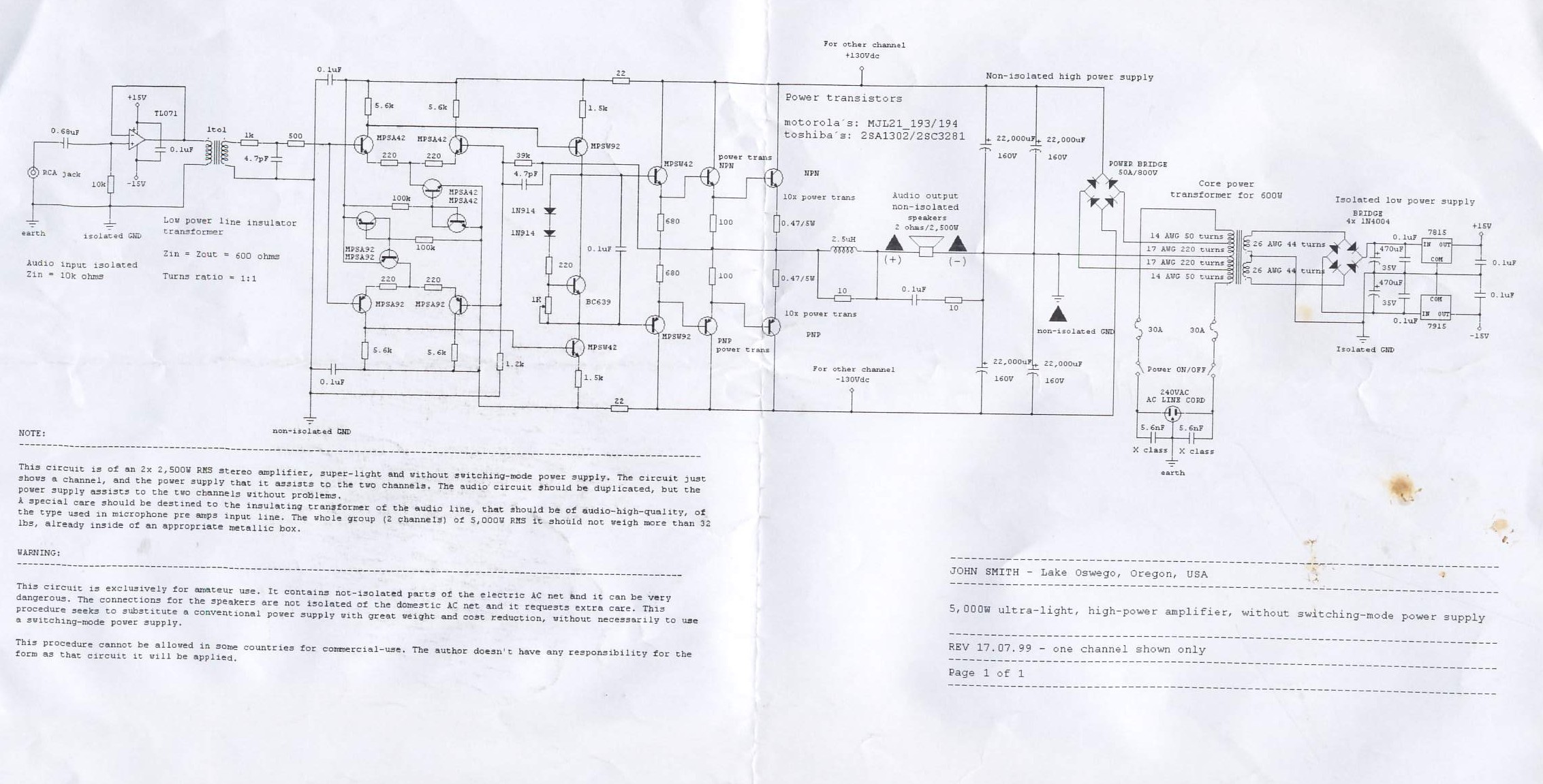
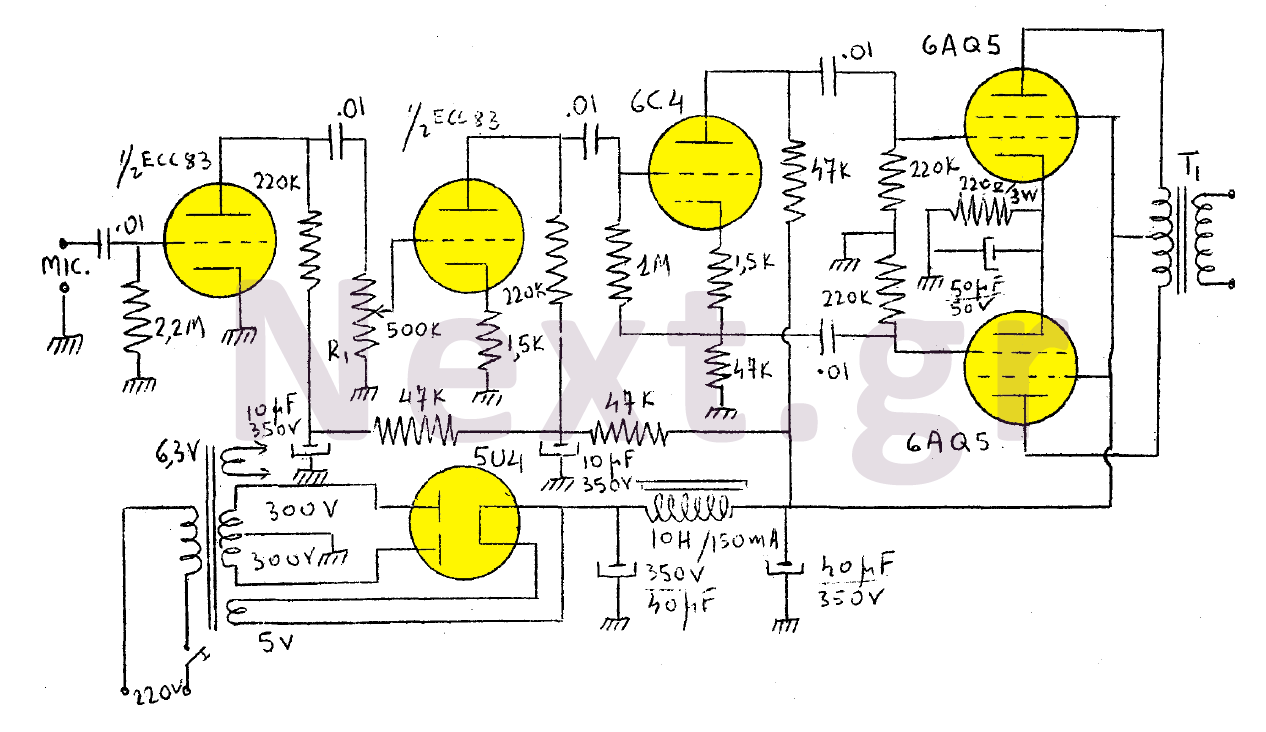
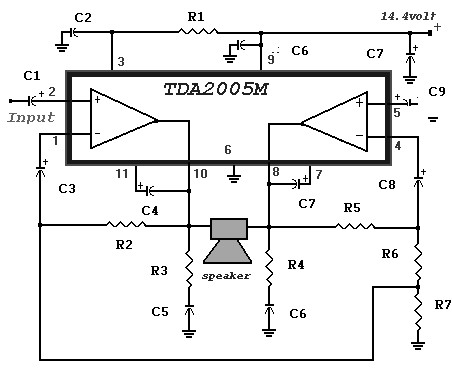
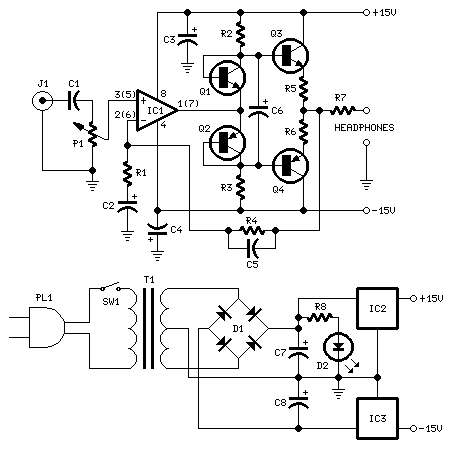
200Mhz cascode amplifier
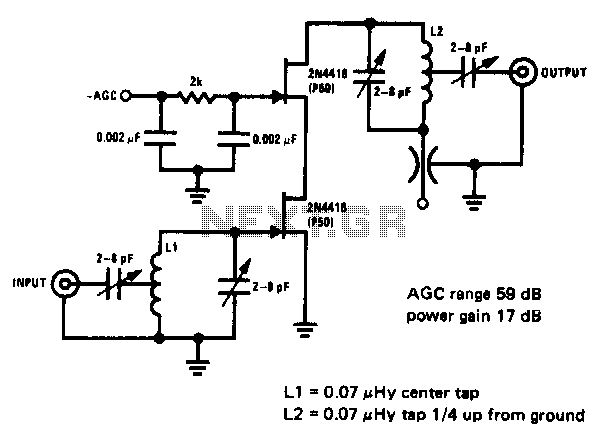
This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit exhibits low cross-modulation, significant signal handling capability, no need for neutralization, and automatic gain control (AGC) managed by adjusting the bias of the upper cascode JFET. A specific requirement for this circuit is that the Idss of the upper unit must exceed that of the lower unit.
