60 watt switching power supply
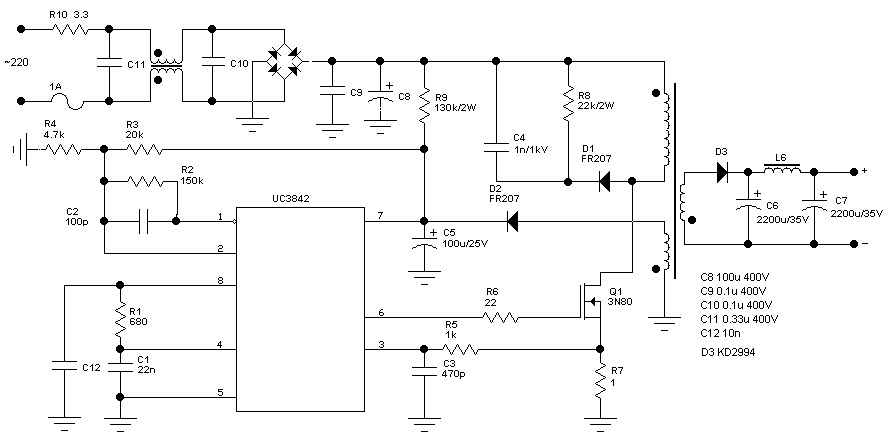
60 Watt Switching Power Supply. Visit the page for an explanation of the related circuit diagram.
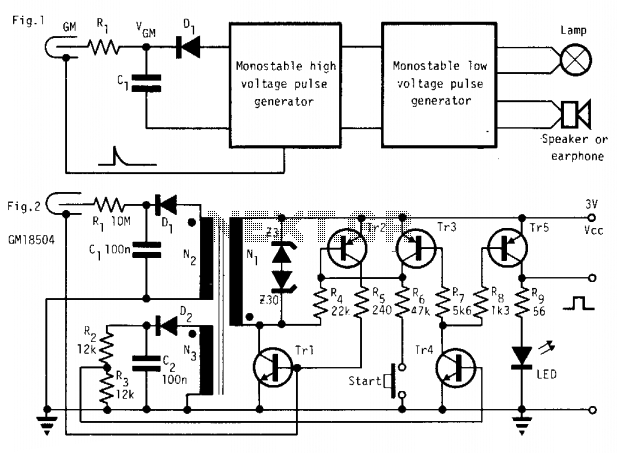
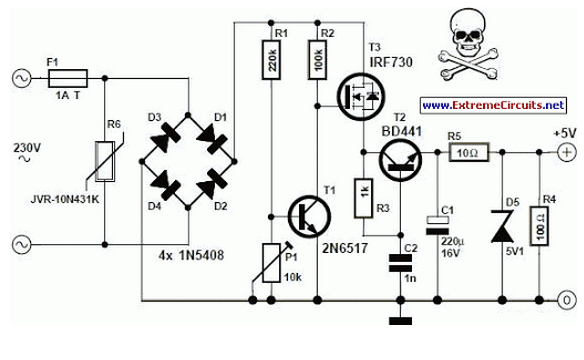
The 60 Watt Switching Power Supply is designed to convert an input voltage to a regulated output voltage while maintaining high efficiency and compact size. This power supply typically employs a switching regulator topology, which utilizes high-frequency switching elements to minimize energy loss during the conversion process.
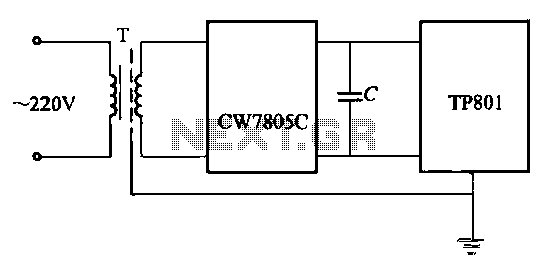
The circuit generally consists of several key components: a transformer, switching transistors, diodes, capacitors, and control circuitry. The transformer is crucial for voltage step-down and isolation, while the switching transistors, often MOSFETs, are responsible for rapidly turning on and off to control the energy transfer to the transformer.
Diodes are used for rectification, converting the AC output from the transformer back to DC. Capacitors smooth the output voltage, reducing ripple and ensuring a stable supply. The control circuitry monitors the output voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching transistors to maintain the desired output level under varying load conditions.
The efficiency of a switching power supply can be significantly higher than that of linear power supplies, often exceeding 85%, making them suitable for applications where thermal management and size constraints are critical. This type of power supply is widely used in various electronic devices, including computers, telecommunications equipment, and industrial applications.
Understanding the schematic diagram associated with this power supply is essential for troubleshooting and design enhancement, as it provides insights into the interconnections and operational principles of the components involved.60 Watt Switching Power Supply power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The 60 Watt Switching Power Supply is designed to convert an input voltage to a regulated output voltage while maintaining high efficiency and compact size. This power supply typically employs a switching regulator topology, which utilizes high-frequency switching elements to minimize energy loss during the conversion process.
The circuit generally consists of several key components: a transformer, switching transistors, diodes, capacitors, and control circuitry. The transformer is crucial for voltage step-down and isolation, while the switching transistors, often MOSFETs, are responsible for rapidly turning on and off to control the energy transfer to the transformer.
Diodes are used for rectification, converting the AC output from the transformer back to DC. Capacitors smooth the output voltage, reducing ripple and ensuring a stable supply. The control circuitry monitors the output voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching transistors to maintain the desired output level under varying load conditions.
The efficiency of a switching power supply can be significantly higher than that of linear power supplies, often exceeding 85%, making them suitable for applications where thermal management and size constraints are critical. This type of power supply is widely used in various electronic devices, including computers, telecommunications equipment, and industrial applications.
Understanding the schematic diagram associated with this power supply is essential for troubleshooting and design enhancement, as it provides insights into the interconnections and operational principles of the components involved.60 Watt Switching Power Supply power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference