Window Comparators
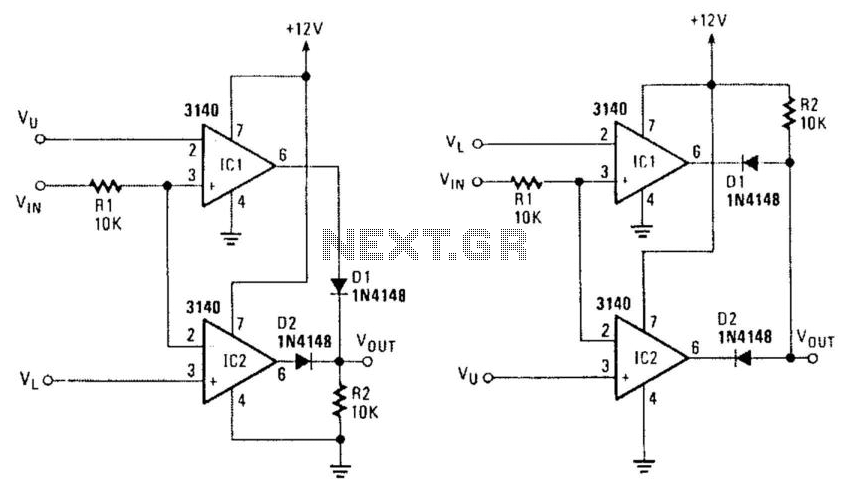
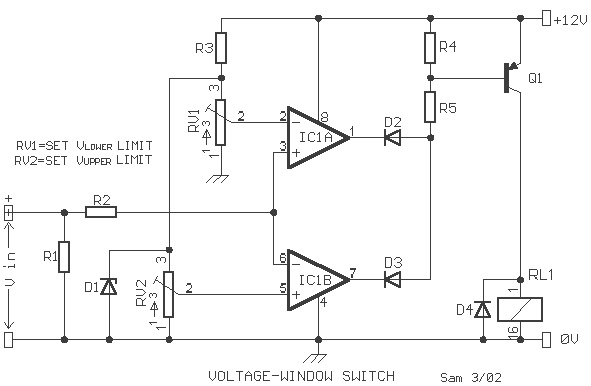
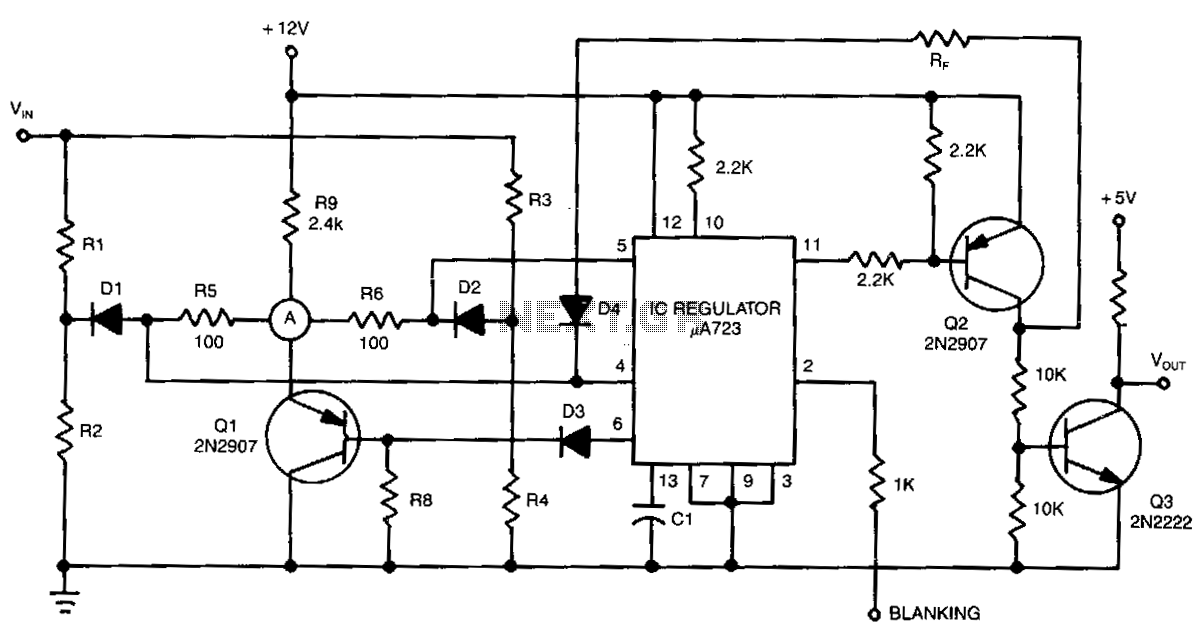
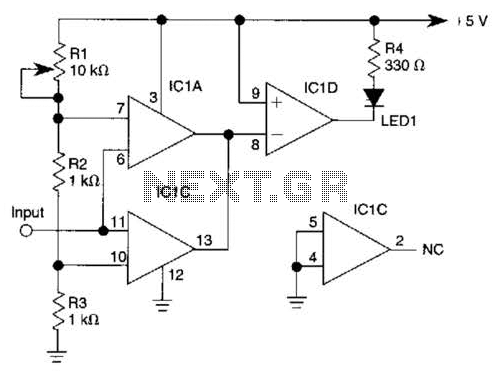
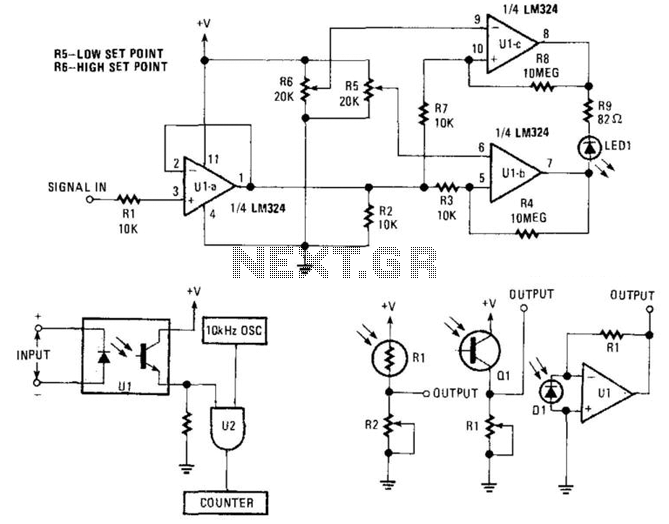
In Figure 104-3(a), when the input voltage (Vin) is between the reference voltages (Vi and Vu), the output voltage (Vout) is low. If Vin exceeds the lower reference voltage (Vl), integrated circuit IC2 generates a low output. Additionally, if Vin is greater than the upper reference voltage (VU), both IC1 and IC2 output low signals, resulting in a low output (Fout). Conversely, if Vin is less than Vl, both IC1 and IC2 output low signals. Figure 104-3(b) operates in the opposite manner, producing a high output when the input voltage (Vin) is between the lower reference voltage (VL) and the upper reference voltage (Vu).
The circuit described involves two integrated circuits (IC1 and IC2) that function as voltage comparators, utilizing reference voltages to determine the output state based on the input voltage (Vin). In the configuration illustrated in Figure 104-3(a), the circuit is designed to produce a low output when Vin is within a specific range defined by the reference voltages Vi and Vu. The behavior of IC2 is particularly crucial; it generates a low signal when Vin exceeds Vl, which in turn influences the output state of the circuit.
When analyzing the conditions of the circuit, if Vin is greater than Vu, both IC1 and IC2 will output low signals, leading to a low state at Fout. This indicates that the circuit is designed to react to input voltages that exceed certain thresholds, effectively creating a logical condition that can be utilized in further electronic applications.
In contrast, Figure 104-3(b) demonstrates an alternative configuration where the circuit is designed to output a high signal when Vin is between the lower reference voltage (VL) and the upper reference voltage (Vu). This behavior highlights the versatility of the circuit design, allowing it to operate in different modes based on the input voltage levels. The use of reference voltages in this manner enables precise control over the output states, making