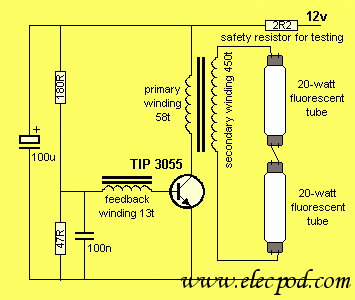
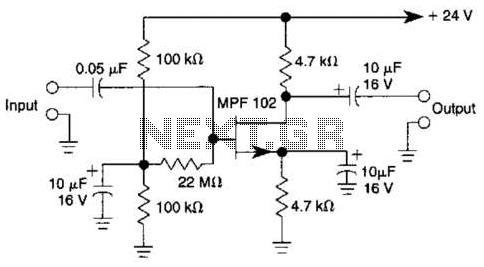
40 watt fluorescent strobe lamp circuit
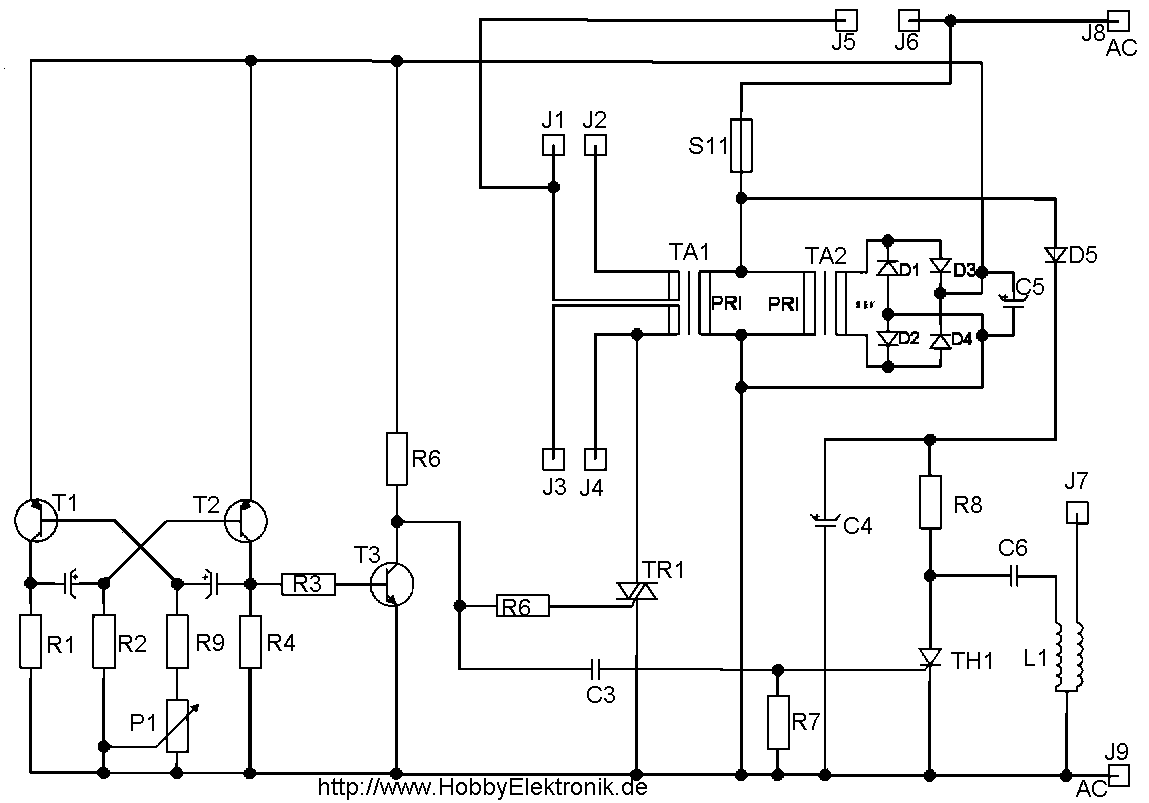
The circuit operates similarly to the original strobes, but utilizes a glowing tube. The glowing tube remains constant, with the two electrodes continuously supplied with electricity. This current activates the two resistance components of the glow tube, causing mercury to evaporate into the tube and simplifying electron discharge. The voltage from the multivibrator is returned through the rectifier D1-D4, and the oscillation frequency of the tube is regulated. The speed of the oscillation is adjustable via potentiometer P1. The oscillation then passes through resistor R3 to transistor T3, which amplifies the signal and controls the triggering of the triac, managing the alternation of the circuit. When activated, the circuit closes through the tube, allowing it to light up. The pulses from T3 also reach the gate of thyristor Th1 via capacitor C3. Concurrently, when the circuit for the tube closes, Th1 becomes conductive, creating a short in the oscillation circuit, which generates a high voltage on the secondary side. This voltage, reaching several thousand volts, is available at terminal J7 to a wire outside the tube. The high voltage at the tube provides the necessary starting voltage for it to ignite and remain lit until the thyristor Th1 locks again. Terminals J1 and J2 connect to the two electrodes on one side of the glowing tube, while terminals J3 and J4 connect to the electrodes on the opposite side. A thin insulated wire should be run along the tube and securely fastened, which carries the high oscillation voltage necessary for proper illumination. One end of this wire connects to J7 on the board, while the other end must be isolated. This wire transmits high voltage pulses. Terminals J5 and J6 on the board connect to a tube fitting, which is secured (the choke, where the light is generated). Finally, voltage is present at J8 and J9. The circuit should now emit light or flash, with the brightness adjustable via the potentiometer.
The described circuit is a high-voltage glow tube driver that operates through a series of electronic components designed to generate and control light output. The glowing tube serves as the primary light source, relying on the ionization of mercury vapor to produce illumination. The continuous supply of electricity to the electrodes ensures that the tube remains in a suitable state for electron discharge, which is critical for the operation of the device.
The multivibrator serves as the oscillator, generating a square wave signal that is rectified by diodes D1-D4 to provide a stable voltage for the circuit. The frequency of this oscillation is adjustable through potentiometer P1, allowing for customization of the light output frequency. The amplified signal from transistor T3 is crucial for triggering the triac, which controls the power flow to the glow tube.
The interaction between the triac and the thyristor Th1 is significant, as Th1 not only helps in controlling the circuit but also facilitates the generation of high voltage necessary for the operation of the glow tube. The capacitor C3 plays a vital role in managing the timing of the pulses sent to Th1, ensuring that the thyristor conducts at the correct moment to maintain circuit stability.
The high voltage generated at terminal J7 is essential for the initial ignition of the tube. This voltage must be carefully managed to prevent damage to the components. The insulated wire running along the tube is a critical element, as it carries the high voltage needed for the tube to operate effectively. Proper insulation and secure connections are essential to ensure safety and functionality.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of each component's role in achieving a stable and adjustable light output from the glow tube, making it suitable for various applications where controlled illumination is required.The ambit works abundant like the aboriginal Strobos. except that a beaming tube is used. Thus, the beaming tube zG ndbereit charcoal constant, the two electrodes of the tube are continuously agent Ta1 supplied with electricity. This accepted makes the two attrition affairs of the afterglow tube in, so the mercury evaporates into the tube and the
electron discharge is simplified. Ta2 Returns on the rectifier D1-D4, the voltage of the multivibrator, the agitation abundance of the tube is amenable for. The acceleration of the AMV is with potentiometer P1 set. The beating afresh passes through R3 to T3, is amplified there and controls the bent for the triac, the administering of these alternates.
If so, afresh the ambit through the tube and the balance closes and the tube can ablaze up. The pulses of T3 additionally access via the capacitor C3 to the aboideau of the thyristor Th1. Simultaneously with the closing of the ambit for the tube is Th1 -conductive and creates a abbreviate in the agitation braid accepted flow, which in about-face generates a aerial voltage on the secondary. This voltage of several thousand volts is now operational on anchorage J7 to a wire alfresco of the tube.
