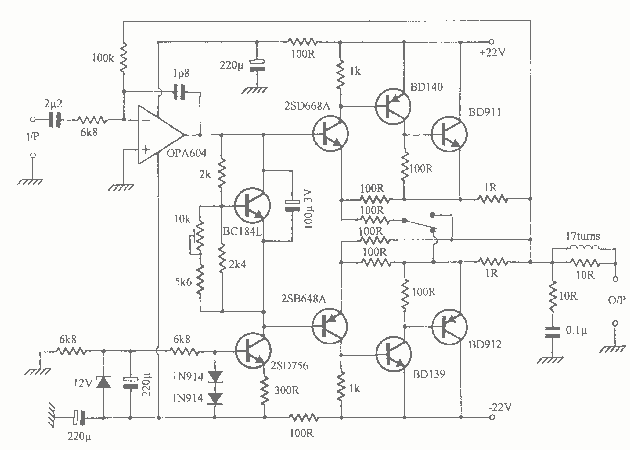
Audio continuity tester
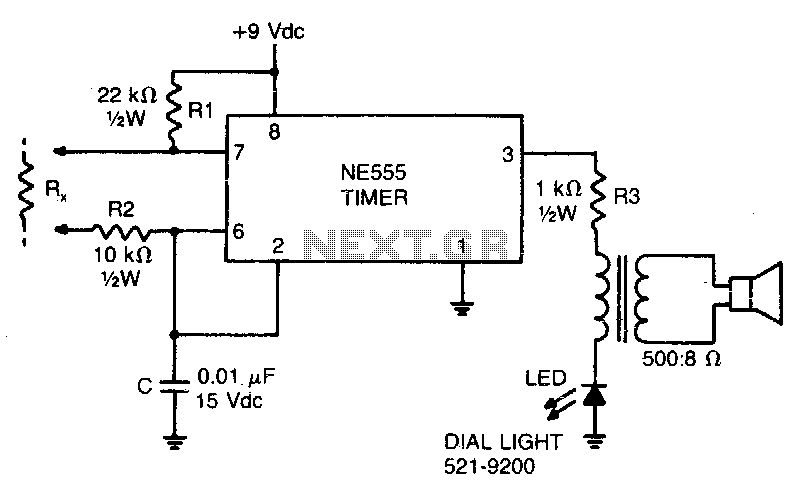
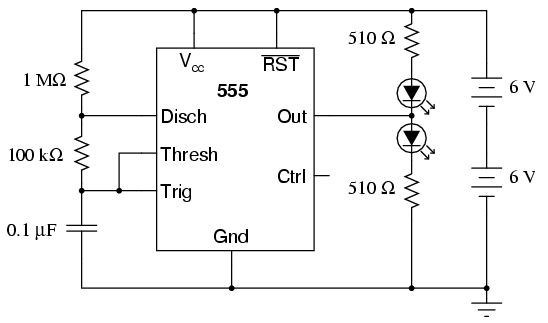
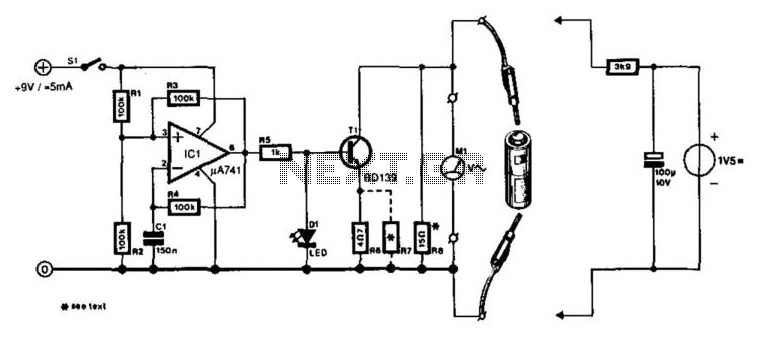
This low-current audio continuity tester indicates the unknown resistance value by the frequency of the audio tone. A high tone indicates a low resistance, while a tone of a few pulses per second indicates a resistance as high as 30 megohms.
The low-current audio continuity tester is designed to provide a visual and auditory indication of resistance levels in electronic circuits. The principle of operation is based on generating an audio tone whose frequency varies in accordance with the resistance measured. This device typically employs a simple oscillator circuit that produces a continuous audio signal.
In practical applications, when the resistance is low, the audio frequency increases, resulting in a high-pitched tone. Conversely, as the resistance increases, the frequency of the audio tone decreases, producing a slower pulsing sound. This functionality allows users to quickly assess the integrity of components and connections within a circuit, making it an invaluable tool for troubleshooting and maintenance.
The tester can measure resistances up to 30 megohms, which is particularly useful for testing high-resistance components such as capacitors or insulators. The device is often powered by a low-voltage battery to ensure safety and minimize current draw during testing.
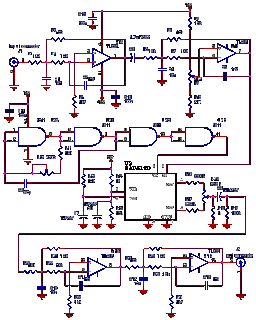
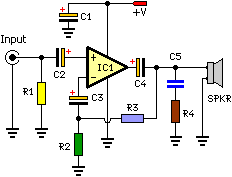
The schematic for such a continuity tester typically includes an oscillator circuit, often built around a transistor or an operational amplifier, connected to a speaker or a piezo buzzer for audio output. Additionally, a variable resistor may be included to calibrate the frequency response, ensuring accurate tone generation across the specified resistance range. Proper design considerations must be taken into account to ensure that the tester operates effectively without introducing significant loading effects on the circuit being tested.This low-current audio continuity tester indicates the unknown resistance value by the frequency of audio tone A high tone indicates a low resistance, and a tone of a few pulses per second indicates a resistance as high as 30 megohms. 🔗 External reference
The low-current audio continuity tester is designed to provide a visual and auditory indication of resistance levels in electronic circuits. The principle of operation is based on generating an audio tone whose frequency varies in accordance with the resistance measured. This device typically employs a simple oscillator circuit that produces a continuous audio signal.
In practical applications, when the resistance is low, the audio frequency increases, resulting in a high-pitched tone. Conversely, as the resistance increases, the frequency of the audio tone decreases, producing a slower pulsing sound. This functionality allows users to quickly assess the integrity of components and connections within a circuit, making it an invaluable tool for troubleshooting and maintenance.
The tester can measure resistances up to 30 megohms, which is particularly useful for testing high-resistance components such as capacitors or insulators. The device is often powered by a low-voltage battery to ensure safety and minimize current draw during testing.
The schematic for such a continuity tester typically includes an oscillator circuit, often built around a transistor or an operational amplifier, connected to a speaker or a piezo buzzer for audio output. Additionally, a variable resistor may be included to calibrate the frequency response, ensuring accurate tone generation across the specified resistance range. Proper design considerations must be taken into account to ensure that the tester operates effectively without introducing significant loading effects on the circuit being tested.This low-current audio continuity tester indicates the unknown resistance value by the frequency of audio tone A high tone indicates a low resistance, and a tone of a few pulses per second indicates a resistance as high as 30 megohms. 🔗 External reference