555 Flasher II
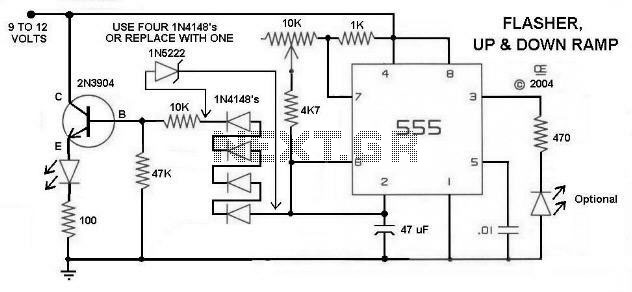
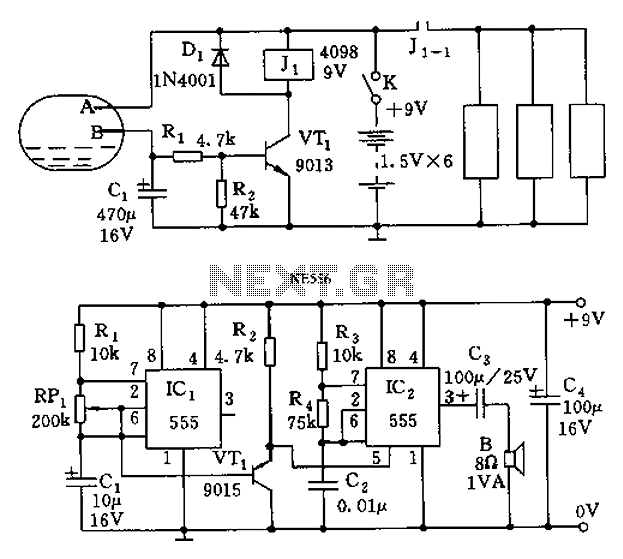
Here is a Simple Circuit to give a Flashing LED, With a "Rising and Falling" Brightness. It Uses the Sawtooth waveform from pins 2 and 6 to create the rise and fall. The Resistor and LED on Pin 3 are Optional. The 10K Potentiometer give a reasonable range of Speed.
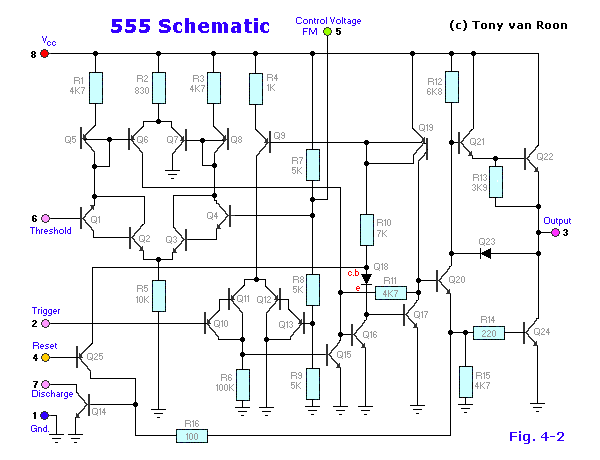
The circuit described utilizes a sawtooth waveform to modulate the brightness of an LED, creating a visually appealing effect of rising and falling light intensity. This effect can be achieved using a simple oscillator circuit, often implemented with a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode or using an operational amplifier in a feedback loop.
The sawtooth waveform is generated at pins 2 and 6, which are critical for establishing the timing characteristics of the circuit. The frequency of the waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistance of a 10K potentiometer, allowing for a range of flashing speeds. The potentiometer is connected in such a way that it influences the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor, thus affecting the frequency of the sawtooth signal.
An LED is connected to pin 3, which serves as the output for the varying brightness. A resistor may also be added in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, ensuring that the LED operates within its specified current ratings. This component is optional; however, it is generally recommended to prevent potential damage to the LED.
The circuit can be powered by a standard DC voltage source, typically ranging from 5V to 15V, depending on the specifications of the components used. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included near the power supply pins of the IC to ensure stable operation and to minimize noise.
In summary, this simple circuit effectively demonstrates the use of a sawtooth waveform to control LED brightness, providing an engaging visual effect that can be utilized in various applications, such as decorative lighting or indicators.Here is a Simple Circuit to give a Flashing LED, With a "Rising and Falling" Brightness. It Uses the Sawtooth waveform from pins 2 and 6 to create the rise and fall. The Resistor and LED on Pin 3 are Optional. The 10K Potentiometer give a reasonable range of Speed. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes a sawtooth waveform to modulate the brightness of an LED, creating a visually appealing effect of rising and falling light intensity. This effect can be achieved using a simple oscillator circuit, often implemented with a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode or using an operational amplifier in a feedback loop.
The sawtooth waveform is generated at pins 2 and 6, which are critical for establishing the timing characteristics of the circuit. The frequency of the waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistance of a 10K potentiometer, allowing for a range of flashing speeds. The potentiometer is connected in such a way that it influences the charge and discharge times of the timing capacitor, thus affecting the frequency of the sawtooth signal.
An LED is connected to pin 3, which serves as the output for the varying brightness. A resistor may also be added in series with the LED to limit the current flowing through it, ensuring that the LED operates within its specified current ratings. This component is optional; however, it is generally recommended to prevent potential damage to the LED.
The circuit can be powered by a standard DC voltage source, typically ranging from 5V to 15V, depending on the specifications of the components used. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included near the power supply pins of the IC to ensure stable operation and to minimize noise.
In summary, this simple circuit effectively demonstrates the use of a sawtooth waveform to control LED brightness, providing an engaging visual effect that can be utilized in various applications, such as decorative lighting or indicators.Here is a Simple Circuit to give a Flashing LED, With a "Rising and Falling" Brightness. It Uses the Sawtooth waveform from pins 2 and 6 to create the rise and fall. The Resistor and LED on Pin 3 are Optional. The 10K Potentiometer give a reasonable range of Speed. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713