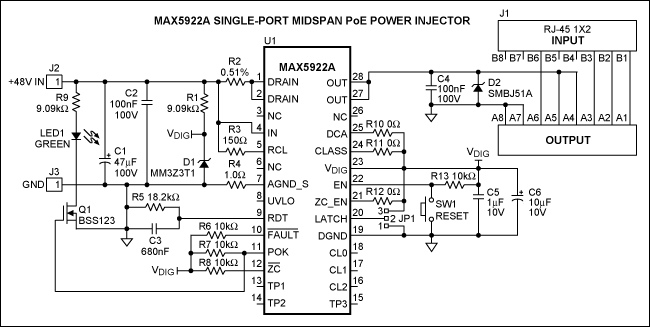
Variable Dc Power Supply
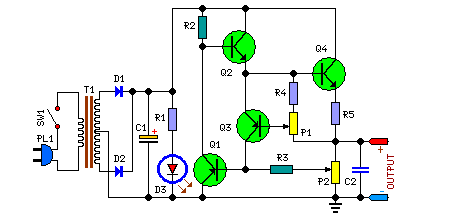
The transformer can be selected based on the required maximum voltage and current output. Recommended options include: 36V, 40V, or 48V center-tapped configurations, with power ratings of 50VA, 75VA, 80VA, or 100VA. It is essential to mount Q4 on an adequate heatsink to handle prolonged output short-circuit conditions. In certain instances, the rear panel of the metal enclosure housing the circuit can serve this purpose effectively.
To design a robust power supply circuit, the selection of a transformer is critical. The transformer must be chosen according to the maximum voltage and current requirements of the application. For typical use cases, center-tapped transformers with output voltages of 36V, 40V, or 48V are suitable, depending on the specific voltage needs of the circuit. Additionally, the power rating of the transformer should be considered, with options of 50VA, 75VA, 80VA, or 100VA available to accommodate the load.
Transistor Q4 plays a vital role in the circuit, particularly in regulating output and protecting against short circuits. To ensure reliable operation, Q4 must be mounted on a heatsink that can dissipate heat effectively, especially during sustained periods of short-circuit conditions. This is crucial to prevent thermal overload and potential failure of the component. In some designs, the rear panel of the metal enclosure can be utilized as a heatsink if it has sufficient thermal mass and conductivity, providing an additional method to manage heat dissipation.
Overall, careful consideration of the transformer specifications and proper thermal management for Q4 will enhance the reliability and performance of the power supply circuit.You can choose the Transformer on the grounds of maximum voltage and current output needed. Best choices are: 36, 40 or 48V center-tapped and 50, 75, 80 or 100VA. Q4 must be mounted on a good heatsink in order to withstand sustained output short-circuit. In some cases the rear panel of the metal box in which you will enclose the circuit can do the job. 🔗 External reference
To design a robust power supply circuit, the selection of a transformer is critical. The transformer must be chosen according to the maximum voltage and current requirements of the application. For typical use cases, center-tapped transformers with output voltages of 36V, 40V, or 48V are suitable, depending on the specific voltage needs of the circuit. Additionally, the power rating of the transformer should be considered, with options of 50VA, 75VA, 80VA, or 100VA available to accommodate the load.
Transistor Q4 plays a vital role in the circuit, particularly in regulating output and protecting against short circuits. To ensure reliable operation, Q4 must be mounted on a heatsink that can dissipate heat effectively, especially during sustained periods of short-circuit conditions. This is crucial to prevent thermal overload and potential failure of the component. In some designs, the rear panel of the metal enclosure can be utilized as a heatsink if it has sufficient thermal mass and conductivity, providing an additional method to manage heat dissipation.
Overall, careful consideration of the transformer specifications and proper thermal management for Q4 will enhance the reliability and performance of the power supply circuit.You can choose the Transformer on the grounds of maximum voltage and current output needed. Best choices are: 36, 40 or 48V center-tapped and 50, 75, 80 or 100VA. Q4 must be mounted on a good heatsink in order to withstand sustained output short-circuit. In some cases the rear panel of the metal box in which you will enclose the circuit can do the job. 🔗 External reference