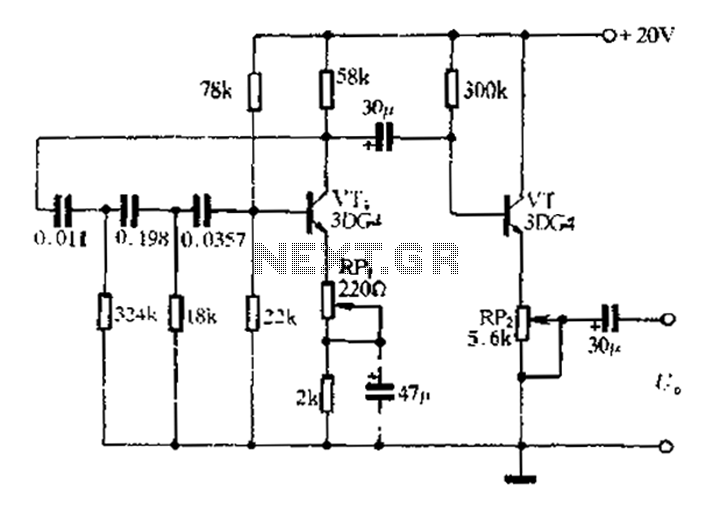
Asymmetric third order Butterworth active crossover network circuit diagram
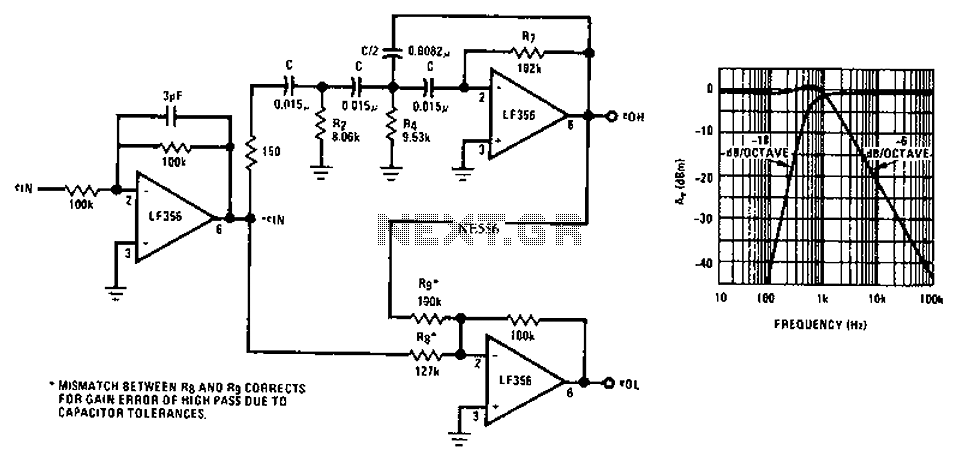
Asymmetric third-order Butterworth active crossover network circuit diagram.
The asymmetric third-order Butterworth active crossover network is a sophisticated circuit designed to split an audio signal into two separate frequency bands, typically for use in multi-way speaker systems. This type of crossover employs active components, such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), to achieve a precise frequency response and a smooth transition between the low-pass and high-pass outputs.
In this circuit, the Butterworth filter design is chosen for its maximally flat frequency response within the passband, ensuring minimal signal distortion. The third-order configuration provides a steeper roll-off rate of 18 dB per octave, which enhances the separation between the audio bands, thereby improving overall sound quality.
The circuit typically consists of two main sections: the low-pass filter and the high-pass filter. Each section utilizes multiple op-amps configured in a feedback arrangement to achieve the desired filter characteristics. The cutoff frequency, where the signal begins to attenuate, is determined by the values of resistors and capacitors used in the circuit.
To implement an asymmetric design, the component values can be adjusted to create differing slopes or cutoff frequencies for the low-pass and high-pass sections, allowing for tailored audio performance based on specific speaker characteristics or user preferences.
Power supply considerations are essential for active crossover networks; typically, a dual power supply is employed to provide the necessary positive and negative voltage rails for the op-amps. Additionally, careful attention must be paid to grounding and layout to minimize noise and interference, ensuring high-fidelity audio output.
In summary, the asymmetric third-order Butterworth active crossover network is an advanced circuit that provides effective frequency separation and high-quality audio performance, making it a valuable component in professional audio systems. Asymmetric third order Butterworth active crossover network circuit diagram as follows:
The asymmetric third-order Butterworth active crossover network is a sophisticated circuit designed to split an audio signal into two separate frequency bands, typically for use in multi-way speaker systems. This type of crossover employs active components, such as operational amplifiers (op-amps), to achieve a precise frequency response and a smooth transition between the low-pass and high-pass outputs.
In this circuit, the Butterworth filter design is chosen for its maximally flat frequency response within the passband, ensuring minimal signal distortion. The third-order configuration provides a steeper roll-off rate of 18 dB per octave, which enhances the separation between the audio bands, thereby improving overall sound quality.
The circuit typically consists of two main sections: the low-pass filter and the high-pass filter. Each section utilizes multiple op-amps configured in a feedback arrangement to achieve the desired filter characteristics. The cutoff frequency, where the signal begins to attenuate, is determined by the values of resistors and capacitors used in the circuit.
To implement an asymmetric design, the component values can be adjusted to create differing slopes or cutoff frequencies for the low-pass and high-pass sections, allowing for tailored audio performance based on specific speaker characteristics or user preferences.
Power supply considerations are essential for active crossover networks; typically, a dual power supply is employed to provide the necessary positive and negative voltage rails for the op-amps. Additionally, careful attention must be paid to grounding and layout to minimize noise and interference, ensuring high-fidelity audio output.
In summary, the asymmetric third-order Butterworth active crossover network is an advanced circuit that provides effective frequency separation and high-quality audio performance, making it a valuable component in professional audio systems. Asymmetric third order Butterworth active crossover network circuit diagram as follows: