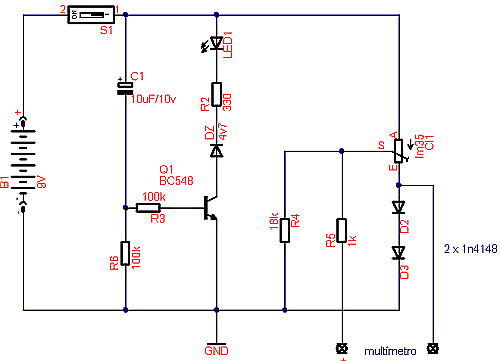
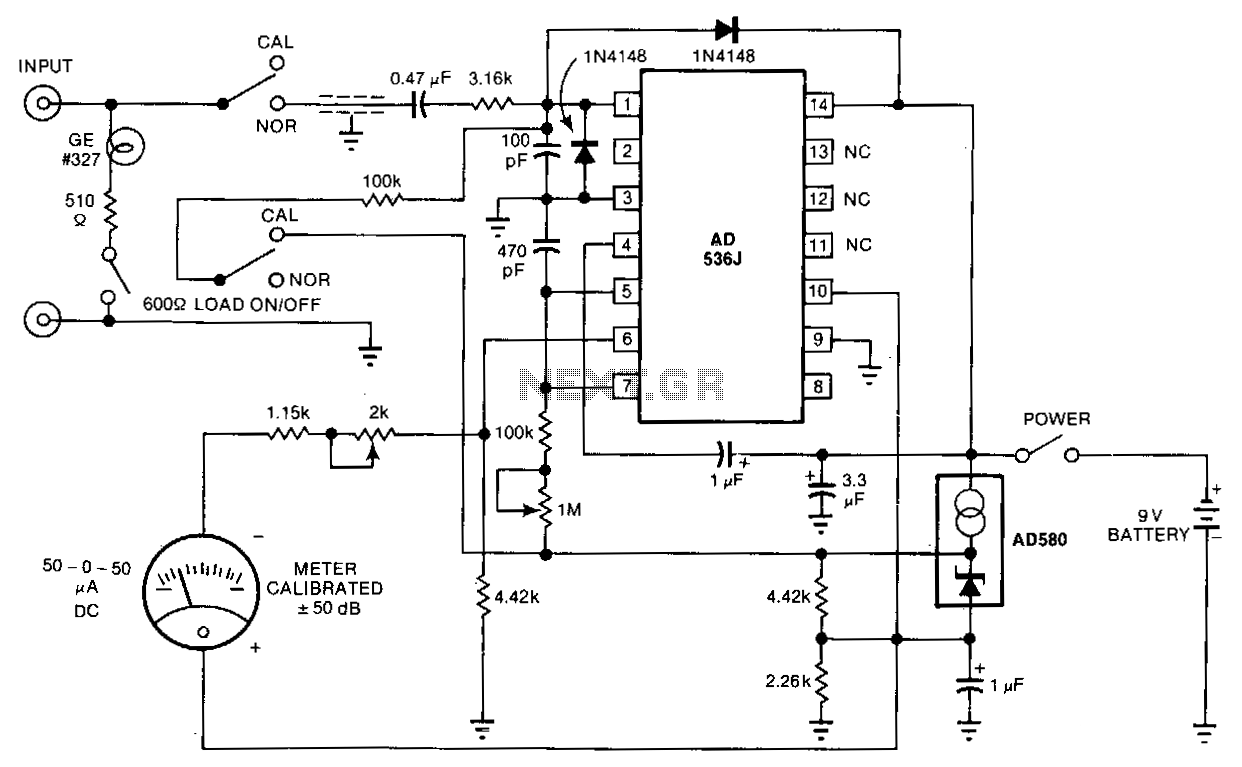
vu meter
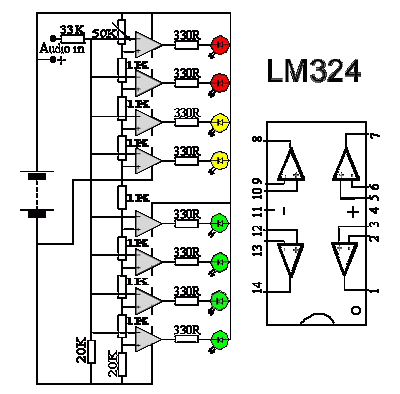
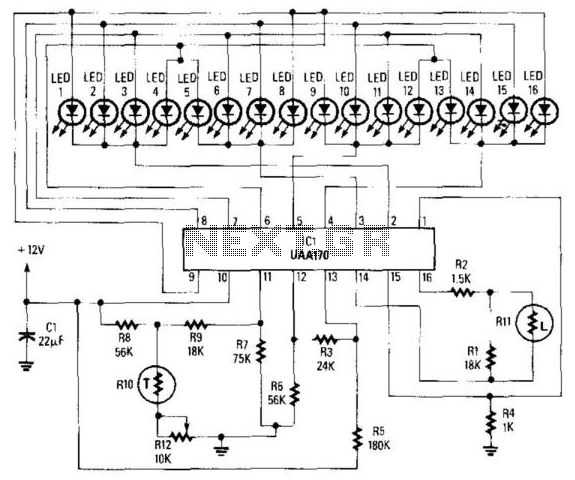
The 1K resistors in the circuit are essential for enabling the LEDs to activate at varying audio levels. This circuit is easily expandable with additional operational amplifiers and is not restricted to the use of the LM324. The 33K resistor in the schematic serves to maintain a low signal level at the circuit's input. In its current configuration, the circuit can accept line-level inputs from sources such as the auxiliary output of a Hi-Fi system, although it could be modified to accommodate speaker inputs.
The circuit utilizes 1K resistors to provide a threshold for LED activation, allowing them to illuminate in response to different audio signal levels. This feature is particularly useful in applications where visual indicators of audio signal strength are desired. The operational amplifiers can be configured in various ways, and the circuit's design allows for the integration of additional op-amps to enhance functionality or increase the number of channels monitored.
The inclusion of a 33K resistor at the input stage is crucial for ensuring that the signal remains at a manageable level, preventing distortion that could arise from excessively high input voltages. This resistor effectively acts as a voltage divider when combined with other components in the circuit, thus protecting sensitive elements from damage.
The circuit's capability to accept line-level inputs makes it suitable for integration with various audio devices, such as mixers, sound interfaces, or Hi-Fi systems. Moreover, with minor modifications, it can be adapted to handle speaker-level inputs, broadening its applicability in audio processing environments. This adaptability makes the circuit a versatile choice for audio signal monitoring and visual representation.The 1K resistors in the circuit are essential so that the LED`s turn on at different audio levels. This circuit is easily expandable with more op-amps, and is not limited to use with the LM324. The 33K resistor on the schematic is to keep the signal input to the circuit at a low level. The circuit in it`s current form will accept line level inputs from sources such as the aux out on a Hi-Fi, all though could be easily modified to accept speaker inputs. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes 1K resistors to provide a threshold for LED activation, allowing them to illuminate in response to different audio signal levels. This feature is particularly useful in applications where visual indicators of audio signal strength are desired. The operational amplifiers can be configured in various ways, and the circuit's design allows for the integration of additional op-amps to enhance functionality or increase the number of channels monitored.
The inclusion of a 33K resistor at the input stage is crucial for ensuring that the signal remains at a manageable level, preventing distortion that could arise from excessively high input voltages. This resistor effectively acts as a voltage divider when combined with other components in the circuit, thus protecting sensitive elements from damage.
The circuit's capability to accept line-level inputs makes it suitable for integration with various audio devices, such as mixers, sound interfaces, or Hi-Fi systems. Moreover, with minor modifications, it can be adapted to handle speaker-level inputs, broadening its applicability in audio processing environments. This adaptability makes the circuit a versatile choice for audio signal monitoring and visual representation.The 1K resistors in the circuit are essential so that the LED`s turn on at different audio levels. This circuit is easily expandable with more op-amps, and is not limited to use with the LM324. The 33K resistor on the schematic is to keep the signal input to the circuit at a low level. The circuit in it`s current form will accept line level inputs from sources such as the aux out on a Hi-Fi, all though could be easily modified to accept speaker inputs. 🔗 External reference