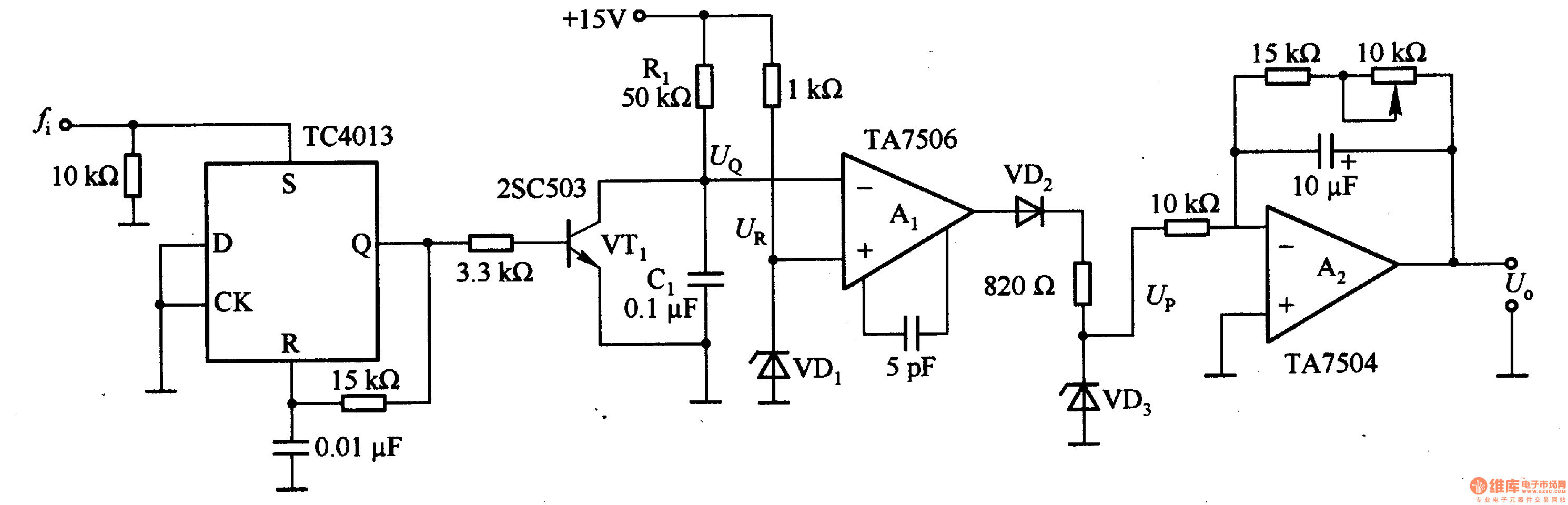
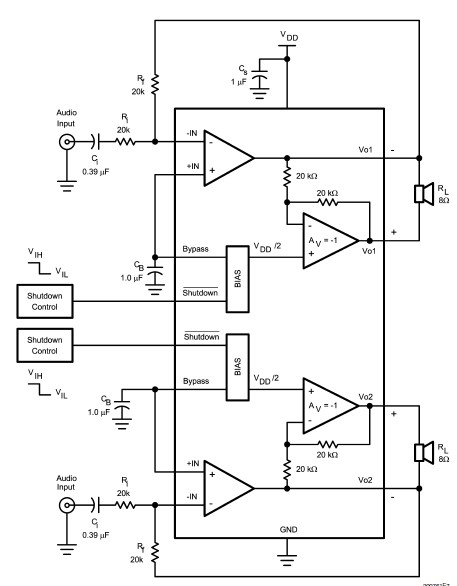
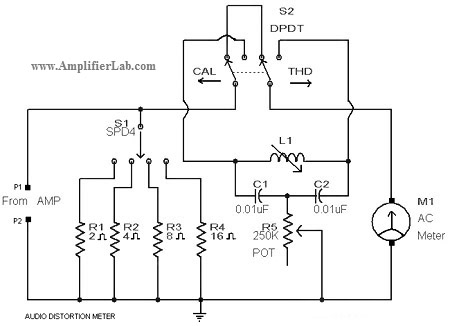
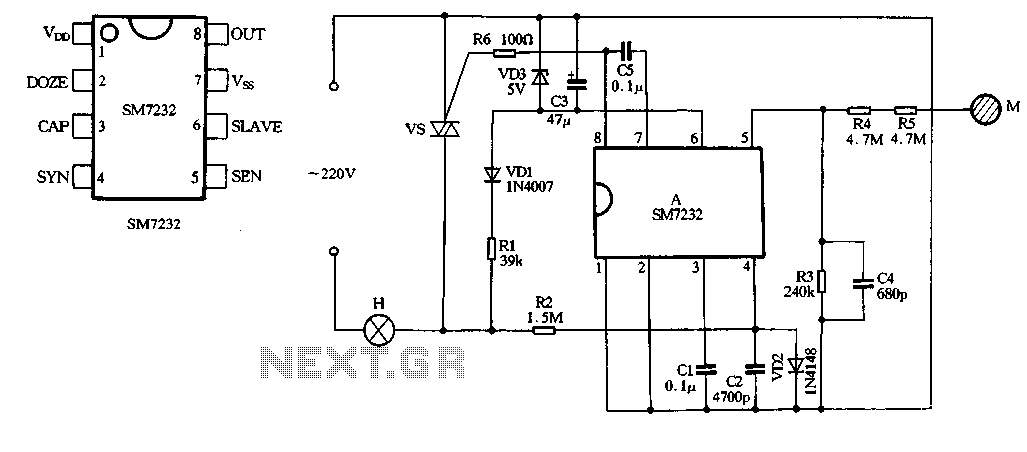
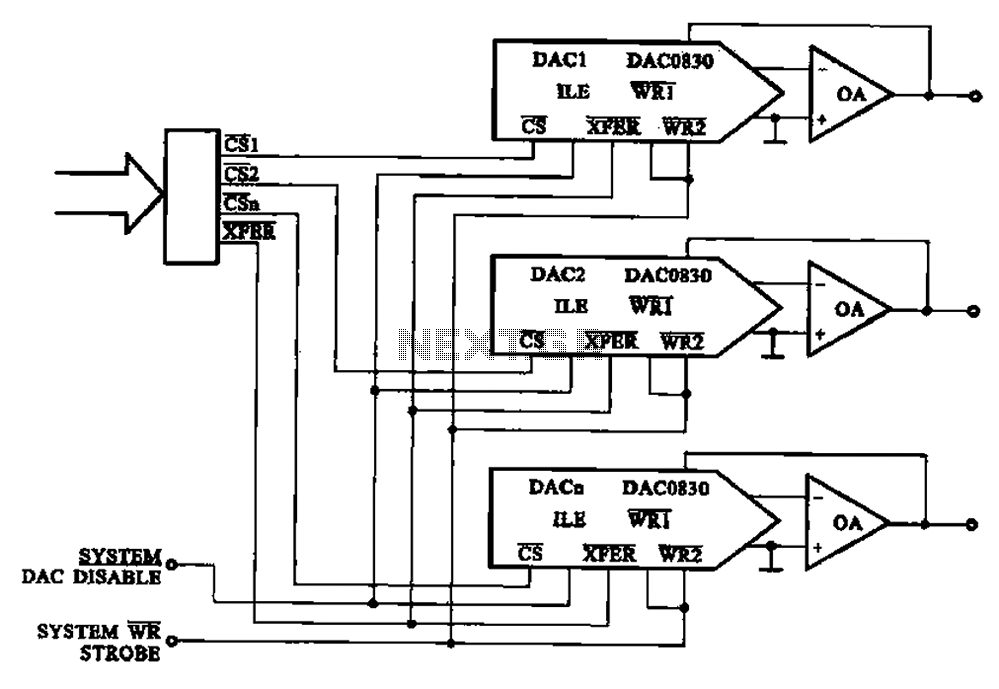
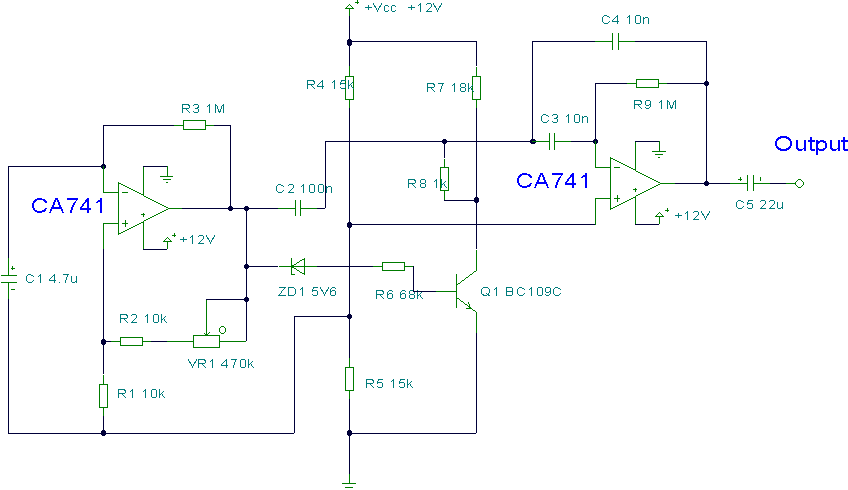
A 555 four-base integrated circuit delay circuits
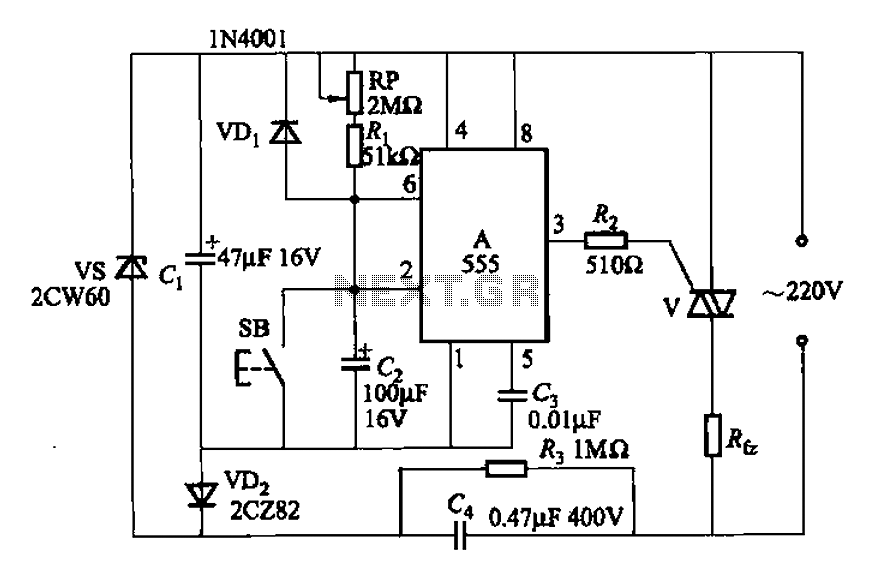
A 555 four-base integrated circuit delay circuit is designed to facilitate a transition from high to low output. When the button SB is pressed, the output is set to high, and after a specified delay, the output transitions to a low level and remains in that state. The delay time can be adjusted using potentiometer RP.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely utilized in various timing applications, including delay circuits. In this configuration, the circuit operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a trigger input. The circuit consists of several key components: the 555 timer IC, a resistor, a capacitor, and a potentiometer for adjustable timing.
Upon pressing the switch SB, a low-to-high transition is detected, triggering the 555 timer. The capacitor connected to the timing circuit begins to charge through the resistor and the potentiometer RP. The time delay before the output transitions from high to low is determined by the values of the resistor and the capacitor, as described by the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
