Zener diode tester
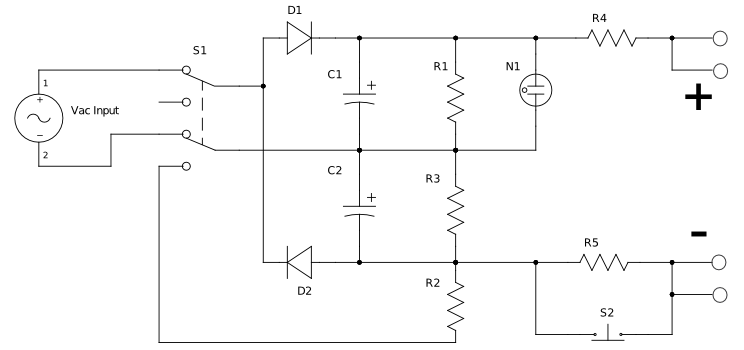
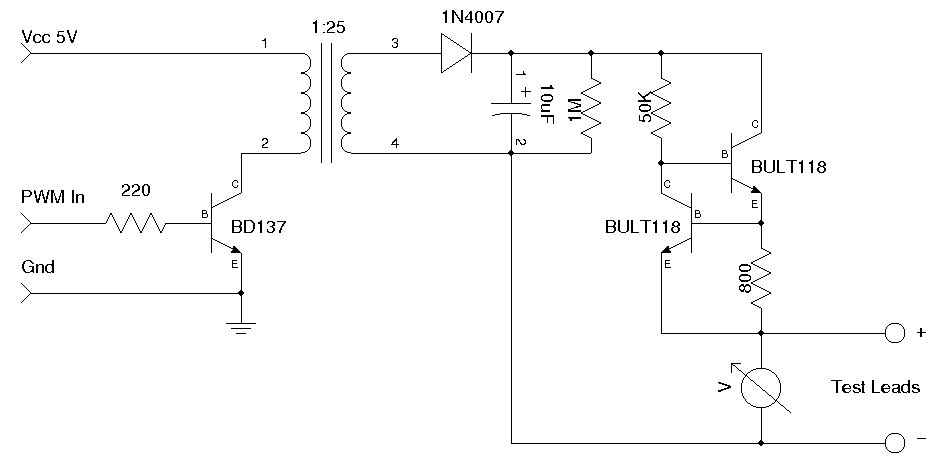
This circuit is designed for testing zener diodes. It connects to a 120V AC line and boosts the output voltage to over 300V, enabling the testing of zener diodes with various voltage ratings. The circuit features a push-button switch that can triple the current if necessary. The output is equipped with two pairs of alligator clips: one pair is for connecting to the diode, while the other pair connects to a multimeter. The voltage across the diode is displayed on the multimeter. It is important to note that this circuit poses a danger due to its direct connection to an AC line and an output voltage of 300V. The output includes resistors on each line that limit the current, enhancing safety, but it can still deliver a significant shock. This circuit employs two rectifiers and capacitors to boost and rectify the AC input voltage to approximately 320V DC. Resistors R4 and R5 are relatively large, limiting the output current to a minimal level. When a zener diode is connected, it creates a shunt circuit, with the output voltage determined by the zener diode. For low voltage zener diodes, the maximum current is about 4mA. Engaging the push-button will triple the current. If a high voltage zener diode is used, the current may be very low, potentially requiring the use of the current tripler button. Given that 320V is a high voltage and can be hazardous, it is critical to reduce the voltage to a safe level before handling the contacts. Resistor R3 is used to discharge the lower capacitor, while R2 quickly discharges the lower capacitor when power is turned off. Resistor R1 is responsible for discharging the upper capacitor, and a neon lamp discharges the top capacitor when its voltage exceeds 80V. When the switches are turned off, the lower capacitor discharges rapidly, reducing the output voltage to approximately 160V almost instantly. The upper capacitor discharges at a slower rate, taking about 2-3 seconds to drop to 80V, at which point the lamp turns off, and around 7 seconds to decrease to 10 volts. Once the lamp turns off, it is safe to touch and connect or disconnect the diode.
This circuit operates as a high-voltage zener diode testing apparatus, featuring a robust design that incorporates safety measures to mitigate risks associated with high voltage. The primary components include two rectifiers that convert the AC input voltage into a DC output, and capacitors that store and stabilize the voltage levels. The use of resistors R4 and R5 is critical in controlling the output current, ensuring that the circuit remains within safe operational limits while allowing for effective testing of zener diodes.
The push-button switch provides an additional functionality to increase the current output, which is particularly useful when working with zener diodes that require higher test currents to function correctly. The output configuration with alligator clips facilitates easy connection to both the zener diode under test and a multimeter, allowing for real-time voltage readings.
