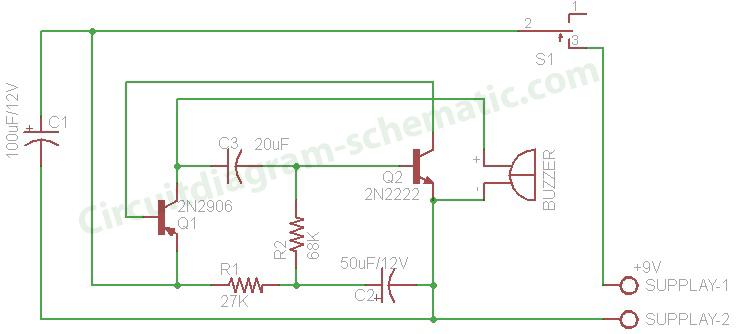
Fet Amplifier With Offset Gate Bias Circuit
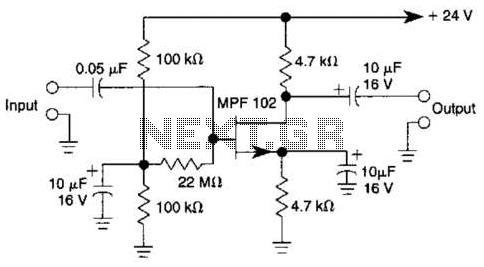
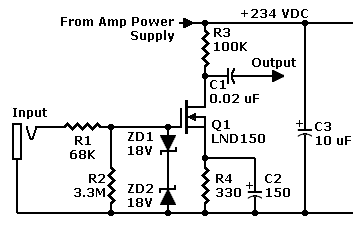
In this amplifier circuit, the gate of the MPF 102 is biased with an external voltage. This circuit achieves tighter control of the operating point and biasing conditions.
The amplifier circuit utilizing the MPF 102 field-effect transistor (FET) is designed to enhance the stability and performance of the amplification process. The MPF 102, known for its low noise characteristics and high input impedance, is particularly suitable for applications requiring precise signal amplification.
In this configuration, the gate of the MPF 102 is connected to an external voltage source, which serves to set the bias point of the transistor. This external biasing allows for improved control over the operating point, ensuring that the transistor remains in the desired region of operation, typically the saturation region for amplification purposes. The use of an external voltage rather than relying solely on the inherent characteristics of the transistor helps mitigate variations that may arise due to temperature changes or component tolerances.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to form a biasing network, which further refines the operating conditions. Resistors connected to the gate can help stabilize the bias point by providing a defined path for the gate current, while capacitors can be employed for coupling and decoupling purposes, ensuring that AC signals are amplified effectively without distortion.
Overall, this amplifier circuit configuration is beneficial for applications that demand high fidelity and low distortion in signal processing, making it suitable for audio amplification, sensor signal conditioning, and communication systems. The precise control of the operating point achieved through external voltage biasing contributes significantly to the reliability and performance of the amplification circuitry. In this amplifier circuit, the gate of the MPF 102 is biased with an external voltage. This circuit achieves tighter control of the operating point and biasing conditions. 🔗 External reference
The amplifier circuit utilizing the MPF 102 field-effect transistor (FET) is designed to enhance the stability and performance of the amplification process. The MPF 102, known for its low noise characteristics and high input impedance, is particularly suitable for applications requiring precise signal amplification.
In this configuration, the gate of the MPF 102 is connected to an external voltage source, which serves to set the bias point of the transistor. This external biasing allows for improved control over the operating point, ensuring that the transistor remains in the desired region of operation, typically the saturation region for amplification purposes. The use of an external voltage rather than relying solely on the inherent characteristics of the transistor helps mitigate variations that may arise due to temperature changes or component tolerances.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to form a biasing network, which further refines the operating conditions. Resistors connected to the gate can help stabilize the bias point by providing a defined path for the gate current, while capacitors can be employed for coupling and decoupling purposes, ensuring that AC signals are amplified effectively without distortion.
Overall, this amplifier circuit configuration is beneficial for applications that demand high fidelity and low distortion in signal processing, making it suitable for audio amplification, sensor signal conditioning, and communication systems. The precise control of the operating point achieved through external voltage biasing contributes significantly to the reliability and performance of the amplification circuitry. In this amplifier circuit, the gate of the MPF 102 is biased with an external voltage. This circuit achieves tighter control of the operating point and biasing conditions. 🔗 External reference