The 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit is designed to enhance performance in high-frequency applications while minimizing unwanted interactions between signals. The cascode configuration, which consists of two JFETs arranged in series, effectively increases the overall gain and bandwidth of the circuit. The lower JFET operates as the input stage, while the upper JFET serves as a cascode stage that isolates the lower device from the output load, thereby reducing the Miller effect and enhancing stability.
Low cross-modulation is a critical feature of this circuit, as it ensures that the presence of one signal does not adversely affect the amplification of another signal. This characteristic is particularly valuable in communication systems where multiple signals may be present simultaneously. The ability to handle large signals without distortion is achieved through careful biasing and selection of JFETs, ensuring that the devices operate within their optimal range.
The absence of neutralization simplifies the circuit design and reduces the potential for instability that can arise from feedback loops. Instead, the circuit relies on AGC to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input signal strength. The biasing of the upper cascode JFET is crucial for controlling the gain and ensuring that the circuit responds appropriately to changes in signal amplitude.
The requirement that the Idss of the upper JFET be greater than that of the lower JFET is essential for maintaining the desired operating conditions. Idss, or the drain-source saturation current, influences the transconductance and overall gain of the JFET. By ensuring that the upper JFET has a higher Idss, the circuit can achieve better performance and stability, particularly in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this JFET cascode circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring high-frequency amplification with minimal distortion and robust performance under varying signal conditions.This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit features low cross-modulation, large signal handling ability, no neutralization, and AGC controlled by biasing the upper cascode JFET The only special requirement of this circuit is that Idss of the upper unit must be greater than that of the lower unit. 🔗 External reference
The 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit is designed to enhance performance in high-frequency applications while minimizing unwanted interactions between signals. The cascode configuration, which consists of two JFETs arranged in series, effectively increases the overall gain and bandwidth of the circuit. The lower JFET operates as the input stage, while the upper JFET serves as a cascode stage that isolates the lower device from the output load, thereby reducing the Miller effect and enhancing stability.
Low cross-modulation is a critical feature of this circuit, as it ensures that the presence of one signal does not adversely affect the amplification of another signal. This characteristic is particularly valuable in communication systems where multiple signals may be present simultaneously. The ability to handle large signals without distortion is achieved through careful biasing and selection of JFETs, ensuring that the devices operate within their optimal range.
The absence of neutralization simplifies the circuit design and reduces the potential for instability that can arise from feedback loops. Instead, the circuit relies on AGC to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input signal strength. The biasing of the upper cascode JFET is crucial for controlling the gain and ensuring that the circuit responds appropriately to changes in signal amplitude.
The requirement that the Idss of the upper JFET be greater than that of the lower JFET is essential for maintaining the desired operating conditions. Idss, or the drain-source saturation current, influences the transconductance and overall gain of the JFET. By ensuring that the upper JFET has a higher Idss, the circuit can achieve better performance and stability, particularly in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, this JFET cascode circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring high-frequency amplification with minimal distortion and robust performance under varying signal conditions.This 200 MHz JFET cascode circuit features low cross-modulation, large signal handling ability, no neutralization, and AGC controlled by biasing the upper cascode JFET The only special requirement of this circuit is that Idss of the upper unit must be greater than that of the lower unit. 🔗 External reference