12V Inverter Circuit Using 4013
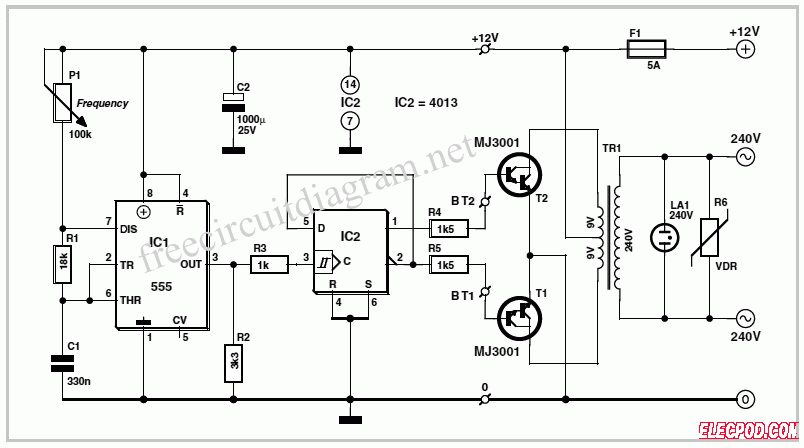
This circuit diagram for a 12V inverter is straightforward to construct, utilizing inexpensive components that many electronics hobbyists may already possess. While it is feasible to design a more powerful circuit, the complexity associated with handling high currents on the low-voltage side can lead to complications. The circuit diagram for the 12V inverter is easy to follow. A classic 555 timer chip, designated as IC1, is configured as an astable multivibrator operating at a frequency close to 100 Hz, which can be fine-tuned using potentiometer P1. This configuration drives a D-type flip-flop implemented with a CMOS 4013 IC, generating complementary square wave signals (in antiphase) on its Q and Q outputs, which are suitable for driving the output power transistors. As the output current from the CMOS 4013 is minimal, Darlington power transistors are utilized to achieve the required output current. The selected transistors are MJ3001s, which are affordable and readily available, although any equivalent power Darlington transistor could be used. These transistors drive a 230V to 9V center-tapped transformer used in reverse to produce a 230V output. The presence of the 230VAC voltage is indicated by a neon light, while a voltage-dependent resistor (VDR) such as S10K250 or S07K250 is employed to suppress spikes and surges that may occur at the transistor switching points.
The 12V inverter circuit operates by converting a low voltage DC input into a high voltage AC output, which is essential for powering devices that require 230V AC. The astable multivibrator configuration of the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave signal, which is critical for the operation of the inverter. The frequency of this signal can be adjusted via the potentiometer, allowing for fine-tuning of the output waveform.
The CMOS 4013 flip-flop receives the square wave signal from the 555 timer and produces two complementary outputs. These outputs are essential for driving the Darlington transistors, which are configured in a push-pull arrangement to amplify the current. The MJ3001 transistors, known for their high gain and ability to handle significant current loads, are ideal for this purpose. They ensure that sufficient current is supplied to the transformer, allowing it to step up the voltage to the desired 230V AC level.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this circuit. By being used in reverse, it converts the low-voltage high-current output from the transistors into a high-voltage low-current output. The center-tapped design of the transformer provides two equal voltages, which are combined to produce the required AC output.
To ensure the safety and reliability of the circuit, a neon indicator light is included to signal the presence of the high voltage output. Additionally, the VDR acts as a protective element, absorbing transient voltage spikes that could otherwise damage the transistors or other components in the circuit.
Overall, this 12V inverter circuit is a practical and efficient solution for converting DC to AC power, making it a valuable project for electronics enthusiasts looking to explore inverter technology.This circuit is a circuit diagram 12V inverter is very easy to build, cheap components that many electronics hobbyists may even already have. Though it is possible to build a more powerful circuit, the complexity caused by the very heavy currents to be handled on the low-voltage side leads to circuits.
The circuit diagram of 12v inverter is easy t o follow. A classic 555 timer chip, identified as IC1, is configured as an astable multivibrator at a frequency close to 100 Hz, which can be adjusted accurately by means of potentiometer P1. It is used to drive a D type flip-flop produced using a CMOS type 4013 IC. This produces perfect complementary squarewave signals (in antiphase) on its Q and Q outputs suitable for driving the output power transistors.
The following is a schematic drawing: As the output current available from the CMOS 4013 is very small, Darlington power transistors are used to arrive at the necessary output current. We have chosen MJ3001s from the now defunct Motorola (only as a semi-conductor manufacturer, of course!) which are cheap and readily available, but any equivalent powerDarlington could be used.
These drive a 230 V to 2 G— 9 V centre tapped transformer used backwards` to produce the 230 V output. The presence of the 230 VAC voltage is indicated by a neon light, while a VDR (voltage dependent resistor) type S10K250 or S07K250 clips off the spikes and surges that may appear at the transistor switching points.
🔗 External reference
The 12V inverter circuit operates by converting a low voltage DC input into a high voltage AC output, which is essential for powering devices that require 230V AC. The astable multivibrator configuration of the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave signal, which is critical for the operation of the inverter. The frequency of this signal can be adjusted via the potentiometer, allowing for fine-tuning of the output waveform.
The CMOS 4013 flip-flop receives the square wave signal from the 555 timer and produces two complementary outputs. These outputs are essential for driving the Darlington transistors, which are configured in a push-pull arrangement to amplify the current. The MJ3001 transistors, known for their high gain and ability to handle significant current loads, are ideal for this purpose. They ensure that sufficient current is supplied to the transformer, allowing it to step up the voltage to the desired 230V AC level.
The transformer plays a crucial role in this circuit. By being used in reverse, it converts the low-voltage high-current output from the transistors into a high-voltage low-current output. The center-tapped design of the transformer provides two equal voltages, which are combined to produce the required AC output.
To ensure the safety and reliability of the circuit, a neon indicator light is included to signal the presence of the high voltage output. Additionally, the VDR acts as a protective element, absorbing transient voltage spikes that could otherwise damage the transistors or other components in the circuit.
Overall, this 12V inverter circuit is a practical and efficient solution for converting DC to AC power, making it a valuable project for electronics enthusiasts looking to explore inverter technology.This circuit is a circuit diagram 12V inverter is very easy to build, cheap components that many electronics hobbyists may even already have. Though it is possible to build a more powerful circuit, the complexity caused by the very heavy currents to be handled on the low-voltage side leads to circuits.
The circuit diagram of 12v inverter is easy t o follow. A classic 555 timer chip, identified as IC1, is configured as an astable multivibrator at a frequency close to 100 Hz, which can be adjusted accurately by means of potentiometer P1. It is used to drive a D type flip-flop produced using a CMOS type 4013 IC. This produces perfect complementary squarewave signals (in antiphase) on its Q and Q outputs suitable for driving the output power transistors.
The following is a schematic drawing: As the output current available from the CMOS 4013 is very small, Darlington power transistors are used to arrive at the necessary output current. We have chosen MJ3001s from the now defunct Motorola (only as a semi-conductor manufacturer, of course!) which are cheap and readily available, but any equivalent powerDarlington could be used.
These drive a 230 V to 2 G— 9 V centre tapped transformer used backwards` to produce the 230 V output. The presence of the 230 VAC voltage is indicated by a neon light, while a VDR (voltage dependent resistor) type S10K250 or S07K250 clips off the spikes and surges that may appear at the transistor switching points.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713