Audio Analogue Level Meter
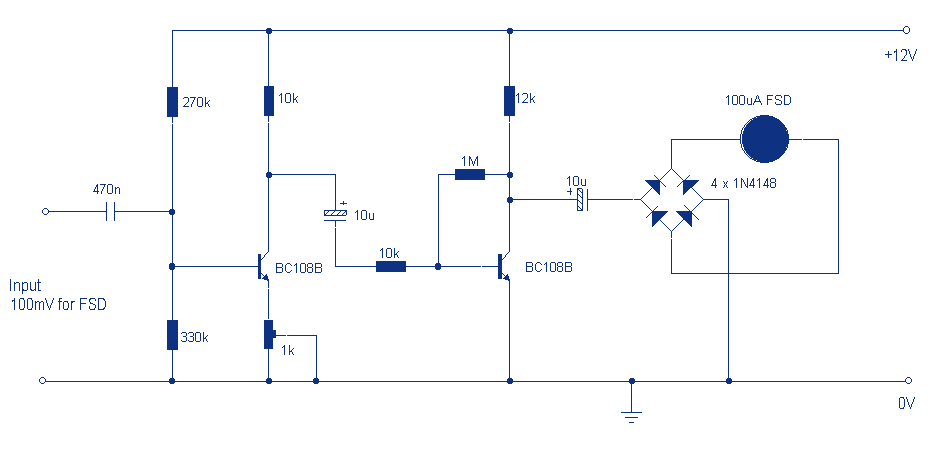
Audio levels can be monitored using a small panel meter with this circuit built from discrete components. The circuit has a flat frequency response from about 20Hz to well over 50Khz. Input sensitivity is 100mV for a full scale deflection on a 100uA meter. Built on two common emitter amplifiers, the first stage has a preset resistor which may be adjusted for a FSD. More: The last stage is biased to operate at roughly half the supply voltage for maximum ac voltage swing. Audio frequencies are passed through the 10u dc blocking capacitor and the full wave bridge rectifier converts the signal to a varying dc voltage.
This audio level monitoring circuit utilizes a small panel meter to provide visual feedback of audio signal levels. The design incorporates discrete components and is structured around two common emitter amplifier stages, which are essential for achieving the desired gain and frequency response characteristics. The circuit is capable of operating effectively within the audio frequency range, specifically from 20 Hz to over 50 kHz, ensuring that it can accurately monitor a wide variety of audio signals.
The input sensitivity of the circuit is set at 100 mV, which corresponds to a full-scale deflection on a 100 µA meter. This sensitivity allows for the detection of low-level audio signals, making it suitable for various applications in audio engineering and testing. The first amplifier stage features a preset resistor that can be adjusted to calibrate the full-scale deflection (FSD) of the meter, providing flexibility in accommodating different input signal levels.
The last stage of the circuit is designed to be biased at approximately half the supply voltage. This biasing technique maximizes the AC voltage swing, ensuring that the output can accurately reflect the variations in the audio signal. The audio frequencies are coupled into the circuit through a 10 µF DC blocking capacitor, which prevents any DC offset from affecting the measurement.
To convert the AC audio signal into a varying DC voltage suitable for the meter, a full-wave bridge rectifier is employed. This rectification process allows for the measurement of both the positive and negative halves of the audio waveform, providing a more accurate representation of the audio levels. The output from the rectifier is a varying DC voltage that corresponds to the amplitude of the incoming audio signal, which can then be displayed on the panel meter.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for monitoring audio levels, combining simplicity with functionality to provide reliable performance in various audio applications.Audio levels can be monitored using a small panel meter with this circuit built from discrete components. The circuit has a flat frequency response from about 20Hz to well over 50Khz. Input sensitivity is 100mV for a full scale deflection on a 100uA meter. Built on two common emitter amplifiers, the first stage has a preset resistor which may be adjusted for a FSD.
The last stage is biased to operate at roughly half the supply voltage for maximum ac voltage swing. Audio frequencies are passed through the 10u dc blocking capacitor and the full wave bridge rectifier converts the signal to a varying dc voltage. Note th 🔗 External reference
This audio level monitoring circuit utilizes a small panel meter to provide visual feedback of audio signal levels. The design incorporates discrete components and is structured around two common emitter amplifier stages, which are essential for achieving the desired gain and frequency response characteristics. The circuit is capable of operating effectively within the audio frequency range, specifically from 20 Hz to over 50 kHz, ensuring that it can accurately monitor a wide variety of audio signals.
The input sensitivity of the circuit is set at 100 mV, which corresponds to a full-scale deflection on a 100 µA meter. This sensitivity allows for the detection of low-level audio signals, making it suitable for various applications in audio engineering and testing. The first amplifier stage features a preset resistor that can be adjusted to calibrate the full-scale deflection (FSD) of the meter, providing flexibility in accommodating different input signal levels.
The last stage of the circuit is designed to be biased at approximately half the supply voltage. This biasing technique maximizes the AC voltage swing, ensuring that the output can accurately reflect the variations in the audio signal. The audio frequencies are coupled into the circuit through a 10 µF DC blocking capacitor, which prevents any DC offset from affecting the measurement.
To convert the AC audio signal into a varying DC voltage suitable for the meter, a full-wave bridge rectifier is employed. This rectification process allows for the measurement of both the positive and negative halves of the audio waveform, providing a more accurate representation of the audio levels. The output from the rectifier is a varying DC voltage that corresponds to the amplitude of the incoming audio signal, which can then be displayed on the panel meter.
Overall, this circuit design is an effective solution for monitoring audio levels, combining simplicity with functionality to provide reliable performance in various audio applications.Audio levels can be monitored using a small panel meter with this circuit built from discrete components. The circuit has a flat frequency response from about 20Hz to well over 50Khz. Input sensitivity is 100mV for a full scale deflection on a 100uA meter. Built on two common emitter amplifiers, the first stage has a preset resistor which may be adjusted for a FSD.
The last stage is biased to operate at roughly half the supply voltage for maximum ac voltage swing. Audio frequencies are passed through the 10u dc blocking capacitor and the full wave bridge rectifier converts the signal to a varying dc voltage. Note th 🔗 External reference