
Wideband-500khz-1ghz-hybrid-amplifier
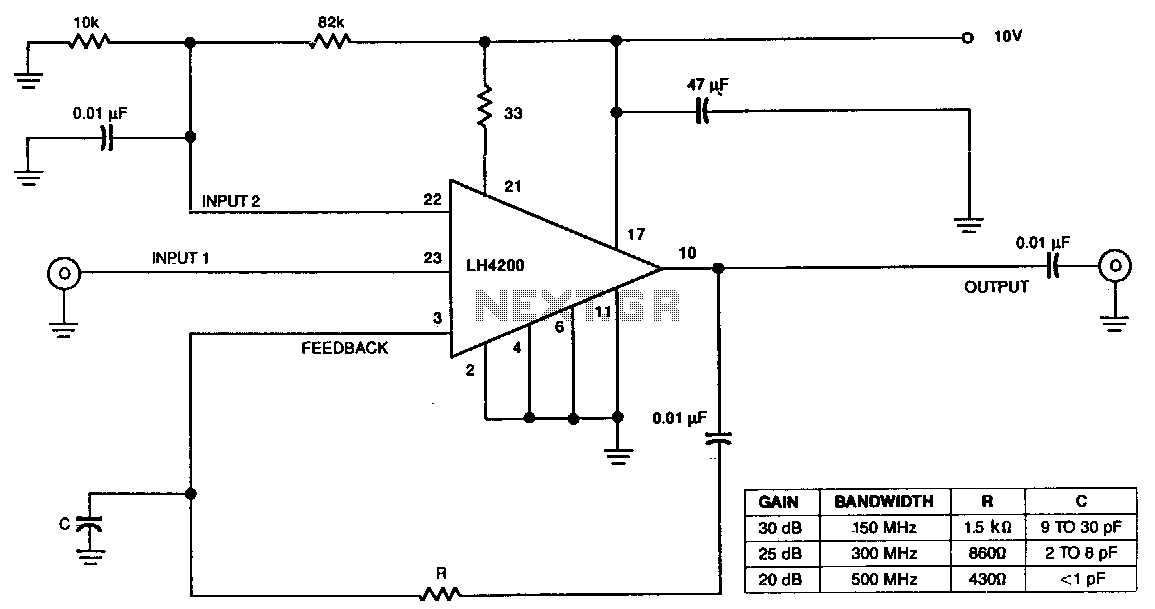
The amplifier's input stage features a dual-gate GaAs FET, which offers low input capacitance and high transconductance. The first input accepts the signal, while the second input regulates the amplifier's gain. Additionally, there is a third input for series feedback. The output is connected to pin 3 through a single resistor that manages the overall power gain of the amplifier. At 10 MHz, the output can deliver 12 dBm into a 50-ohm load with 1 dB of signal compression. This AC-coupled amplifier exhibits a gain of 37 dB at 100 MHz and 3 dB at 1 GHz.
The described amplifier circuit utilizes a dual-gate Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) Field Effect Transistor (FET) in its input stage, which is essential for achieving high performance in RF applications. The low input capacitance of the FET minimizes signal distortion and allows for greater frequency response, making it suitable for high-frequency operations. The dual-gate configuration enhances the control over the gain, with the first gate receiving the input signal and the second gate serving as a gain control element. This arrangement allows for precise adjustments to the amplifier's performance based on the requirements of the application.
The inclusion of a third input for series feedback is a critical feature that enables the amplifier to maintain stability and linearity across its operating range. Feedback is provided through a resistor connected to pin 3, which plays a significant role in determining the overall power gain of the amplifier. By adjusting the resistance value, the designer can tailor the amplifier's gain characteristics to suit specific needs, ensuring optimal performance under varying conditions.
At a frequency of 10 MHz, the amplifier's output capability is noteworthy, delivering 12 dBm into a 50-ohm load while exhibiting only 1 dB of signal compression. This performance indicates that the amplifier can operate effectively without significant distortion, making it suitable for applications requiring high fidelity. The AC coupling in the amplifier design further enhances its versatility, allowing it to handle a wide range of input signal types.
The gain characteristics of the amplifier are impressive, with a gain of 37 dB at 100 MHz, which indicates strong amplification capabilities for signals in this frequency range. However, as the frequency increases to 1 GHz, the gain decreases to 3 dB, which is a common behavior in amplifiers due to factors such as parasitic capacitances and losses that become more pronounced at higher frequencies. This information is crucial for engineers when selecting the amplifier for specific applications, as it highlights the frequency-dependent nature of the amplifier's performance. Overall, the design and specifications of this amplifier make it a robust choice for high-frequency signal processing in various electronic applications.The amplifier"s input stage is a dual-gate GaAs FET, which provides low input capacitance and high transconductance. The dual-gate structure accepts the signal on input 1. Input 2 controls the gain of the amplifier. The amplifier has a third input for use in series feedback. The output feeds back to pin 3 via a single resistor, which controls the overall power gain of the amplifier.
At 10 MHz, the output is capable of delivering 12 dBm into a 50-0 load with 1 dB of signal compression. The ac-coupled amplifier has a gain of 37 dB at 100 MHz and 3 dB at 1 GHz.
The described amplifier circuit utilizes a dual-gate Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) Field Effect Transistor (FET) in its input stage, which is essential for achieving high performance in RF applications. The low input capacitance of the FET minimizes signal distortion and allows for greater frequency response, making it suitable for high-frequency operations. The dual-gate configuration enhances the control over the gain, with the first gate receiving the input signal and the second gate serving as a gain control element. This arrangement allows for precise adjustments to the amplifier's performance based on the requirements of the application.
The inclusion of a third input for series feedback is a critical feature that enables the amplifier to maintain stability and linearity across its operating range. Feedback is provided through a resistor connected to pin 3, which plays a significant role in determining the overall power gain of the amplifier. By adjusting the resistance value, the designer can tailor the amplifier's gain characteristics to suit specific needs, ensuring optimal performance under varying conditions.
At a frequency of 10 MHz, the amplifier's output capability is noteworthy, delivering 12 dBm into a 50-ohm load while exhibiting only 1 dB of signal compression. This performance indicates that the amplifier can operate effectively without significant distortion, making it suitable for applications requiring high fidelity. The AC coupling in the amplifier design further enhances its versatility, allowing it to handle a wide range of input signal types.
The gain characteristics of the amplifier are impressive, with a gain of 37 dB at 100 MHz, which indicates strong amplification capabilities for signals in this frequency range. However, as the frequency increases to 1 GHz, the gain decreases to 3 dB, which is a common behavior in amplifiers due to factors such as parasitic capacitances and losses that become more pronounced at higher frequencies. This information is crucial for engineers when selecting the amplifier for specific applications, as it highlights the frequency-dependent nature of the amplifier's performance. Overall, the design and specifications of this amplifier make it a robust choice for high-frequency signal processing in various electronic applications.The amplifier"s input stage is a dual-gate GaAs FET, which provides low input capacitance and high transconductance. The dual-gate structure accepts the signal on input 1. Input 2 controls the gain of the amplifier. The amplifier has a third input for use in series feedback. The output feeds back to pin 3 via a single resistor, which controls the overall power gain of the amplifier.
At 10 MHz, the output is capable of delivering 12 dBm into a 50-0 load with 1 dB of signal compression. The ac-coupled amplifier has a gain of 37 dB at 100 MHz and 3 dB at 1 GHz.