Safety is a paramount concern with this circuit, as indicated by the inclusion of discharge resistors and a neon lamp for voltage indication. The resistors R1, R2, and R3 serve to safely discharge the capacitors, preventing accidental shocks when the circuit is not in use. The neon lamp acts as a visual indicator of high voltage, ensuring that users are aware of the circuit's status before attempting to interact with it. Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and efficient means of testing zener diodes, with necessary precautions in place to protect users from high voltage hazards.This is a circuit to test zener diodes. It hooks up to a 120V AC line and boosts the output voltage to over 300V allowing you to test zener diodes of any voltage. The circuit also has a push button switch to triple the current, if needed. The output is attached to 2 pairs of alligator clips. One pair is to attach to the diode. The second pair is to attach to a multimeter. The voltage across the diode is show on you multimeter. It should be noted that this circuit could be dangerous. It is tied directly to an AC line, and has an output of 300V. The output has resistors on each line, which limits the current making it a bit safer, but will still give you quite a shock. This circuit uses the two rectifiers and capacitors to boost and rectifies the AC input voltage to about 320V DC.
R4 and R5 are relatively large, and limit the output current to a small amount. So when you attach the zener diode it creates a shunt circuit, and the output voltage is set by the zener diode. R4 and R5 are relatively large, and limit the output current to a small amount. With a low voltage diode the max current is about 4mA. If you press the push-button the current is tripled. If the zener diode is large, the current will be very low, perhaps too low, so you may need to used the current tripler button.
320V is a high voltage and can be dangerous. So its important to lower the voltage to a safe level before you touch the contacts. R3 is used to discharge the bottom capacitor, and R2 is used to quickly discharge the lower capacitor when power is switched off. R1 is used to discharge the top capacitor and the neon lamp discharges the top capacitor when its voltage is above 80V.
So when the switches are turned off the bottom capacitor quickly discharges and the output voltage is almost instantly lowered to around 160V. The upper capacitor discharges more slowly. It takes about 2-3 seconds to lower to 80V and the lamp turns off, and it takes about 7 seconds to drop to 10 Volts.
But when the lamp turns off its safe to touch, and add/remove the diode. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates as a high-voltage zener diode testing apparatus, featuring a robust design that incorporates safety measures to mitigate risks associated with high voltage. The primary components include two rectifiers that convert the AC input voltage into a DC output, and capacitors that store and stabilize the voltage levels. The use of resistors R4 and R5 is critical in controlling the output current, ensuring that the circuit remains within safe operational limits while allowing for effective testing of zener diodes.
The push-button switch provides an additional functionality to increase the current output, which is particularly useful when working with zener diodes that require higher test currents to function correctly. The output configuration with alligator clips facilitates easy connection to both the zener diode under test and a multimeter, allowing for real-time voltage readings.
Safety is a paramount concern with this circuit, as indicated by the inclusion of discharge resistors and a neon lamp for voltage indication. The resistors R1, R2, and R3 serve to safely discharge the capacitors, preventing accidental shocks when the circuit is not in use. The neon lamp acts as a visual indicator of high voltage, ensuring that users are aware of the circuit's status before attempting to interact with it. Overall, this circuit provides a reliable and efficient means of testing zener diodes, with necessary precautions in place to protect users from high voltage hazards.This is a circuit to test zener diodes. It hooks up to a 120V AC line and boosts the output voltage to over 300V allowing you to test zener diodes of any voltage. The circuit also has a push button switch to triple the current, if needed. The output is attached to 2 pairs of alligator clips. One pair is to attach to the diode. The second pair is to attach to a multimeter. The voltage across the diode is show on you multimeter. It should be noted that this circuit could be dangerous. It is tied directly to an AC line, and has an output of 300V. The output has resistors on each line, which limits the current making it a bit safer, but will still give you quite a shock. This circuit uses the two rectifiers and capacitors to boost and rectifies the AC input voltage to about 320V DC.
R4 and R5 are relatively large, and limit the output current to a small amount. So when you attach the zener diode it creates a shunt circuit, and the output voltage is set by the zener diode. R4 and R5 are relatively large, and limit the output current to a small amount. With a low voltage diode the max current is about 4mA. If you press the push-button the current is tripled. If the zener diode is large, the current will be very low, perhaps too low, so you may need to used the current tripler button.
320V is a high voltage and can be dangerous. So its important to lower the voltage to a safe level before you touch the contacts. R3 is used to discharge the bottom capacitor, and R2 is used to quickly discharge the lower capacitor when power is switched off. R1 is used to discharge the top capacitor and the neon lamp discharges the top capacitor when its voltage is above 80V.
So when the switches are turned off the bottom capacitor quickly discharges and the output voltage is almost instantly lowered to around 160V. The upper capacitor discharges more slowly. It takes about 2-3 seconds to lower to 80V and the lamp turns off, and it takes about 7 seconds to drop to 10 Volts.
But when the lamp turns off its safe to touch, and add/remove the diode. 🔗 External reference