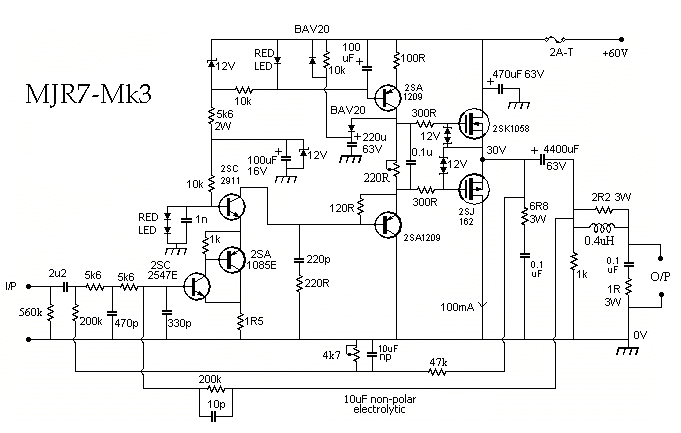
20w mosfet power amplifier
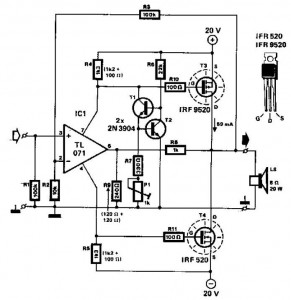
This audio power amplifier employs two complementary MOSFETs (IRF9520 and IRF520) to provide up to 20W output into an 8-ohm speaker. A TL071 operational amplifier functions as the input amplifier. The MOSFETs require heatsinking with a thermal resistance of better than 50°C/W. Total harmonic distortion (THD) is less than 0.15% across the frequency range of 100Hz to 10kHz.
The audio power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high-quality sound amplification with minimal distortion. The circuit utilizes two complementary MOSFETs, specifically the IRF9520 (P-channel) and IRF520 (N-channel), which are selected for their high efficiency and ability to handle significant power levels. These MOSFETs are configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for effective amplification of both halves of the audio signal.
The TL071 operational amplifier serves as the input stage of the amplifier, providing the necessary gain and buffering for the audio signal before it is fed into the power stage. The TL071 is known for its low noise and high slew rate, making it suitable for audio applications where fidelity is critical. The input stage is designed to accommodate standard audio signal levels, ensuring compatibility with various audio sources.
Proper thermal management is essential for the reliable operation of the MOSFETs. The specified heatsink, with a thermal resistance of better than 50°C/W, is necessary to maintain the junction temperature of the MOSFETs within safe limits during operation. An inadequate heatsink could lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure of the components, thus it is crucial to ensure that the heatsinking is appropriately sized and installed.
The amplifier achieves a total harmonic distortion (THD) of less than 0.15% within the frequency range of 100Hz to 10kHz. This low level of distortion indicates that the amplifier can reproduce audio signals with high fidelity, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The performance characteristics of the amplifier make it an ideal choice for driving 8-ohm speakers in various audio systems, from home audio setups to professional sound reinforcement applications.
Overall, this audio power amplifier design provides a robust and efficient solution for audio amplification, ensuring high performance with minimal distortion while maintaining the thermal integrity of the circuit components.This audio power amplifier uses two complementary MOSFETs (IRF9520 and IRF520) to deliver up to 20W into 8 © speaker. A TL071 op amp is used as an input amplifier. The MOSFETs should be heatsinked with a heatsink of better than 50C/ W capability. THD is less than 0. 15% from 100Hz to 10KHz. 🔗 External reference
The audio power amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high-quality sound amplification with minimal distortion. The circuit utilizes two complementary MOSFETs, specifically the IRF9520 (P-channel) and IRF520 (N-channel), which are selected for their high efficiency and ability to handle significant power levels. These MOSFETs are configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing for effective amplification of both halves of the audio signal.
The TL071 operational amplifier serves as the input stage of the amplifier, providing the necessary gain and buffering for the audio signal before it is fed into the power stage. The TL071 is known for its low noise and high slew rate, making it suitable for audio applications where fidelity is critical. The input stage is designed to accommodate standard audio signal levels, ensuring compatibility with various audio sources.
Proper thermal management is essential for the reliable operation of the MOSFETs. The specified heatsink, with a thermal resistance of better than 50°C/W, is necessary to maintain the junction temperature of the MOSFETs within safe limits during operation. An inadequate heatsink could lead to thermal runaway and eventual failure of the components, thus it is crucial to ensure that the heatsinking is appropriately sized and installed.
The amplifier achieves a total harmonic distortion (THD) of less than 0.15% within the frequency range of 100Hz to 10kHz. This low level of distortion indicates that the amplifier can reproduce audio signals with high fidelity, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The performance characteristics of the amplifier make it an ideal choice for driving 8-ohm speakers in various audio systems, from home audio setups to professional sound reinforcement applications.
Overall, this audio power amplifier design provides a robust and efficient solution for audio amplification, ensuring high performance with minimal distortion while maintaining the thermal integrity of the circuit components.This audio power amplifier uses two complementary MOSFETs (IRF9520 and IRF520) to deliver up to 20W into 8 © speaker. A TL071 op amp is used as an input amplifier. The MOSFETs should be heatsinked with a heatsink of better than 50C/ W capability. THD is less than 0. 15% from 100Hz to 10KHz. 🔗 External reference