A circuit diagram of a switching power supply
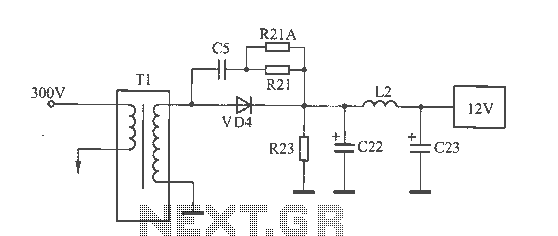
The 12V voltage instability should first be investigated by checking the output section of the switching power supply, as illustrated in the accompanying figure. The secondary winding of the transformer and the switch VD4 have been examined and found to be normal, with no evidence of welding in inductor L2. The filter capacitors C22 and C23 are rated at 1000pF / 16V. Measurements taken with a capacitance meter indicate that C23 is functioning normally, although its capacitance has slightly decreased. In contrast, the capacitance of C22 has fallen to less than 80µF. The analysis of C22 and C23 reveals that the main power supply is mounted within the base of the monitor, where space is limited and heat dissipation is poor. C22 and C23 are located near the 12V rectifier diode, particularly C22, which is situated closer to it. The decreased capacitance of these capacitors, due to thermal stress, has resulted in the deterioration of the 12V output under load conditions. Despite this instability in the 12V output, the derived 5V and 3.3V supplies remain stable, as they do not fall below the converter limits, thus masking the underlying fault.
The schematic for the switching power supply includes a transformer with a secondary winding, which is responsible for stepping down the voltage. The output from this winding feeds into the rectifier circuit, which consists of diodes, including VD4, that convert the AC voltage to DC. The filter capacitors, C22 and C23, are critical components that smooth out the rectified output, ensuring a stable DC voltage. The design of the power supply must account for thermal management due to the compact layout within the monitor's base. The proximity of the capacitors to the rectifier diode leads to increased thermal stress, which can accelerate the aging process of the capacitors.
In this scenario, the failure of C22, due to its significant drop in capacitance, has a direct impact on the stability of the 12V output. The power supply's ability to maintain stable voltages for the 5V and 3.3V outputs is a result of their respective regulation circuits, which may compensate for fluctuations in the input voltage. However, the underlying issue with the 12V output remains a concern, as it can lead to potential operational failures in devices relying on this voltage level. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the power supply components, especially in heat-sensitive environments, are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and performance.12V voltage instability, you should first check the switching power supply output section, as shown in FIG. The secondary winding of the transformer and the switch VD4 examination were normal, no inductor L2 Weld phenomenon. Filter capacitors C22 and C23 parameters are 1000pF / 16V, measuring capacitance meter C23, normal (capacity decreased slightly), but the C22 capacity has dropped to less than 80 F, the C22, C23 with the analysis of the reasons is the machine's main power mounted within the base of the monitor, the space is small, poor heat dissipation, and C22, C23 are close to 12V rectifier diode (especially C22 closer together), decreased capacity after being baked to make 12V with a load capacity deteriorates, and then this failure. Although derived from the 5V and 3.3V 12V, 12V instability but not down to 5V and 3.3V supply voltage converter limit or less, so the two voltages have been normal, and thus conceal the nature of the fault.
The schematic for the switching power supply includes a transformer with a secondary winding, which is responsible for stepping down the voltage. The output from this winding feeds into the rectifier circuit, which consists of diodes, including VD4, that convert the AC voltage to DC. The filter capacitors, C22 and C23, are critical components that smooth out the rectified output, ensuring a stable DC voltage. The design of the power supply must account for thermal management due to the compact layout within the monitor's base. The proximity of the capacitors to the rectifier diode leads to increased thermal stress, which can accelerate the aging process of the capacitors.
In this scenario, the failure of C22, due to its significant drop in capacitance, has a direct impact on the stability of the 12V output. The power supply's ability to maintain stable voltages for the 5V and 3.3V outputs is a result of their respective regulation circuits, which may compensate for fluctuations in the input voltage. However, the underlying issue with the 12V output remains a concern, as it can lead to potential operational failures in devices relying on this voltage level. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the power supply components, especially in heat-sensitive environments, are essential for ensuring long-term reliability and performance.12V voltage instability, you should first check the switching power supply output section, as shown in FIG. The secondary winding of the transformer and the switch VD4 examination were normal, no inductor L2 Weld phenomenon. Filter capacitors C22 and C23 parameters are 1000pF / 16V, measuring capacitance meter C23, normal (capacity decreased slightly), but the C22 capacity has dropped to less than 80 F, the C22, C23 with the analysis of the reasons is the machine's main power mounted within the base of the monitor, the space is small, poor heat dissipation, and C22, C23 are close to 12V rectifier diode (especially C22 closer together), decreased capacity after being baked to make 12V with a load capacity deteriorates, and then this failure. Although derived from the 5V and 3.3V 12V, 12V instability but not down to 5V and 3.3V supply voltage converter limit or less, so the two voltages have been normal, and thus conceal the nature of the fault.