it suitable for various applications in electronic systems where voltage thresholds are critical for operation. In Fig. 104-3(a), when Vin is between reference voltages Vi and Vu, output Vout goes low. If Vin> Vl, IC2 produces a low . Because IC1 outputs low, if V^>VUf both outputs are low and F0ut is low. If Fin < Vl, both IC1 and IC2 are low. Figure 104-3(b) operates the reverse of this; it produces a high when VL
The circuit described involves two integrated circuits (IC1 and IC2) that function as voltage comparators, utilizing reference voltages to determine the output state based on the input voltage (Vin). In the configuration illustrated in Figure 104-3(a), the circuit is designed to produce a low output when Vin is within a specific range defined by the reference voltages Vi and Vu. The behavior of IC2 is particularly crucial; it generates a low signal when Vin exceeds Vl, which in turn influences the output state of the circuit.
When analyzing the conditions of the circuit, if Vin is greater than Vu, both IC1 and IC2 will output low signals, leading to a low state at Fout. This indicates that the circuit is designed to react to input voltages that exceed certain thresholds, effectively creating a logical condition that can be utilized in further electronic applications.
In contrast, Figure 104-3(b) demonstrates an alternative configuration where the circuit is designed to output a high signal when Vin is between the lower reference voltage (VL) and the upper reference voltage (Vu). This behavior highlights the versatility of the circuit design, allowing it to operate in different modes based on the input voltage levels. The use of reference voltages in this manner enables precise control over the output states, making it suitable for various applications in electronic systems where voltage thresholds are critical for operation. In Fig. 104-3(a), when Vin is between reference voltages Vi and Vu, output Vout goes low. If Vin> Vl, IC2 produces a low . Because IC1 outputs low, if V^>VUf both outputs are low and F0ut is low. If Fin < Vl, both IC1 and IC2 are low. Figure 104-3(b) operates the reverse of this; it produces a high when VL