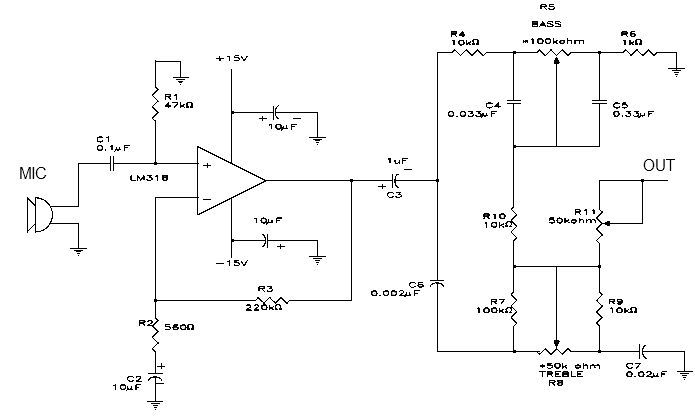
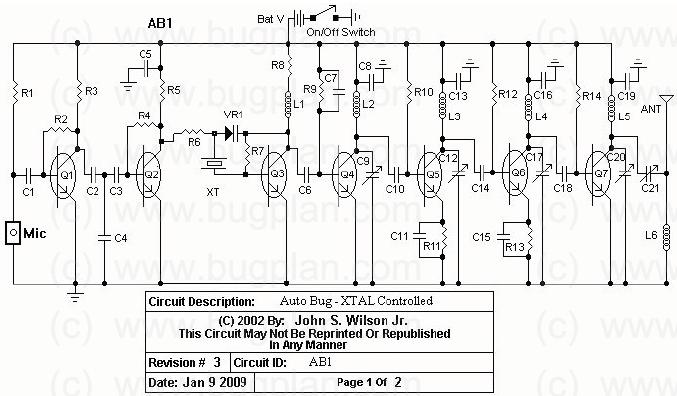
DC motor armature series resistance start dynamic braking circuit of the two-way operation
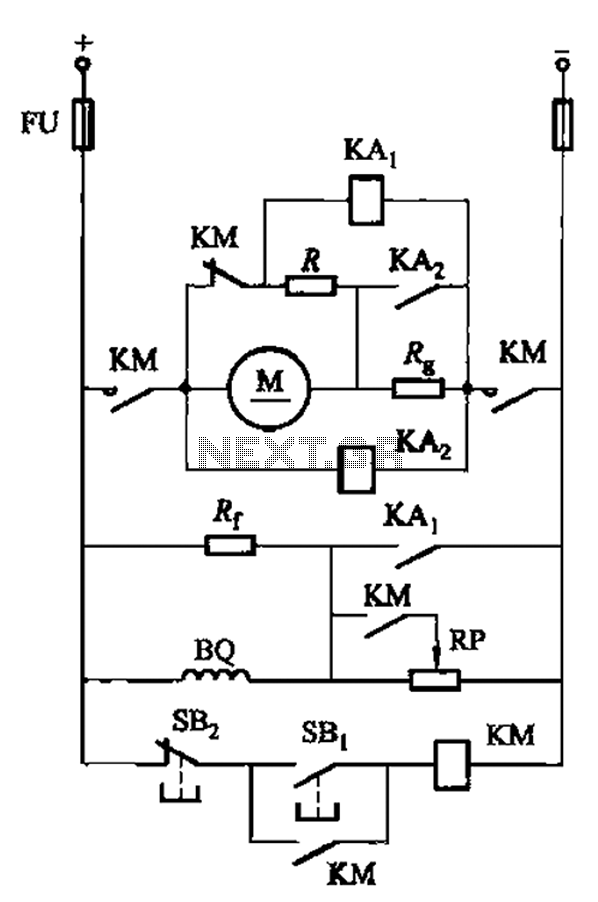
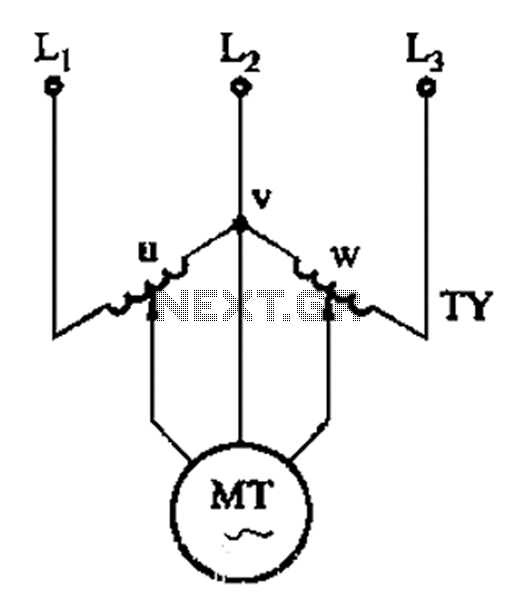
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-197 features a dish adjust rheostat (RP) that allows for the adjustment of field current, which in turn modifies the motor speed.
The circuit operates by utilizing a rheostat, which is a variable resistor that can be adjusted to change the resistance in the circuit. By altering the resistance of the rheostat RP, the field current flowing through the motor can be varied. This change in field current directly influences the strength of the magnetic field generated by the motor, ultimately affecting its speed.
In practical applications, the adjustment of the rheostat may be implemented through a manual knob or electronically via a control system, allowing for precise control over motor performance. The circuit should be designed to handle the expected voltage and current ratings, ensuring that the rheostat can dissipate any heat generated during operation without failure.
Additionally, it is important to consider the characteristics of the motor being used, as different types (e.g., DC motors, stepper motors) respond differently to changes in field current. Proper selection of the rheostat and the inclusion of protective components, such as fuses or circuit breakers, is also essential to safeguard the circuit from overcurrent conditions.
Overall, this circuit design provides a straightforward method for controlling motor speed through field current adjustment, making it suitable for various applications where variable speed operation is required. Circuit shown in Figure 3-197. Dish adjust rheostat RP, can change the field current to change the motor speed.
The circuit operates by utilizing a rheostat, which is a variable resistor that can be adjusted to change the resistance in the circuit. By altering the resistance of the rheostat RP, the field current flowing through the motor can be varied. This change in field current directly influences the strength of the magnetic field generated by the motor, ultimately affecting its speed.
In practical applications, the adjustment of the rheostat may be implemented through a manual knob or electronically via a control system, allowing for precise control over motor performance. The circuit should be designed to handle the expected voltage and current ratings, ensuring that the rheostat can dissipate any heat generated during operation without failure.
Additionally, it is important to consider the characteristics of the motor being used, as different types (e.g., DC motors, stepper motors) respond differently to changes in field current. Proper selection of the rheostat and the inclusion of protective components, such as fuses or circuit breakers, is also essential to safeguard the circuit from overcurrent conditions.
Overall, this circuit design provides a straightforward method for controlling motor speed through field current adjustment, making it suitable for various applications where variable speed operation is required. Circuit shown in Figure 3-197. Dish adjust rheostat RP, can change the field current to change the motor speed.