Bistable circuit control motor reversing circuit
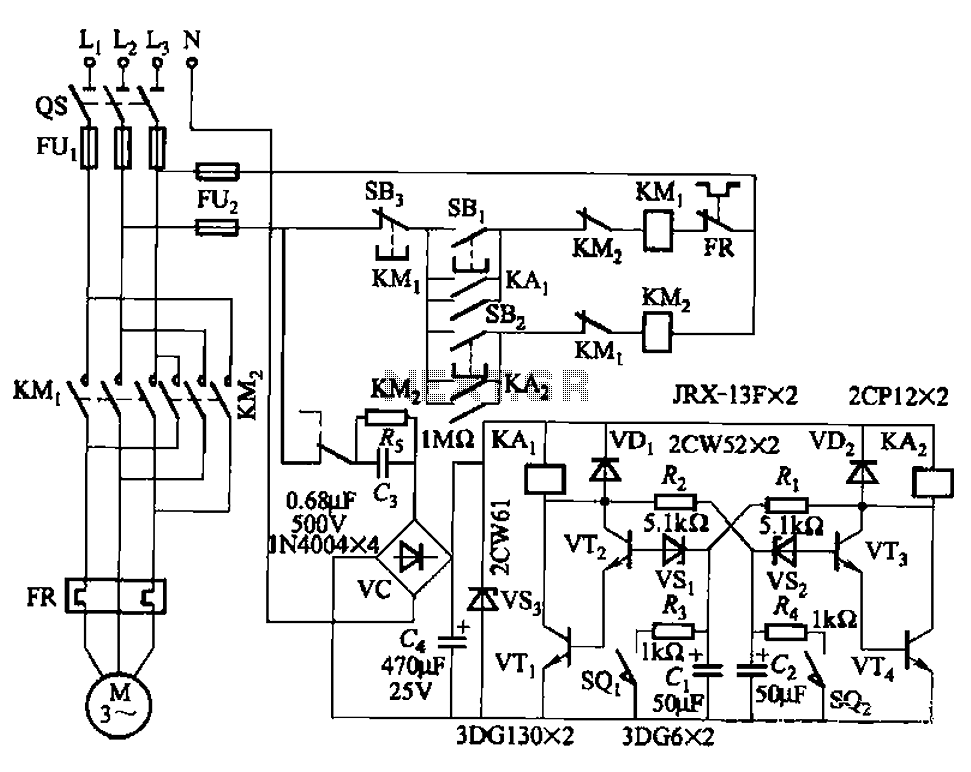
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-72 employs a deformable bistable reversing motor control mechanism that automatically initiates and halts operation during a user-defined time delay. This feature is designed to safeguard the motor from potential impacts during the reversing transition. In the circuit, terminals sQi and SQ2 serve as the forward and reverse limit switch connections. By adjusting the values of resistors R1, R2, capacitors C1, C2, and selecting various models and specifications of the voltage regulator, the stop (delay) time can be modified.
The schematic represents a bistable motor control circuit that is capable of reversing the direction of a motor while ensuring a safe transition between operational states. The circuit consists of a microcontroller or a relay-based control unit that manages the motor's direction based on inputs from the limit switches. The limit switches, sQi and SQ2, are critical components that detect the motor's position, allowing for precise control over its operation.
The time delay feature is achieved through the use of timing components, specifically resistors and capacitors (R1, R2, C1, C2). The values of these components can be adjusted to set the desired delay time, which is crucial for preventing mechanical stress on the motor during direction changes. The voltage regulator's specifications also play a significant role in ensuring that the circuit operates within optimal voltage levels, contributing to the reliability and longevity of the motor.
When the motor reaches a limit switch, the circuit responds by reversing the motor's direction after the specified delay. This functionality is essential in applications where the motor must operate in both forward and reverse directions without causing damage to the mechanical components. The design of the circuit allows for flexibility in adjusting the timing and operational parameters, making it suitable for various applications in automation and control systems. Circuit shown in Figure 3-72. The circuit uses deformable bistable reversing motor control circuit automatically run and stop there during the time delay (time adjustable), to protect the motor from impact when the motor reversing conversion. Figure, sQi and SQ2 are forward and reverse limit switch terminals. Adjustment R], R2, C, Cz values and choose different models, specifications of the regulator and Vsl vs, Can change the stop (delay) time.
The schematic represents a bistable motor control circuit that is capable of reversing the direction of a motor while ensuring a safe transition between operational states. The circuit consists of a microcontroller or a relay-based control unit that manages the motor's direction based on inputs from the limit switches. The limit switches, sQi and SQ2, are critical components that detect the motor's position, allowing for precise control over its operation.
The time delay feature is achieved through the use of timing components, specifically resistors and capacitors (R1, R2, C1, C2). The values of these components can be adjusted to set the desired delay time, which is crucial for preventing mechanical stress on the motor during direction changes. The voltage regulator's specifications also play a significant role in ensuring that the circuit operates within optimal voltage levels, contributing to the reliability and longevity of the motor.
When the motor reaches a limit switch, the circuit responds by reversing the motor's direction after the specified delay. This functionality is essential in applications where the motor must operate in both forward and reverse directions without causing damage to the mechanical components. The design of the circuit allows for flexibility in adjusting the timing and operational parameters, making it suitable for various applications in automation and control systems. Circuit shown in Figure 3-72. The circuit uses deformable bistable reversing motor control circuit automatically run and stop there during the time delay (time adjustable), to protect the motor from impact when the motor reversing conversion. Figure, sQi and SQ2 are forward and reverse limit switch terminals. Adjustment R], R2, C, Cz values and choose different models, specifications of the regulator and Vsl vs, Can change the stop (delay) time.