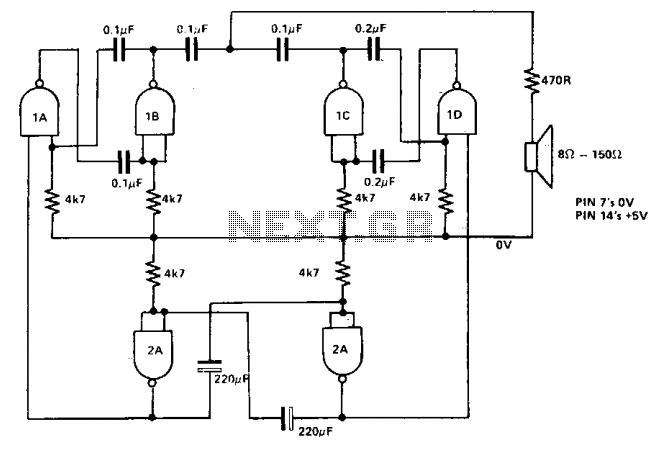
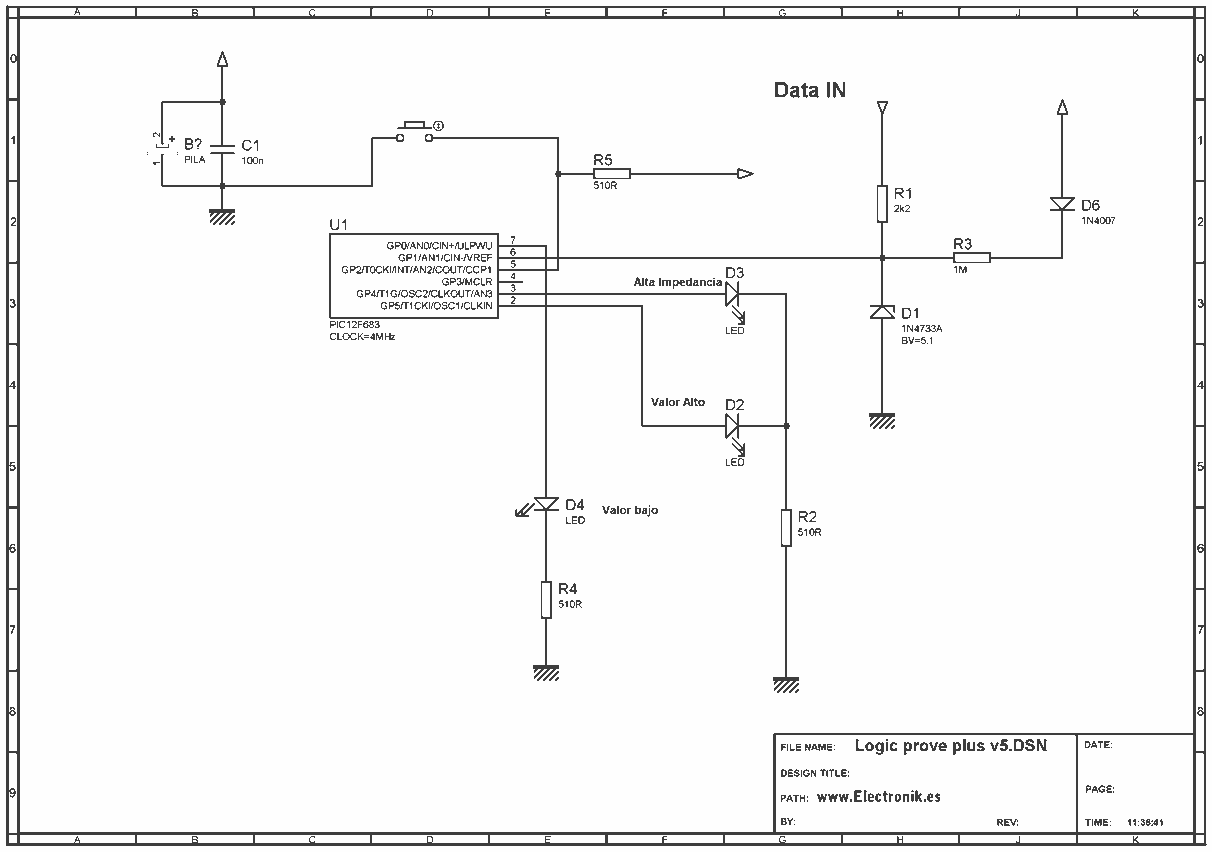
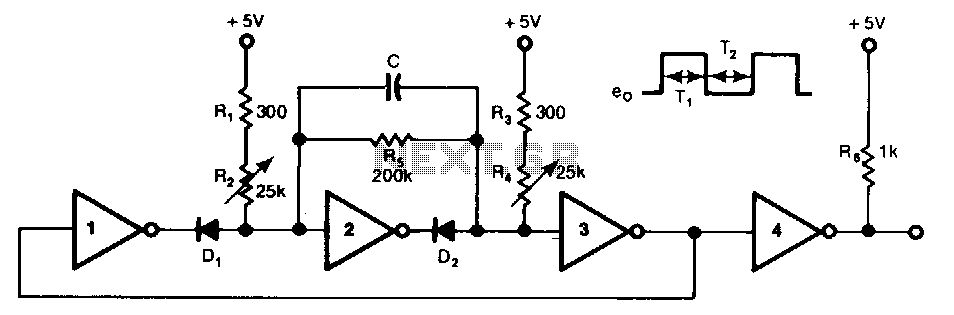
Audible ttl probe
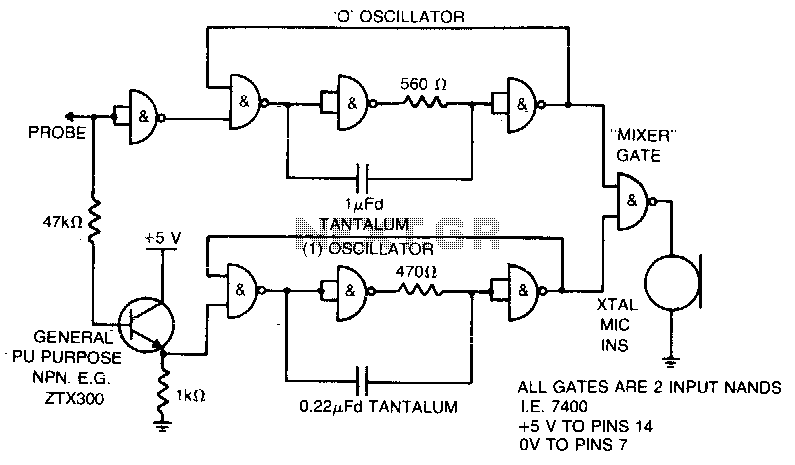
When the probe contacts a TTL low (0), it emits a low note. Conversely, when it contacts a TTL high (1), it emits a high note. The power for this operation is supplied by the circuit under test.
The described circuit operates as a simple audio output device that responds to digital logic levels. It utilizes a probe mechanism to detect TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) signals. The probe's function is to provide auditory feedback based on the logic state detected at its tip.
The circuit comprises a small audio oscillator, which generates sound frequencies corresponding to the logic levels. When the probe touches a point in the circuit that outputs a TTL low (0), the audio oscillator produces a low-frequency tone. This is typically achieved using a simple transistor-based oscillator or a dedicated audio IC configured to generate low frequencies. The frequency of the sound produced is determined by the components used in the oscillator circuit, such as resistors and capacitors.
In the case of a TTL high (1) signal, the circuit responds by generating a high-frequency tone. This can be accomplished by switching the oscillator's configuration or using a different oscillator circuit that is designed to produce higher frequencies. The transition between low and high tones provides a clear auditory indication of the detected signal state.
Powering the circuit from the circuit under test allows for portability and ease of use, as it eliminates the need for an external power source. The circuit must be designed to handle the voltage levels present in the circuit under test, typically ranging from 0 to 5 volts for TTL logic levels. Proper isolation and protection mechanisms should be implemented to prevent damage to the probe or the circuit under test.