Where T is the time delay in seconds, R is the resistance in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. By adjusting the potentiometer RP, the resistance can be varied, allowing for precise control over the timing interval.
Once the capacitor reaches approximately 63.2% of the supply voltage, the output of the 555 timer switches from high to low. The output remains low until the circuit is reset or the button SB is pressed again, which restarts the cycle. This functionality makes the 555 timer IC an excellent choice for applications requiring delayed actions, such as timers, pulse generators, and automatic switches in various electronic devices.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as diodes for protection against reverse polarity or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the specific application requirements.A 555 four-base integrated circuit delay circuits They are a jump from high to low transition of the delay circuit. That button is pressed SB snow, the output is high, after so me delay, the output of the transition to the low level and remain low. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the delay time.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely utilized in various timing applications, including delay circuits. In this configuration, the circuit operates in monostable mode, where it generates a single output pulse in response to a trigger input. The circuit consists of several key components: the 555 timer IC, a resistor, a capacitor, and a potentiometer for adjustable timing.
Upon pressing the switch SB, a low-to-high transition is detected, triggering the 555 timer. The capacitor connected to the timing circuit begins to charge through the resistor and the potentiometer RP. The time delay before the output transitions from high to low is determined by the values of the resistor and the capacitor, as described by the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
Where T is the time delay in seconds, R is the resistance in ohms, and C is the capacitance in farads. By adjusting the potentiometer RP, the resistance can be varied, allowing for precise control over the timing interval.
Once the capacitor reaches approximately 63.2% of the supply voltage, the output of the 555 timer switches from high to low. The output remains low until the circuit is reset or the button SB is pressed again, which restarts the cycle. This functionality makes the 555 timer IC an excellent choice for applications requiring delayed actions, such as timers, pulse generators, and automatic switches in various electronic devices.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components, such as diodes for protection against reverse polarity or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the specific application requirements.A 555 four-base integrated circuit delay circuits They are a jump from high to low transition of the delay circuit. That button is pressed SB snow, the output is high, after so me delay, the output of the transition to the low level and remain low. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the delay time.