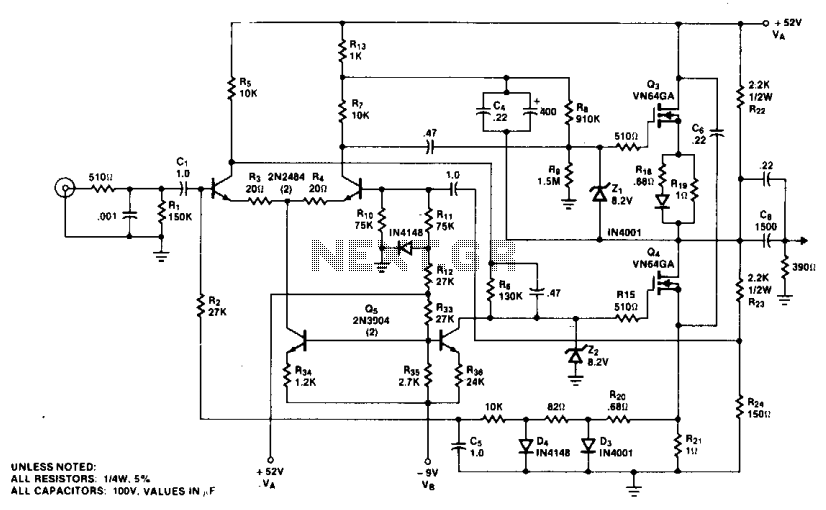
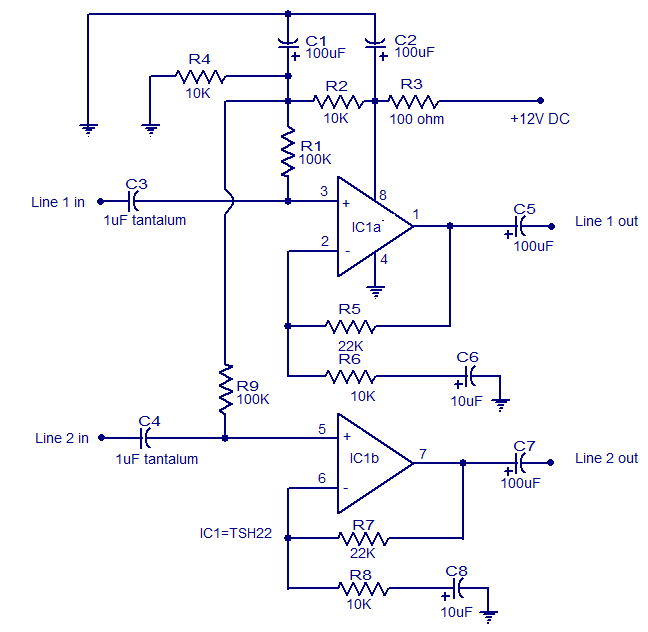
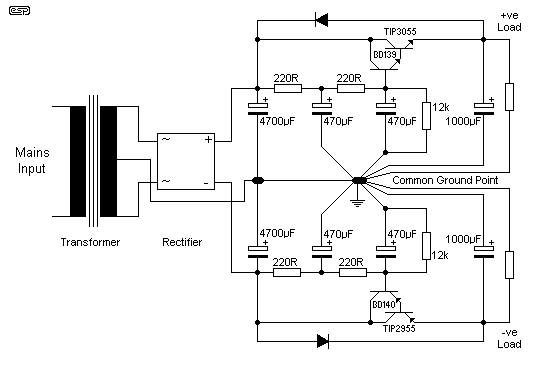
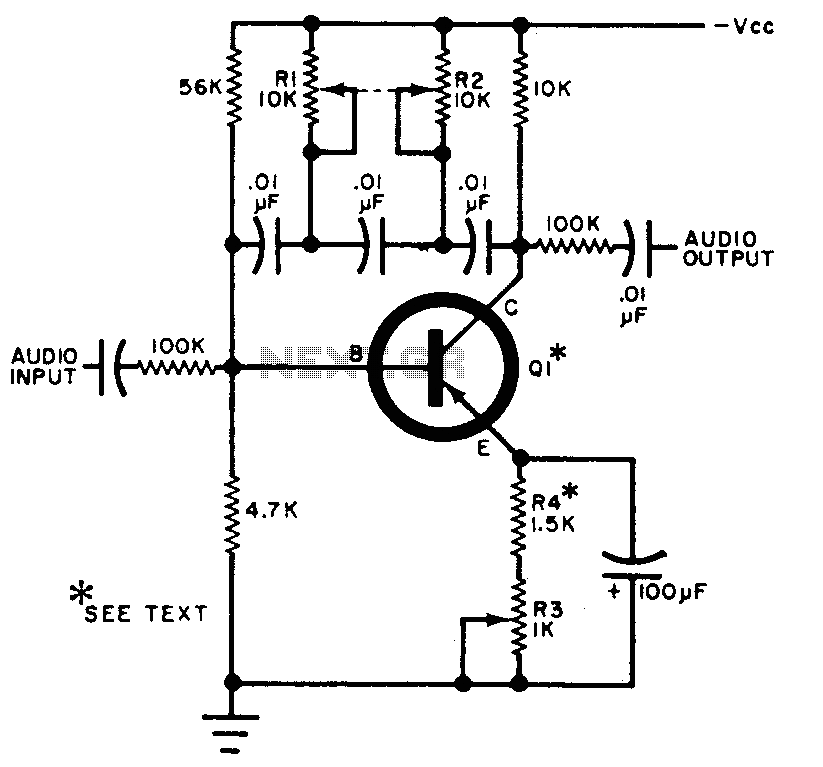
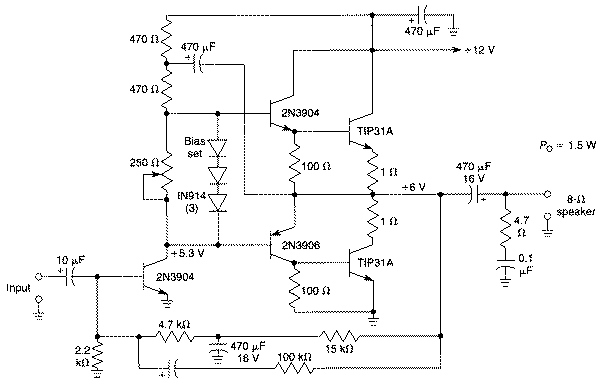
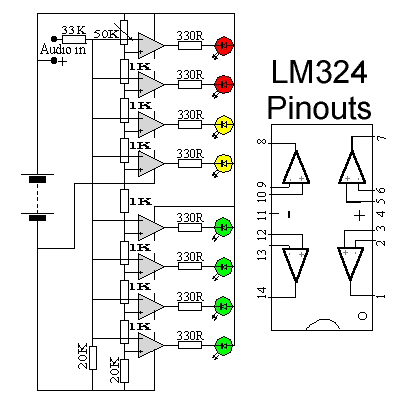
8W Audio Amplifier
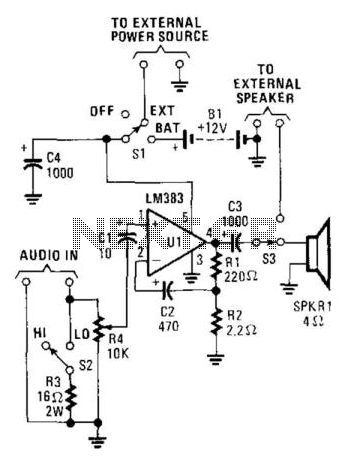
This audio power amplifier, built around an LM383 8-W audio power amplifier, is designed to enhance an audio signal to a sufficient level for audibility in high-noise environments. It is important to note that the LM383 requires a heatsink for proper thermal management.
The LM383 audio power amplifier is a versatile component suitable for applications where audio amplification is necessary, particularly in environments with significant background noise. The device is capable of delivering up to 8 watts of output power, making it suitable for driving speakers in various settings, including public address systems, musical instruments, and home audio systems.
In the circuit design, the LM383 is typically configured in a standard amplifier configuration, where the input audio signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the amplifier. The gain can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback resistors, allowing for customization based on the required output level. Additionally, bypass capacitors should be employed to filter out any unwanted noise and ensure a stable power supply to the amplifier.
Thermal management is critical for the reliable operation of the LM383. The device should be mounted on a heatsink to dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing thermal overload and ensuring long-term reliability. The heatsink should be appropriately sized based on the expected power output and ambient temperature conditions.
For optimal performance, it is advisable to use high-quality capacitors and resistors in the circuit to minimize distortion and maintain signal integrity. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be implemented to reduce electromagnetic interference, which can be particularly problematic in high-noise environments.
Overall, this audio power amplifier circuit utilizing the LM383 is an effective solution for enhancing audio signals in challenging acoustic conditions. Its design considerations, such as thermal management and component selection, play a crucial role in achieving desired performance levels. This audio power amp (built around an LM383 8-W, audio power amplifier) can be used to boost an audio signal to a suffi cient level so that it can be heard in a high-noise environment. Note that LM383 should be heatsinked.
The LM383 audio power amplifier is a versatile component suitable for applications where audio amplification is necessary, particularly in environments with significant background noise. The device is capable of delivering up to 8 watts of output power, making it suitable for driving speakers in various settings, including public address systems, musical instruments, and home audio systems.
In the circuit design, the LM383 is typically configured in a standard amplifier configuration, where the input audio signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the amplifier. The gain can be adjusted by selecting appropriate feedback resistors, allowing for customization based on the required output level. Additionally, bypass capacitors should be employed to filter out any unwanted noise and ensure a stable power supply to the amplifier.
Thermal management is critical for the reliable operation of the LM383. The device should be mounted on a heatsink to dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing thermal overload and ensuring long-term reliability. The heatsink should be appropriately sized based on the expected power output and ambient temperature conditions.
For optimal performance, it is advisable to use high-quality capacitors and resistors in the circuit to minimize distortion and maintain signal integrity. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be implemented to reduce electromagnetic interference, which can be particularly problematic in high-noise environments.
Overall, this audio power amplifier circuit utilizing the LM383 is an effective solution for enhancing audio signals in challenging acoustic conditions. Its design considerations, such as thermal management and component selection, play a crucial role in achieving desired performance levels. This audio power amp (built around an LM383 8-W, audio power amplifier) can be used to boost an audio signal to a suffi cient level so that it can be heard in a high-noise environment. Note that LM383 should be heatsinked.