Overall, this circuit serves as a practical tool for troubleshooting and testing digital circuits, providing immediate feedback through sound to indicate the state of the logic levels being probed.When the probe is in contact with a TTL low (0) the probe emits a low note. With a TTL high (1), a high note is emitted Power is supplied by the circuit under test. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a simple audio output device that responds to digital logic levels. It utilizes a probe mechanism to detect TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) signals. The probe's function is to provide auditory feedback based on the logic state detected at its tip.
The circuit comprises a small audio oscillator, which generates sound frequencies corresponding to the logic levels. When the probe touches a point in the circuit that outputs a TTL low (0), the audio oscillator produces a low-frequency tone. This is typically achieved using a simple transistor-based oscillator or a dedicated audio IC configured to generate low frequencies. The frequency of the sound produced is determined by the components used in the oscillator circuit, such as resistors and capacitors.
In the case of a TTL high (1) signal, the circuit responds by generating a high-frequency tone. This can be accomplished by switching the oscillator's configuration or using a different oscillator circuit that is designed to produce higher frequencies. The transition between low and high tones provides a clear auditory indication of the detected signal state.
Powering the circuit from the circuit under test allows for portability and ease of use, as it eliminates the need for an external power source. The circuit must be designed to handle the voltage levels present in the circuit under test, typically ranging from 0 to 5 volts for TTL logic levels. Proper isolation and protection mechanisms should be implemented to prevent damage to the probe or the circuit under test.
Overall, this circuit serves as a practical tool for troubleshooting and testing digital circuits, providing immediate feedback through sound to indicate the state of the logic levels being probed.When the probe is in contact with a TTL low (0) the probe emits a low note. With a TTL high (1), a high note is emitted Power is supplied by the circuit under test. 🔗 External reference