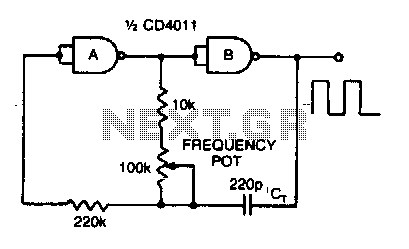
12vdc 220vac inverter using cmos cd4047
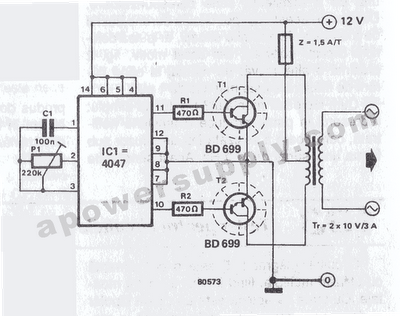
The inverter circuit features the CMOS 4047 as its primary component, converting a 12V DC voltage to a 220V AC voltage. The 4047 operates as an astable multivibrator. A symmetrical rectangular signal is generated at pins 10 and 11, which is subsequently amplified by two Darlington transistors, T1 and T2, before reaching the secondary coil of a transformer network rated at 2 x 10V/1. The primary coil terminals produce a 220V AC output. To enhance performance, it is recommended to use a toroidal core transformer to minimize losses. The output frequency can be adjusted within the range of 50 to 400 Hz using potentiometer P1.
The inverter circuit utilizing the CMOS 4047 offers a robust solution for converting low-voltage DC power to high-voltage AC power, making it suitable for various applications such as powering household appliances or for use in renewable energy systems. The CMOS 4047 is configured as an astable multivibrator, which generates a continuous square wave output. This output is crucial for driving the subsequent amplification stage.
The use of Darlington transistors T1 and T2 serves to significantly increase the current output of the circuit, allowing for effective driving of the transformer. These transistors are known for their high current gain, which ensures that the signal from the 4047 can be amplified sufficiently to drive the transformer without distortion.
The transformer plays a critical role in stepping up the voltage from the secondary coil. The specification of the transformer as 2 x 10V/1 indicates that it is designed for a specific winding configuration, which allows it to handle the required power rating. The choice of a toroidal core transformer is advantageous due to its efficiency and reduced electromagnetic interference, which contributes to overall performance improvement by minimizing losses during operation.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a potentiometer, P1, for frequency adjustment allows for flexibility in the output frequency, catering to different application requirements. The ability to vary the frequency from 50 Hz to 400 Hz offers versatility, enabling the inverter to be tailored for specific devices that may operate at different frequencies. This feature is particularly useful in applications where precise frequency control is necessary for optimal performance.
Overall, this inverter circuit design is efficient, adaptable, and capable of providing a reliable source of AC power from a DC input, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems.The inverter circuit has a central component, the CMOS 4047, and converts a 12V DC voltage to 220V AC voltage. 4047 is utilised as a astable multivibrator. At pin 10 and 11 we find a rectangular symmetrically signal which is amplified by tow Darlington transistors T1 and T2 and finally reaches the secondary coil of a transformer network (2 x 10V/1
00VA). Primary coil terminals voltage is 220 alternative voltage. To obtain a better performance use a toroidal core transformer with reduced losses. With P1 the output frequency can be regulated between certain limits (50 400Hz). 🔗 External reference
The inverter circuit utilizing the CMOS 4047 offers a robust solution for converting low-voltage DC power to high-voltage AC power, making it suitable for various applications such as powering household appliances or for use in renewable energy systems. The CMOS 4047 is configured as an astable multivibrator, which generates a continuous square wave output. This output is crucial for driving the subsequent amplification stage.
The use of Darlington transistors T1 and T2 serves to significantly increase the current output of the circuit, allowing for effective driving of the transformer. These transistors are known for their high current gain, which ensures that the signal from the 4047 can be amplified sufficiently to drive the transformer without distortion.
The transformer plays a critical role in stepping up the voltage from the secondary coil. The specification of the transformer as 2 x 10V/1 indicates that it is designed for a specific winding configuration, which allows it to handle the required power rating. The choice of a toroidal core transformer is advantageous due to its efficiency and reduced electromagnetic interference, which contributes to overall performance improvement by minimizing losses during operation.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a potentiometer, P1, for frequency adjustment allows for flexibility in the output frequency, catering to different application requirements. The ability to vary the frequency from 50 Hz to 400 Hz offers versatility, enabling the inverter to be tailored for specific devices that may operate at different frequencies. This feature is particularly useful in applications where precise frequency control is necessary for optimal performance.
Overall, this inverter circuit design is efficient, adaptable, and capable of providing a reliable source of AC power from a DC input, making it a valuable component in modern electronic systems.The inverter circuit has a central component, the CMOS 4047, and converts a 12V DC voltage to 220V AC voltage. 4047 is utilised as a astable multivibrator. At pin 10 and 11 we find a rectangular symmetrically signal which is amplified by tow Darlington transistors T1 and T2 and finally reaches the secondary coil of a transformer network (2 x 10V/1
00VA). Primary coil terminals voltage is 220 alternative voltage. To obtain a better performance use a toroidal core transformer with reduced losses. With P1 the output frequency can be regulated between certain limits (50 400Hz). 🔗 External reference