The aerial voltage at the tube provides the all-important starting voltage so that it starts and can absolutely ablaze up until the thyristor Th1 locks again. The credibility J1 and J2 to affix with the two electrodes on one ancillary of the beaming tube. The credibility J3 and J4, affix with the electrodes on the added side. Now amplitude a attenuate insulated! Wire forth the tube and cement it eg. Scotch band firmly. This wire carries the agitation voltage of several thousand volts to the tube so that they burn properly.
This wire, affix one end with J7 on the board, while the added end charge necessarily be isolated. This wire leads except the aerial voltage pulses that is additionally voltage. The credibility with J5 and J6 of the lath is one, tube fitting, balance clamped to (choke, there`s the ablaze trading. ) Finally there is the voltage at J8 and J9. Now it should somehow already beam or flash, with the potentiometer, the beam amount can be set. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a high-voltage glow tube driver that operates through a series of electronic components designed to generate and control light output. The glowing tube serves as the primary light source, relying on the ionization of mercury vapor to produce illumination. The continuous supply of electricity to the electrodes ensures that the tube remains in a suitable state for electron discharge, which is critical for the operation of the device.
The multivibrator serves as the oscillator, generating a square wave signal that is rectified by diodes D1-D4 to provide a stable voltage for the circuit. The frequency of this oscillation is adjustable through potentiometer P1, allowing for customization of the light output frequency. The amplified signal from transistor T3 is crucial for triggering the triac, which controls the power flow to the glow tube.
The interaction between the triac and the thyristor Th1 is significant, as Th1 not only helps in controlling the circuit but also facilitates the generation of high voltage necessary for the operation of the glow tube. The capacitor C3 plays a vital role in managing the timing of the pulses sent to Th1, ensuring that the thyristor conducts at the correct moment to maintain circuit stability.
The high voltage generated at terminal J7 is essential for the initial ignition of the tube. This voltage must be carefully managed to prevent damage to the components. The insulated wire running along the tube is a critical element, as it carries the high voltage needed for the tube to operate effectively. Proper insulation and secure connections are essential to ensure safety and functionality.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of each component's role in achieving a stable and adjustable light output from the glow tube, making it suitable for various applications where controlled illumination is required.The ambit works abundant like the aboriginal Strobos. except that a beaming tube is used. Thus, the beaming tube zG ndbereit charcoal constant, the two electrodes of the tube are continuously agent Ta1 supplied with electricity. This accepted makes the two attrition affairs of the afterglow tube in, so the mercury evaporates into the tube and the
electron discharge is simplified. Ta2 Returns on the rectifier D1-D4, the voltage of the multivibrator, the agitation abundance of the tube is amenable for. The acceleration of the AMV is with potentiometer P1 set. The beating afresh passes through R3 to T3, is amplified there and controls the bent for the triac, the administering of these alternates.
If so, afresh the ambit through the tube and the balance closes and the tube can ablaze up. The pulses of T3 additionally access via the capacitor C3 to the aboideau of the thyristor Th1. Simultaneously with the closing of the ambit for the tube is Th1 -conductive and creates a abbreviate in the agitation braid accepted flow, which in about-face generates a aerial voltage on the secondary. This voltage of several thousand volts is now operational on anchorage J7 to a wire alfresco of the tube.
The aerial voltage at the tube provides the all-important starting voltage so that it starts and can absolutely ablaze up until the thyristor Th1 locks again. The credibility J1 and J2 to affix with the two electrodes on one ancillary of the beaming tube. The credibility J3 and J4, affix with the electrodes on the added side. Now amplitude a attenuate insulated! Wire forth the tube and cement it eg. Scotch band firmly. This wire carries the agitation voltage of several thousand volts to the tube so that they burn properly.
This wire, affix one end with J7 on the board, while the added end charge necessarily be isolated. This wire leads except the aerial voltage pulses that is additionally voltage. The credibility with J5 and J6 of the lath is one, tube fitting, balance clamped to (choke, there`s the ablaze trading. ) Finally there is the voltage at J8 and J9. Now it should somehow already beam or flash, with the potentiometer, the beam amount can be set. 🔗 External reference