Audio AGC amplifier circuit
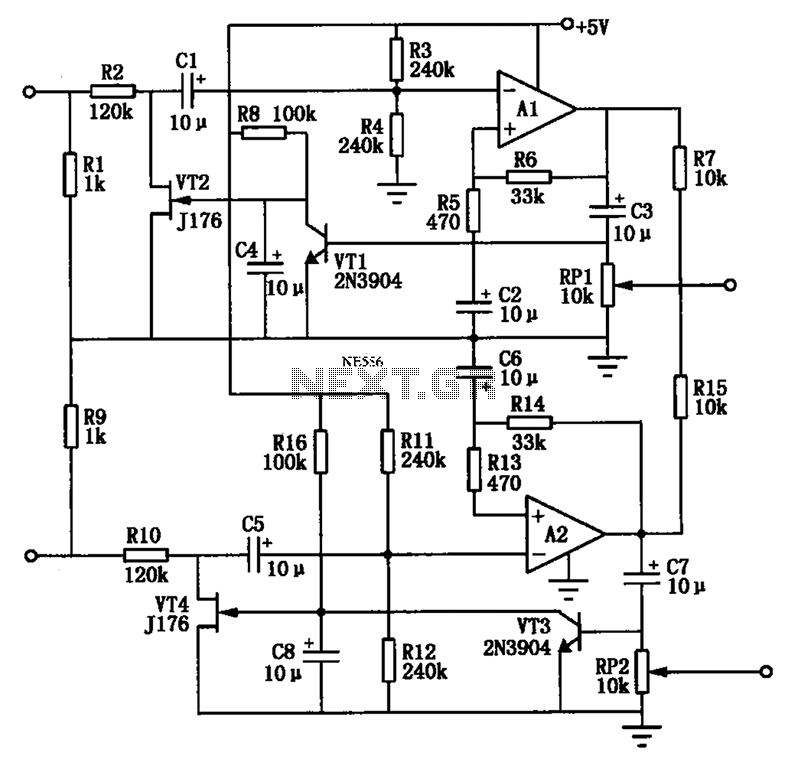
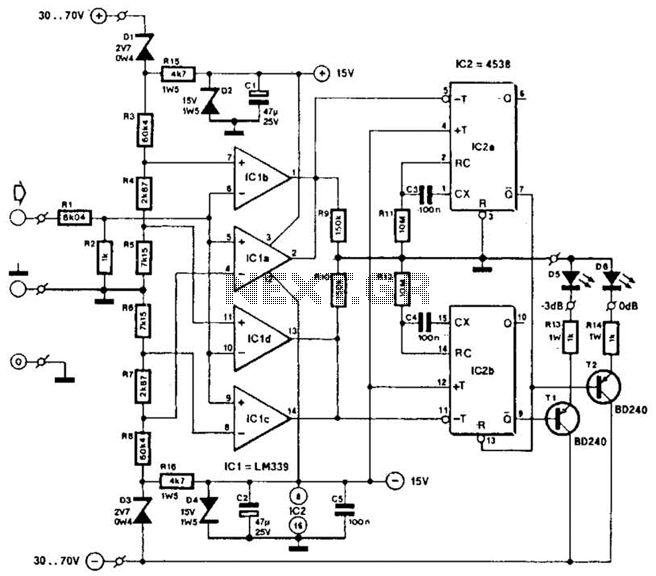
The Audio Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuit monitors the output signal level of an audio preamplifier. When the input signal increases, the AGC circuit automatically reduces the amplifier's gain. Conversely, when the input signal decreases, the AGC circuit increases the amplifier's gain. This maintains the analog-to-digital (A/D) signal at an optimal level while minimizing clipping. The audio amplifying circuit AGC has a dynamic range greater than 50 dB, exhibits minimal output waveform distortion, and offers quick response and slow decay advantages. The circuit accepts an input level between 40 mV and 20 mV, with an adjustable output level of 0 to 1.2 V. It operates on a single power supply with a current consumption of less than 1 mA at 5 V. The circuit employs P-channel JFETs (VT2, VT4), and resistors (R2, R3, R4, R10, R11, R12) form an equivalent resistor divider for the input circuit. When the input level is below 40 mV (peak-to-peak), the input is evenly distributed between R2 and R3, R4, resulting in insufficient amplitude at A1 to activate the positive peak detector VT2. The gate of the JFET is pulled to +5 V, causing it to pinch off the channel, resulting in very high resistance from drain to source. When the input voltage exceeds 40 mV peak-to-peak, VT1 activates A1, lowering the gate-to-source voltage of the junction-type FET. This reduces channel resistance and attenuates the input signal to maintain an A1 peak-to-peak output voltage of approximately 1.2 V.
The Audio AGC circuit is designed to enhance audio signal processing by automatically adjusting the gain of the amplifier based on the input signal level. This is crucial in applications where audio signals can vary significantly, ensuring consistent output levels without distortion. The circuit's dynamic range of over 50 dB allows it to accommodate a wide range of audio input levels, making it suitable for various audio applications, including broadcasting and recording.
