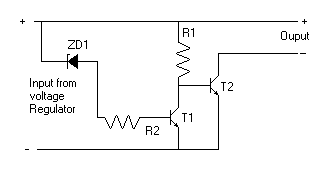
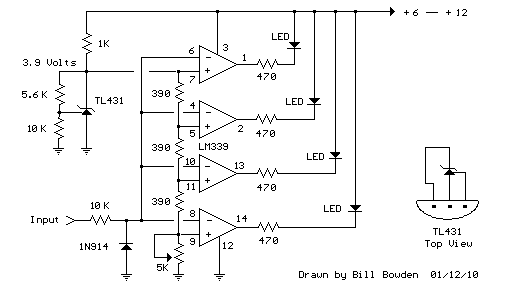
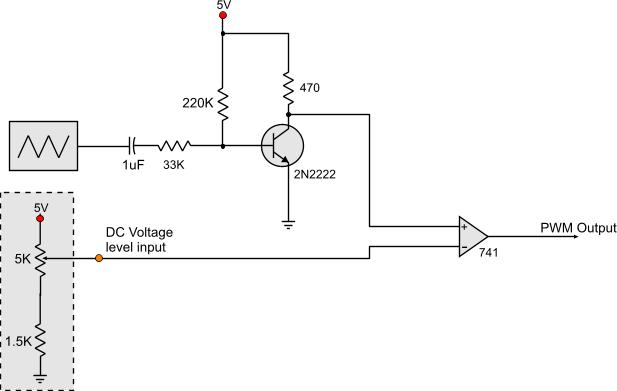
12 Volt Supply Regulated
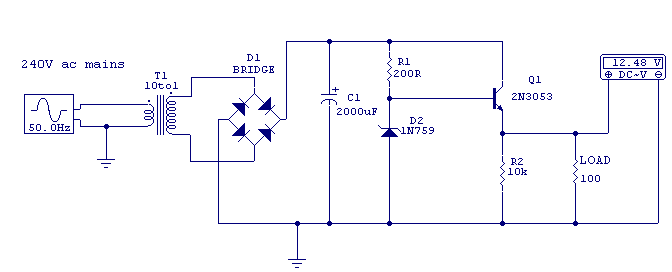
This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Approximately 0.7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12.3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit.
The described circuit employs a 13-volt zener diode (D2) to achieve voltage regulation. The zener diode functions by maintaining a stable output voltage across its terminals when reverse-biased, effectively clamping the voltage to approximately 13 volts. In this configuration, the voltage drop across the base-emitter (b-e) junction of the transistors is approximately 0.7 volts. This drop is typical for silicon transistors and is necessary for their operation in the active region.
The output voltage available from the circuit is approximately 12.3 volts, which is calculated by subtracting the 0.7 volts from the zener voltage. This output is suitable for powering various electronic loads, with the circuit capable of supplying a maximum current of 500 mA.
The amplified zener circuit design enhances the current drive capability of the zener diode, allowing it to handle higher loads without compromising voltage stability. The inclusion of transistors in the design serves to amplify the current, enabling the circuit to maintain the desired output voltage even under varying load conditions.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in power supply systems where a stable voltage is crucial, such as in sensor applications, microcontroller power supplies, or other electronic devices requiring a regulated voltage source. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered, as the transistors may generate heat during operation, especially when supplying currents near the maximum rating.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0.7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12.3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a 13-volt zener diode (D2) to achieve voltage regulation. The zener diode functions by maintaining a stable output voltage across its terminals when reverse-biased, effectively clamping the voltage to approximately 13 volts. In this configuration, the voltage drop across the base-emitter (b-e) junction of the transistors is approximately 0.7 volts. This drop is typical for silicon transistors and is necessary for their operation in the active region.
The output voltage available from the circuit is approximately 12.3 volts, which is calculated by subtracting the 0.7 volts from the zener voltage. This output is suitable for powering various electronic loads, with the circuit capable of supplying a maximum current of 500 mA.
The amplified zener circuit design enhances the current drive capability of the zener diode, allowing it to handle higher loads without compromising voltage stability. The inclusion of transistors in the design serves to amplify the current, enabling the circuit to maintain the desired output voltage even under varying load conditions.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in power supply systems where a stable voltage is crucial, such as in sensor applications, microcontroller power supplies, or other electronic devices requiring a regulated voltage source. Proper heat dissipation measures should be considered, as the transistors may generate heat during operation, especially when supplying currents near the maximum rating.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0.7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12.3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference