20Khz-arc-welding-inverter
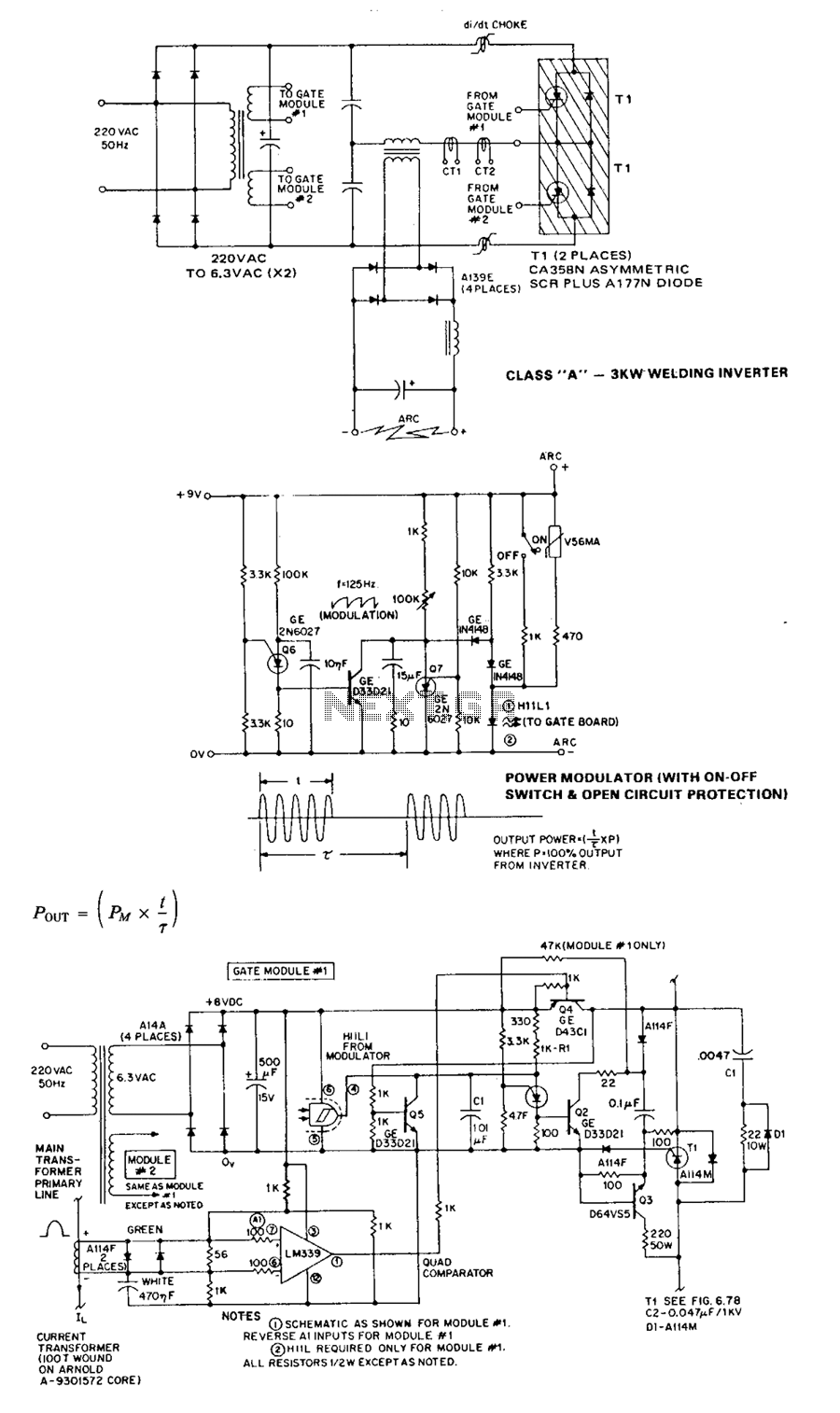
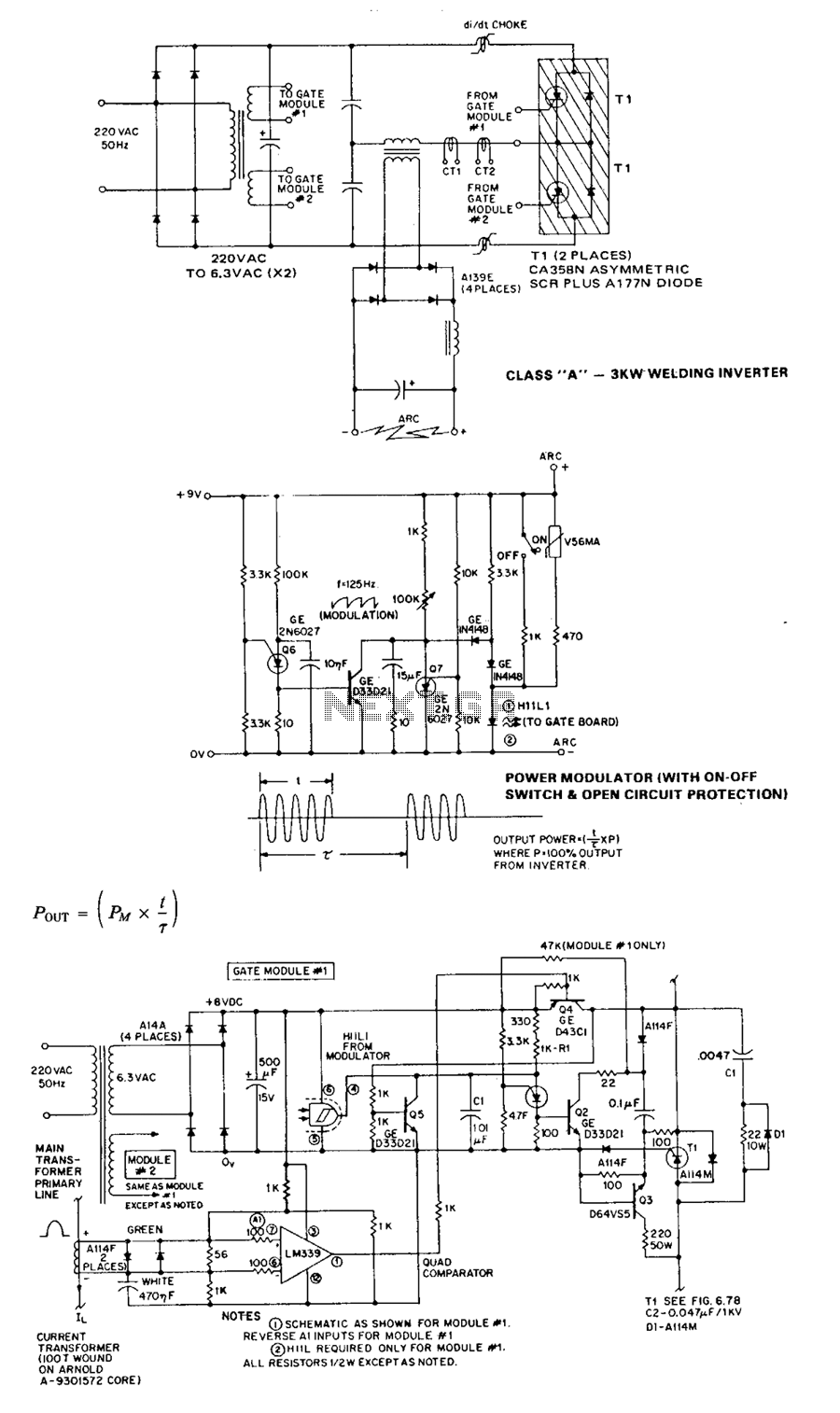
The Class A series resonant inverter is recognized for its high efficiency, low cost, and compact size, provided the operating frequency exceeds approximately 3 kHz. However, it faces challenges, particularly in high power versions, regarding the difficulty of achieving smooth RFI-free output voltage modulation.
The Class A series resonant inverter operates by utilizing resonant circuits to achieve efficient power conversion. When the operating frequency is maintained above 3 kHz, the inverter takes advantage of the resonant characteristics of its components, which leads to reduced switching losses and improved overall efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in applications where size and cost are critical factors, such as in portable electronics and compact power supplies.
The inverter typically consists of a power stage that includes switching devices, such as MOSFETs or IGBTs, and resonant elements, including inductors and capacitors. The resonant tank circuit formed by these elements allows for the generation of a sinusoidal output voltage, which is essential for applications requiring high-quality AC power.
Despite its advantages, the Class A series resonant inverter has notable drawbacks, especially at higher power levels. The modulation of output voltage can become challenging, as achieving smooth modulation while minimizing radio frequency interference (RFI) is complex. This is primarily due to the inherent characteristics of resonant circuits, which can lead to non-linearities and harmonics when modulation is applied. Careful design considerations, including the choice of modulation techniques and filtering methods, are necessary to mitigate these issues and ensure a clean output signal.
In summary, while the Class A series resonant inverter presents a compelling solution for efficient power conversion in compact designs, attention must be given to the challenges associated with output voltage modulation, particularly in high power applications.The Class A series resonant inverter portrayed is well-known and respected for its high efficiency, low cost, and small size, provided that operating frequency is greater than about 3 kHz. The disadvantages are, at least in high power versions, the difficulty in effecting smooth RFI-free output voltage modulation 🔗 External reference
