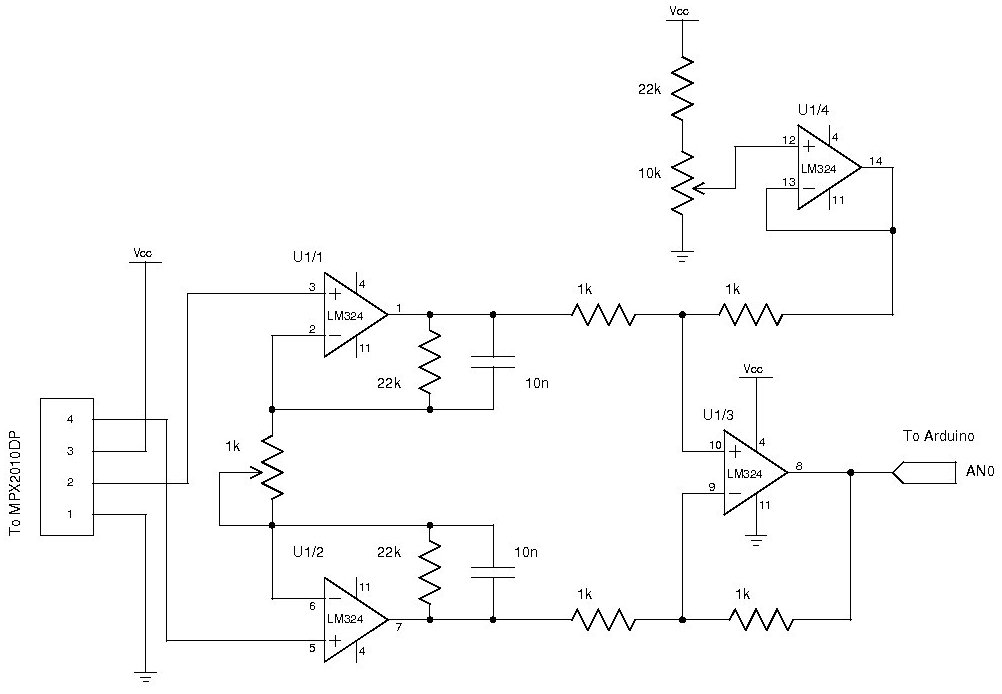
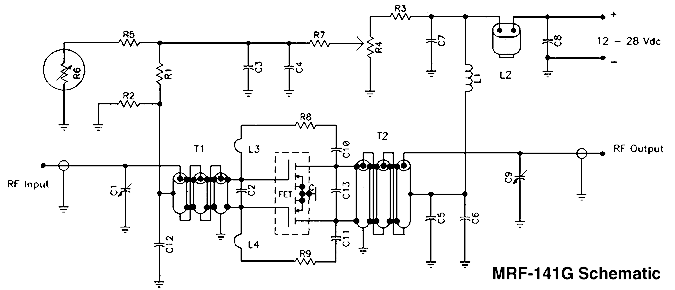
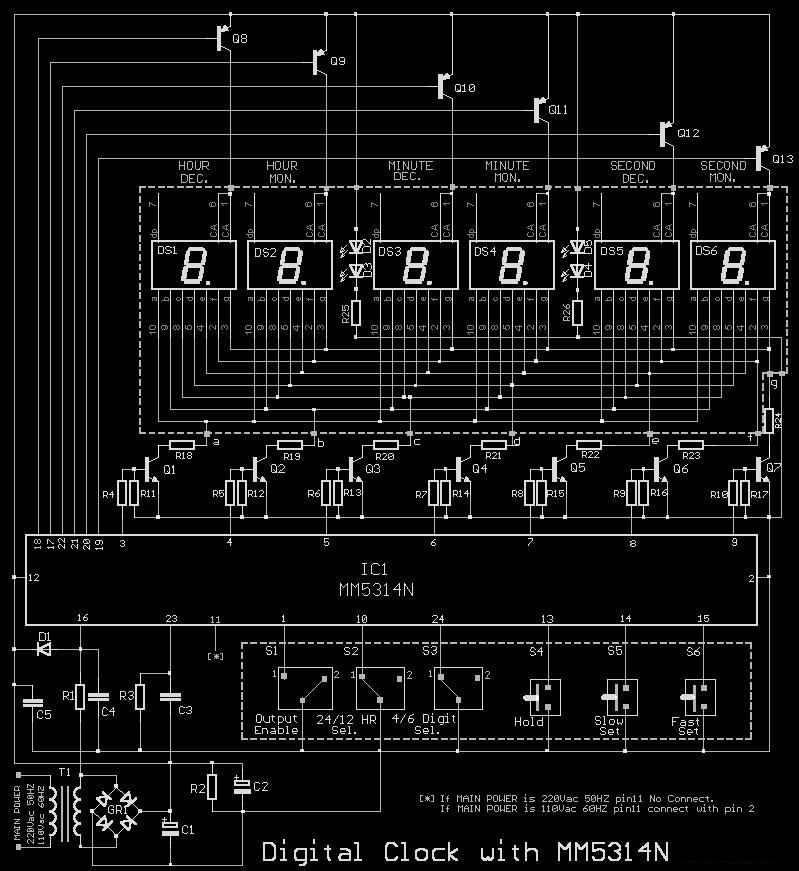
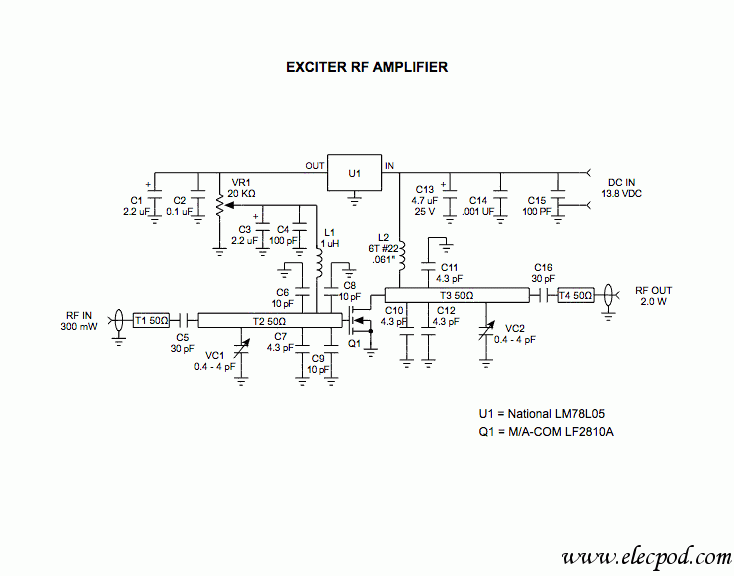
Small Amplifier Using Transistors
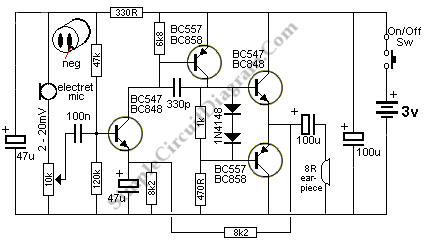
The output of this circuit is push-pull and consumes less than 3 mA (with no signal) but drives the earpiece to a very loud level when audio is detected.
This circuit operates in a push-pull configuration, which allows it to efficiently drive an earpiece or speaker with minimal power consumption. The quiescent current draw is less than 3 mA when idle, indicating a low-power design that is suitable for battery-operated devices. The push-pull arrangement utilizes complementary transistors or amplifying devices to amplify the audio signal while maintaining a balanced output.
When an audio signal is detected, the circuit dynamically adjusts to deliver a significant output power to the earpiece, producing a loud sound. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications where high audio output is required from a compact and energy-efficient circuit.
The design may include additional components such as capacitors for coupling and bypassing, resistors for biasing, and possibly feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and ensure linearity in audio reproduction. The circuit's topology may also feature protection elements to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions or to filter out unwanted noise, ensuring a clear audio signal is delivered to the earpiece.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective solution for applications requiring high audio output with minimal power consumption, making it ideal for portable audio devices.The output of this circuit is push-pull and consumes less than 3mA (with no signal) but drives the earpiece to a very loud level when audio is detected.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit operates in a push-pull configuration, which allows it to efficiently drive an earpiece or speaker with minimal power consumption. The quiescent current draw is less than 3 mA when idle, indicating a low-power design that is suitable for battery-operated devices. The push-pull arrangement utilizes complementary transistors or amplifying devices to amplify the audio signal while maintaining a balanced output.
When an audio signal is detected, the circuit dynamically adjusts to deliver a significant output power to the earpiece, producing a loud sound. This capability is particularly beneficial in applications where high audio output is required from a compact and energy-efficient circuit.
The design may include additional components such as capacitors for coupling and bypassing, resistors for biasing, and possibly feedback mechanisms to stabilize the gain and ensure linearity in audio reproduction. The circuit's topology may also feature protection elements to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions or to filter out unwanted noise, ensuring a clear audio signal is delivered to the earpiece.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies an effective solution for applications requiring high audio output with minimal power consumption, making it ideal for portable audio devices.The output of this circuit is push-pull and consumes less than 3mA (with no signal) but drives the earpiece to a very loud level when audio is detected.. 🔗 External reference