Basic Connection circuit diagram INA326 327 signals and power
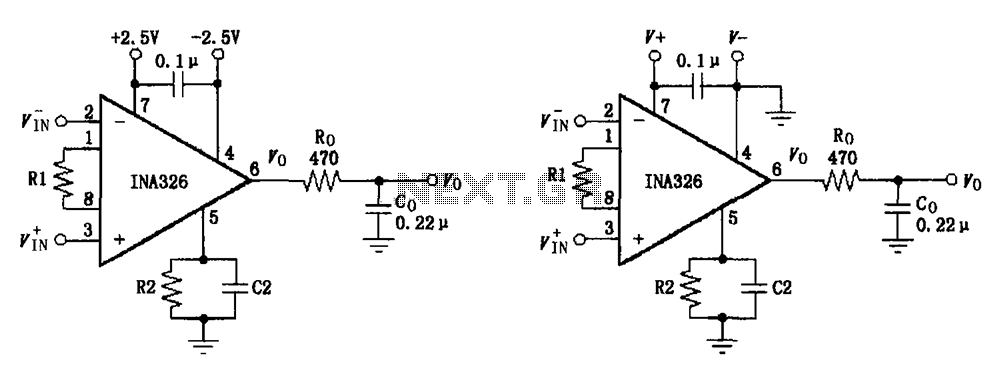
The basic connection circuit for the INA326/327 includes signals and power. A 0.1 µF capacitor is selected for power supply filtering and should be placed as close to the chip's supply pin as possible. Ro and Co serve as the output filter to eliminate noise from the circuit, while also functioning as the input filter for subsequent stages, such as the analog-to-digital converter. The R2 // C2 configuration provides a ground-referenced output voltage. Co and C2 together form a frequency response with -3dB poles at 1 kHz, each pole at 1.5 kHz. The INA326/327 instrumentation amplifiers utilize proprietary technology to achieve a high common-mode rejection ratio (CMR), ensuring that contact resistance, such as that from socket connections, does not significantly reduce the CMR. To enhance high-frequency CMR, a small capacitor can be added between pin 1 and pin 8.
The INA326 and INA327 are precision instrumentation amplifiers designed for high accuracy and low noise applications. The circuit configuration emphasizes the importance of proper power supply decoupling to ensure optimal performance. The choice of a 0.1 µF capacitor for power supply filtering is critical, as it helps to minimize high-frequency noise and provides a stable voltage to the amplifier. The capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the power supply pins of the INA326/327 to reduce inductive effects from the circuit traces.
The output filter, consisting of Ro and Co, is designed to suppress any noise that may be present in the output signal. This filtering is essential when interfacing with sensitive components such as analog-to-digital converters, where noise can affect the accuracy of the digitized signal. The R2 // C2 network provides a ground-referenced output voltage, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity in a mixed-signal environment.
The frequency response characteristics of the circuit are defined by the capacitors Co and C2, which create -3dB poles at 1 kHz, with each pole having a cutoff frequency of 1.5 kHz. This design ensures that the amplifier maintains a flat frequency response within the desired bandwidth, allowing for accurate signal processing.
The INA326/327 amplifiers are equipped with advanced technology that allows for exceptional common-mode rejection, which is particularly beneficial in environments where electrical noise and interference are prevalent. The ability to maintain a high CMR despite the presence of contact resistances, such as those found in socket connections, is a significant advantage. For applications requiring even better high-frequency common-mode rejection, the addition of a small capacitor between pins 1 and 8 can further enhance performance, allowing the amplifier to function effectively in high-frequency applications. This design consideration is vital for ensuring the integrity of the signal in high-speed data acquisition and processing systems. As shown for the basic connection circuit INA326/327 signals and power. Selection of the highest accuracy 0.1 F capacitor as power supply filtering, and should be as close to t he chip supply pin placement. Ro, Co is the output filter can filter out the noise output of the circuit; at the same time as the next stage input filter circuit, such as analog - digital converter input filter. R2 // C2 output voltage is ground referenced. Co and C2 joint formed at 1kHz frequency response of -3dB poles, each pole is 1.5kHz. And other instrumentation amplifiers, INA326/327 with a unique in-house technology to achieve excellent common-mode rejection ratio, and thus there is a connection during the contact resistance (such as socket contact resistance), does not make the common-mode rejection ratio is reduced.
In order to achieve better high-frequency CMR, you can add a small capacitor between 1,8 feet.
The INA326 and INA327 are precision instrumentation amplifiers designed for high accuracy and low noise applications. The circuit configuration emphasizes the importance of proper power supply decoupling to ensure optimal performance. The choice of a 0.1 µF capacitor for power supply filtering is critical, as it helps to minimize high-frequency noise and provides a stable voltage to the amplifier. The capacitor should be placed as close as possible to the power supply pins of the INA326/327 to reduce inductive effects from the circuit traces.
The output filter, consisting of Ro and Co, is designed to suppress any noise that may be present in the output signal. This filtering is essential when interfacing with sensitive components such as analog-to-digital converters, where noise can affect the accuracy of the digitized signal. The R2 // C2 network provides a ground-referenced output voltage, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity in a mixed-signal environment.
The frequency response characteristics of the circuit are defined by the capacitors Co and C2, which create -3dB poles at 1 kHz, with each pole having a cutoff frequency of 1.5 kHz. This design ensures that the amplifier maintains a flat frequency response within the desired bandwidth, allowing for accurate signal processing.
The INA326/327 amplifiers are equipped with advanced technology that allows for exceptional common-mode rejection, which is particularly beneficial in environments where electrical noise and interference are prevalent. The ability to maintain a high CMR despite the presence of contact resistances, such as those found in socket connections, is a significant advantage. For applications requiring even better high-frequency common-mode rejection, the addition of a small capacitor between pins 1 and 8 can further enhance performance, allowing the amplifier to function effectively in high-frequency applications. This design consideration is vital for ensuring the integrity of the signal in high-speed data acquisition and processing systems. As shown for the basic connection circuit INA326/327 signals and power. Selection of the highest accuracy 0.1 F capacitor as power supply filtering, and should be as close to t he chip supply pin placement. Ro, Co is the output filter can filter out the noise output of the circuit; at the same time as the next stage input filter circuit, such as analog - digital converter input filter. R2 // C2 output voltage is ground referenced. Co and C2 joint formed at 1kHz frequency response of -3dB poles, each pole is 1.5kHz. And other instrumentation amplifiers, INA326/327 with a unique in-house technology to achieve excellent common-mode rejection ratio, and thus there is a connection during the contact resistance (such as socket contact resistance), does not make the common-mode rejection ratio is reduced.
In order to achieve better high-frequency CMR, you can add a small capacitor between 1,8 feet.