The Class A series resonant inverter operates by utilizing resonant circuits to achieve efficient power conversion. When the operating frequency is maintained above 3 kHz, the inverter takes advantage of the resonant characteristics of its components, which leads to reduced switching losses and improved overall efficiency. This is particularly beneficial in applications where size and cost are critical factors, such as in portable electronics and compact power supplies.
The inverter typically consists of a power stage that includes switching devices, such as MOSFETs or IGBTs, and resonant elements, including inductors and capacitors. The resonant tank circuit formed by these elements allows for the generation of a sinusoidal output voltage, which is essential for applications requiring high-quality AC power.
Despite its advantages, the Class A series resonant inverter has notable drawbacks, especially at higher power levels. The modulation of output voltage can become challenging, as achieving smooth modulation while minimizing radio frequency interference (RFI) is complex. This is primarily due to the inherent characteristics of resonant circuits, which can lead to non-linearities and harmonics when modulation is applied. Careful design considerations, including the choice of modulation techniques and filtering methods, are necessary to mitigate these issues and ensure a clean output signal.
In summary, while the Class A series resonant inverter presents a compelling solution for efficient power conversion in compact designs, attention must be given to the challenges associated with output voltage modulation, particularly in high power applications.The Class A series resonant inverter portrayed is well-known and respected for its high efficiency, low cost, and small size, provided that operating frequency is greater than about 3 kHz. The disadvantages are, at least in high power versions, the difficulty in effecting smooth RFI-free output voltage modulation 🔗 External reference