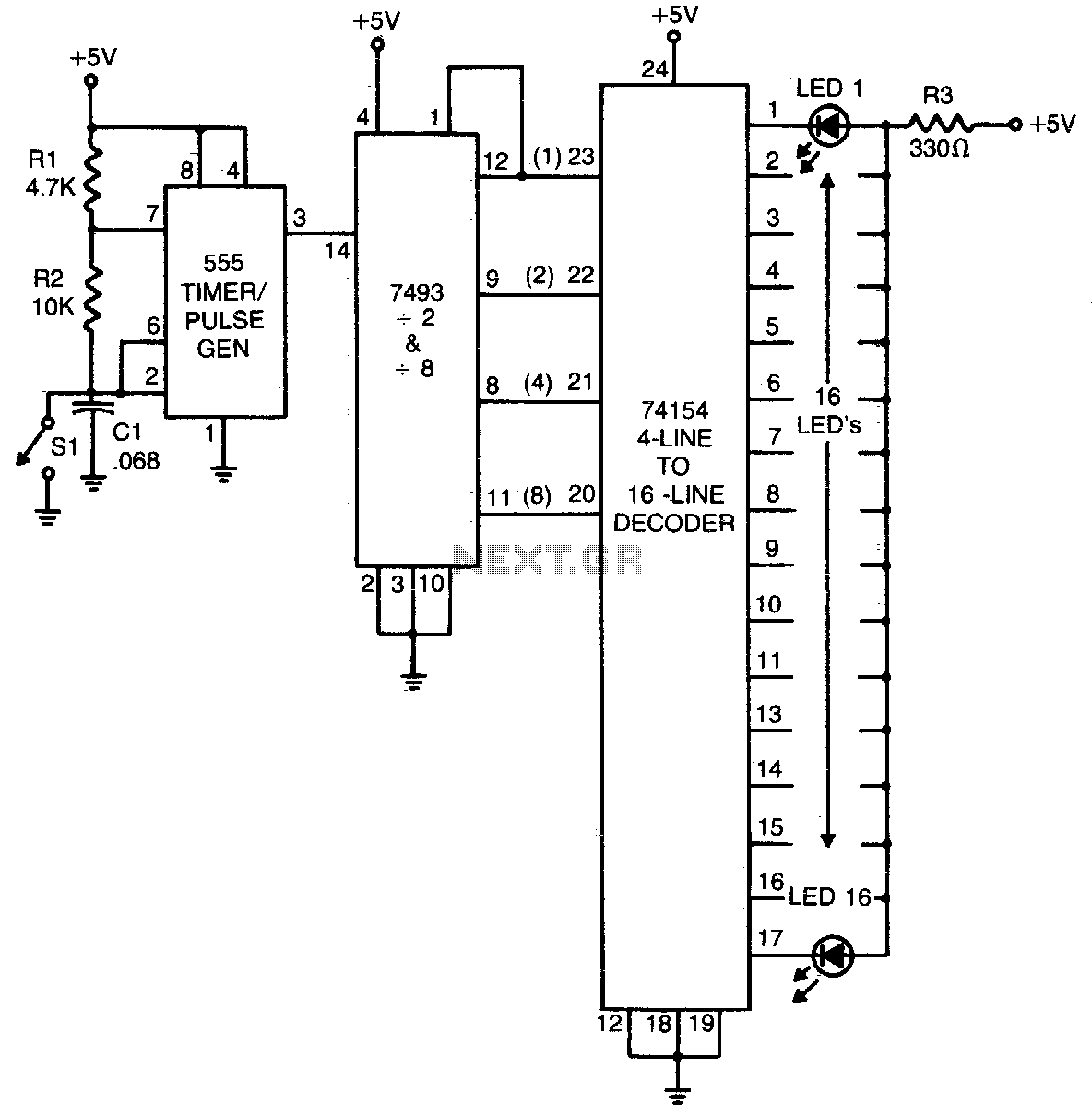
Frequency sensitive rheostat manually start reversing circuit
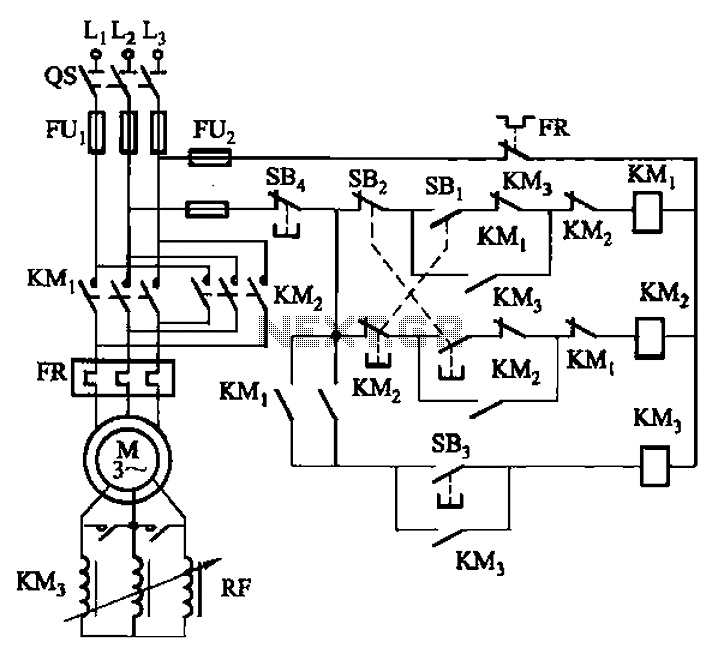
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-166 employs a button control mechanism. To initiate forward motion, the user presses button SB1, which activates the motor rotor through a frequency-sensitive rheostat (RF). As the motor speed approaches its rated speed, a brief press of button SB3 disables the RF operation. For reverse operation, the user presses button SB2 to start the process, which follows the same sequence as the forward motion.
The circuit operates by utilizing a motor control system that integrates a frequency-sensitive rheostat to manage the motor's speed effectively. The button controls (SB1, SB2, and SB3) provide a user-friendly interface for initiating forward and reverse operations. When SB1 is pressed, it sends a signal to the motor control circuitry, allowing current to flow through the frequency-sensitive rheostat (RF). This component adjusts the voltage applied to the motor, thereby controlling its rotational speed based on the frequency of the input signal.
As the motor accelerates and approaches its rated speed, the user can short press button SB3, which triggers a feedback mechanism that momentarily disengages the RF. This allows the motor to run at its rated speed without the additional resistance from the rheostat, optimizing performance and efficiency.
For reverse operations, button SB2 is utilized to initiate the same process as the forward motion. The circuit design ensures that both forward and reverse operations can be performed smoothly, with the ability to adjust speed dynamically based on user input. The inclusion of frequency-sensitive control allows for precise speed management, making this circuit suitable for applications requiring variable motor control. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to motor control using simple button interfaces and responsive electronic components. Circuit shown in Figure 3-166. It uses the button control. When start forward, press SB], the motor rotor string frequency sensitive people rheostat RF operation. When the moto r speed increased to close to the rated speed, short press the button SB3, RF out of operation. Reverse start, press SB2 to startup process forward and start the same process.
