AD589-Dual Supply LVDT Signal Conditioner Design Procedure
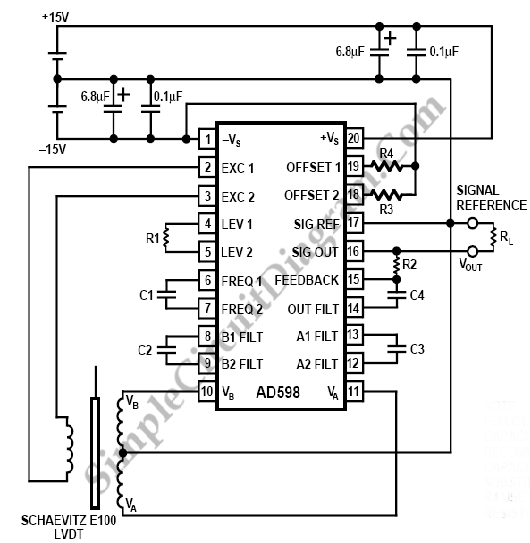
LVDT (linear voltage differential transformer) is widely used as a linear position sensor. The AD589 integrated circuit provides a complete solution for LVDT.
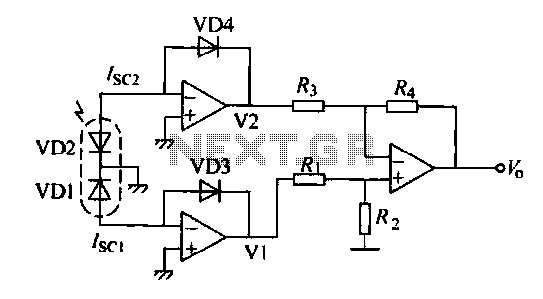
The Linear Voltage Differential Transformer (LVDT) is a highly precise sensor commonly employed for measuring linear displacement. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a primary coil generates a magnetic field that induces voltages in two secondary coils. The differential voltage between these coils is proportional to the position of a movable core within the transformer, enabling accurate position sensing.
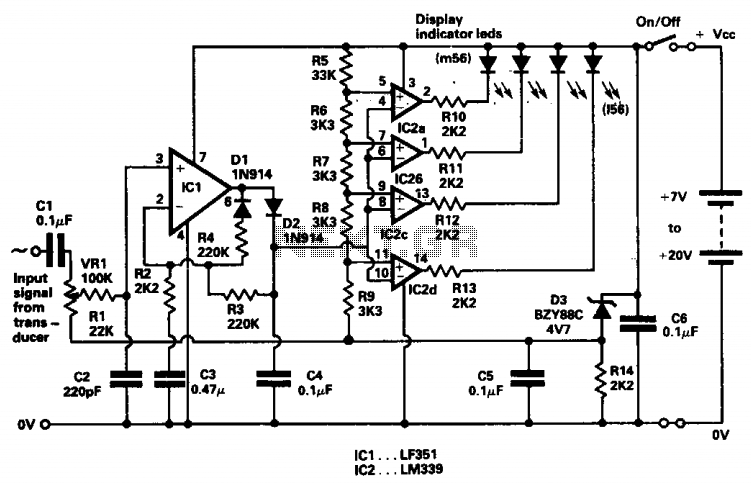
The AD589 integrated circuit is designed to facilitate the signal conditioning necessary for LVDT applications. This precision voltage reference provides a stable output voltage, which is essential for ensuring the accuracy of the LVDT measurements. The AD589 features low noise and low drift characteristics, making it suitable for high-precision applications where environmental factors may influence the sensor's performance.
In a typical LVDT application circuit, the LVDT is connected to the AD589 to amplify the differential output voltage. The output from the AD589 can be further processed using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital signal processing. This integration allows for the development of sophisticated control systems capable of providing real-time feedback on position changes, which is vital in various automation and robotics applications.
The combination of LVDT technology and the AD589 integrated circuit results in a robust solution for linear position sensing, offering high accuracy, reliability, and stability in diverse industrial environments.LVDT (linear voltage differential transformer) is widely used as linear position sensor. AD589 integrated circuit provides a complete solution for LVDT.. 🔗 External reference
The Linear Voltage Differential Transformer (LVDT) is a highly precise sensor commonly employed for measuring linear displacement. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a primary coil generates a magnetic field that induces voltages in two secondary coils. The differential voltage between these coils is proportional to the position of a movable core within the transformer, enabling accurate position sensing.
The AD589 integrated circuit is designed to facilitate the signal conditioning necessary for LVDT applications. This precision voltage reference provides a stable output voltage, which is essential for ensuring the accuracy of the LVDT measurements. The AD589 features low noise and low drift characteristics, making it suitable for high-precision applications where environmental factors may influence the sensor's performance.
In a typical LVDT application circuit, the LVDT is connected to the AD589 to amplify the differential output voltage. The output from the AD589 can be further processed using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital signal processing. This integration allows for the development of sophisticated control systems capable of providing real-time feedback on position changes, which is vital in various automation and robotics applications.
The combination of LVDT technology and the AD589 integrated circuit results in a robust solution for linear position sensing, offering high accuracy, reliability, and stability in diverse industrial environments.LVDT (linear voltage differential transformer) is widely used as linear position sensor. AD589 integrated circuit provides a complete solution for LVDT.. 🔗 External reference