22 Watts Mini Subwoofer Circuit TDA1516 with Adjustable Frequency
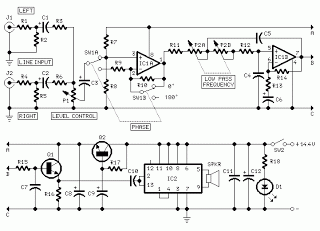
The subwoofer is a speaker designed to reproduce low frequencies, specifically in the range of 20 Hz to 150 Hz. The electronic circuit diagram below illustrates the details of a subwoofer amplifier using the TDA1516, a 22-watt amplifier suitable for a 4-ohm car subwoofer driver. This device is intended to complement an existing stereo amplifier, often requiring the addition of a subwoofer to enhance the music experience. The amplifier employs a BTL (Bridge Tied Load) configuration using a 13-pin IC TDA1516 from Philips (now NXP Semiconductors), which can deliver 22 watts at a 4-ohm load with a default voltage of 12 volts from a car battery. The device comprises several components, including a potentiometer, dual-linear motion potentiometers, 1/4W resistors, electrolytic capacitors rated at 25V and 63V, polyester capacitors, a 100 mA NPN transistor, a dual BIFET Op-Amp, a 24W BTL car radio RCA audio input amplifier, and two 4-ohm or 8-ohm woofers configured in isobaric parallel wiring. The signals from the line outputs are mixed for the amplifier input drive, and the signal level is adjusted using a buffer and a phase control via IC1A. This phase control is beneficial for aligning the subwoofer phase with the existing car radio speakers. Additionally, a variable frequency 12dB/octave low-pass filter is implemented using IC1B, while components Q1, Q2, R17, and C9 form a voltage stabilizer to ensure stable power and filtering to maintain low-level service tracks.
The TDA1516 amplifier circuit is designed for optimal performance in automotive applications, where space and efficiency are critical. The BTL configuration allows for higher power output without requiring a transformer, making it a cost-effective solution for driving subwoofers. The use of dual-linear motion potentiometers enables precise control over the volume and frequency response of the subwoofer, allowing the user to tailor the audio experience to their preference.
The inclusion of the dual BIFET Op-Amp enhances the overall audio fidelity by providing low noise and high input impedance, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity. The RCA audio input ensures compatibility with standard car audio systems, allowing for straightforward installation and integration.
The isobaric configuration of the woofers improves efficiency and reduces the required enclosure size, making it an ideal choice for compact automotive environments. The low-pass filter designed with IC1B effectively attenuates frequencies above the desired cutoff point, ensuring that only low frequencies reach the subwoofer, which is crucial for preventing distortion and enhancing the listening experience.
The voltage stabilizer formed by Q1, Q2, R17, and C9 plays a vital role in maintaining consistent performance by filtering out any voltage fluctuations that could adversely affect the amplifier's operation. This careful consideration of component selection and circuit design results in a robust and reliable subwoofer amplifier suitable for various automotive audio applications.The subwoofer is a subwoofer or a speaker to reproduce low frequencies, devotee of 20 Hz to 150 Hz electronic circuit diagram below shows the details of a scheme of the main amplifier TDA1516 22 watt in 4 ohm car subwoofer driver. This device is designed for an existing stereo amplifier, often requires adding another blow to the music of driving a
subwoofer. The amplifier uses BTL is a good and cheap (Bridge Tied Load channels) 13-pin IC TDA1516 from Philips is now NXP Semiconductors), which may provide a small number of components and 22W at 4 ohm load voltage 12 volt car battery default. The device consists of several parts: the name of the potentiometer, dual-linear motion potentiometers, 1/4W resistors, capacitors, electrolytic 25V, 63V Polyester capacitors, LED, 100 mA NPN transistor, dual BIFET Op-Amp, 24 W BTL car radio RCA audio input amplifier and two speakers 4 ohm or 8 ohm woofers in isobaric parallel wiring.
The signals from the line outputs for stereo mixing amplifier input drive, and taking into account the level of the signal to the buffer and can be reversed IC1A phase SW1. Such control may be useful to the subwoofer in phase with the speaker of the existing car radio. Then, a variable frequency 12dB/octave-pass low IC1B, the components of the Q1 and then you can pass the low frequency of 70 Hz or 150 Q2, R17 and C9 form a voltage stabilizer to facilitate access and filtering circuit to prevent track of the services given power at a low level positive.
🔗 External reference
The TDA1516 amplifier circuit is designed for optimal performance in automotive applications, where space and efficiency are critical. The BTL configuration allows for higher power output without requiring a transformer, making it a cost-effective solution for driving subwoofers. The use of dual-linear motion potentiometers enables precise control over the volume and frequency response of the subwoofer, allowing the user to tailor the audio experience to their preference.
The inclusion of the dual BIFET Op-Amp enhances the overall audio fidelity by providing low noise and high input impedance, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity. The RCA audio input ensures compatibility with standard car audio systems, allowing for straightforward installation and integration.
The isobaric configuration of the woofers improves efficiency and reduces the required enclosure size, making it an ideal choice for compact automotive environments. The low-pass filter designed with IC1B effectively attenuates frequencies above the desired cutoff point, ensuring that only low frequencies reach the subwoofer, which is crucial for preventing distortion and enhancing the listening experience.
The voltage stabilizer formed by Q1, Q2, R17, and C9 plays a vital role in maintaining consistent performance by filtering out any voltage fluctuations that could adversely affect the amplifier's operation. This careful consideration of component selection and circuit design results in a robust and reliable subwoofer amplifier suitable for various automotive audio applications.The subwoofer is a subwoofer or a speaker to reproduce low frequencies, devotee of 20 Hz to 150 Hz electronic circuit diagram below shows the details of a scheme of the main amplifier TDA1516 22 watt in 4 ohm car subwoofer driver. This device is designed for an existing stereo amplifier, often requires adding another blow to the music of driving a
subwoofer. The amplifier uses BTL is a good and cheap (Bridge Tied Load channels) 13-pin IC TDA1516 from Philips is now NXP Semiconductors), which may provide a small number of components and 22W at 4 ohm load voltage 12 volt car battery default. The device consists of several parts: the name of the potentiometer, dual-linear motion potentiometers, 1/4W resistors, capacitors, electrolytic 25V, 63V Polyester capacitors, LED, 100 mA NPN transistor, dual BIFET Op-Amp, 24 W BTL car radio RCA audio input amplifier and two speakers 4 ohm or 8 ohm woofers in isobaric parallel wiring.
The signals from the line outputs for stereo mixing amplifier input drive, and taking into account the level of the signal to the buffer and can be reversed IC1A phase SW1. Such control may be useful to the subwoofer in phase with the speaker of the existing car radio. Then, a variable frequency 12dB/octave-pass low IC1B, the components of the Q1 and then you can pass the low frequency of 70 Hz or 150 Q2, R17 and C9 form a voltage stabilizer to facilitate access and filtering circuit to prevent track of the services given power at a low level positive.
🔗 External reference