The circuit operates by utilizing a motor control system that integrates a frequency-sensitive rheostat to manage the motor's speed effectively. The button controls (SB1, SB2, and SB3) provide a user-friendly interface for initiating forward and reverse operations. When SB1 is pressed, it sends a signal to the motor control circuitry, allowing current to flow through the frequency-sensitive rheostat (RF). This component adjusts the voltage applied to the motor, thereby controlling its rotational speed based on the frequency of the input signal.
As the motor accelerates and approaches its rated speed, the user can short press button SB3, which triggers a feedback mechanism that momentarily disengages the RF. This allows the motor to run at its rated speed without the additional resistance from the rheostat, optimizing performance and efficiency.
For reverse operations, button SB2 is utilized to initiate the same process as the forward motion. The circuit design ensures that both forward and reverse operations can be performed smoothly, with the ability to adjust speed dynamically based on user input. The inclusion of frequency-sensitive control allows for precise speed management, making this circuit suitable for applications requiring variable motor control. Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical approach to motor control using simple button interfaces and responsive electronic components. Circuit shown in Figure 3-166. It uses the button control. When start forward, press SB], the motor rotor string frequency sensitive people rheostat RF operation. When the moto r speed increased to close to the rated speed, short press the button SB3, RF out of operation. Reverse start, press SB2 to startup process forward and start the same process.