The use of P-channel JFETs (VT2 and VT4) is significant due to their high input impedance and low noise characteristics, which are essential for maintaining audio fidelity. The resistor divider network (R2, R3, R4, R10, R11, R12) plays a vital role in setting the input sensitivity of the AGC circuit. By distributing the input signal evenly, it ensures that the AGC reacts appropriately to changes in input levels.
The circuit's functionality is based on the principle of feedback. When the input signal is below the threshold of 40 mV peak-to-peak, the AGC circuit remains inactive, allowing the audio signal to pass through without alteration. However, as the input signal increases beyond this threshold, the AGC circuit engages, effectively controlling the gain to prevent distortion. This is achieved by manipulating the gate voltage of the JFET, which adjusts the channel resistance and allows for precise control over the output signal level.
Overall, the Audio AGC circuit is a sophisticated solution for managing audio signals, providing both stability and quality in audio applications. Its design ensures that the output signal remains within optimal levels, thereby enhancing the overall listening experience. Audio AGC can keep track, monitor audio preamplifier output signal level when the input signal increases, AGC circuit automatically reduces the gain of the amplifier; when the input signal is reduced, AGC circuit automatically increases the gain of the amplifier, so that an a/D signal is maintained at an optimum level, but also make the clipping is minimized. As shown in FIG audio amplifying circuit AGC, dynamic range greater than this amplifier 50dB, the output waveform distortion is very small, and has started fast, slow decay advantages.
Circuit input 40 ~ 20mV and 0 ~ 1.2V adjustable output level, a single power supply, current consumption less than 1mA (5V voltage). VT2, VT4 P-channel JEFT, it R2, R3, R4 (R10, R11, R12) constituting the equivalent resistor divider input circuit access.
When the input level is lower than 40mV (peak to peak), the input evenly between R2 and R3, R4 distribution, A1 output amplitude is not large enough to make a positive peak detector VT2 conduction. The gate of the JFET pulled + 5V, pinch off the channel and it produces a very very high resistance from drain to source.
When the input voltage peak to peak higher than 40mV, VTl turned A1 in positive peak output, lowers the junction-type FET gate-to-source voltage. Channel resistance and to reduce the attenuation of the input signal, in order to keep Al peak to peak output voltage of about 1.2V.
The Audio AGC circuit is designed to enhance audio signal processing by automatically adjusting the gain of the amplifier based on the input signal level. This is crucial in applications where audio signals can vary significantly, ensuring consistent output levels without distortion. The circuit's dynamic range of over 50 dB allows it to accommodate a wide range of audio input levels, making it suitable for various audio applications, including broadcasting and recording.
The use of P-channel JFETs (VT2 and VT4) is significant due to their high input impedance and low noise characteristics, which are essential for maintaining audio fidelity. The resistor divider network (R2, R3, R4, R10, R11, R12) plays a vital role in setting the input sensitivity of the AGC circuit. By distributing the input signal evenly, it ensures that the AGC reacts appropriately to changes in input levels.
The circuit's functionality is based on the principle of feedback. When the input signal is below the threshold of 40 mV peak-to-peak, the AGC circuit remains inactive, allowing the audio signal to pass through without alteration. However, as the input signal increases beyond this threshold, the AGC circuit engages, effectively controlling the gain to prevent distortion. This is achieved by manipulating the gate voltage of the JFET, which adjusts the channel resistance and allows for precise control over the output signal level.
Overall, the Audio AGC circuit is a sophisticated solution for managing audio signals, providing both stability and quality in audio applications. Its design ensures that the output signal remains within optimal levels, thereby enhancing the overall listening experience. Audio AGC can keep track, monitor audio preamplifier output signal level when the input signal increases, AGC circuit automatically reduces the gain of the amplifier; when the input signal is reduced, AGC circuit automatically increases the gain of the amplifier, so that an a/D signal is maintained at an optimum level, but also make the clipping is minimized. As shown in FIG audio amplifying circuit AGC, dynamic range greater than this amplifier 50dB, the output waveform distortion is very small, and has started fast, slow decay advantages.
Circuit input 40 ~ 20mV and 0 ~ 1.2V adjustable output level, a single power supply, current consumption less than 1mA (5V voltage). VT2, VT4 P-channel JEFT, it R2, R3, R4 (R10, R11, R12) constituting the equivalent resistor divider input circuit access.
When the input level is lower than 40mV (peak to peak), the input evenly between R2 and R3, R4 distribution, A1 output amplitude is not large enough to make a positive peak detector VT2 conduction. The gate of the JFET pulled + 5V, pinch off the channel and it produces a very very high resistance from drain to source.
When the input voltage peak to peak higher than 40mV, VTl turned A1 in positive peak output, lowers the junction-type FET gate-to-source voltage. Channel resistance and to reduce the attenuation of the input signal, in order to keep Al peak to peak output voltage of about 1.2V.