Audio Peak / Beat LED indicator
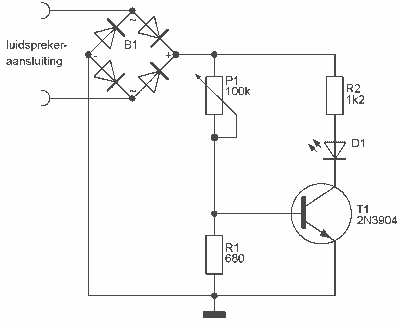
This indicator can be used, or see if your speakers can be damaged by the noise power. With P1 you can set the limit to which D1 LED lights. The pot is 100k here, you can even experiment with other values. If you are a logical port on the switch or LED is an opto coupler would use it so you can switch the signal between the preamp and power amp would fall off. Or that the signal to the speakers using a relay would be removed. More: Parts List R1 = 680 ? R2 = 1.2 kOhm P1 = 100 kOhm linear B1 = B250C1000 or 4 x 1N4003 D1 = LED T1 = 2N3904
The circuit described functions as a noise indicator for audio systems, specifically designed to monitor and prevent potential damage to speakers caused by excessive noise power levels. The key component of this circuit is the adjustable potentiometer P1, which allows the user to set a specific threshold for noise detection. When the noise level exceeds this threshold, the LED indicator D1 is activated, providing a visual cue to the user.
The circuit includes two resistors, R1 and R2, which serve to set up the biasing conditions for the transistor T1 (2N3904). Resistor R1 is specified as 680 ohms, and R2 is 1.2 kOhm, which together form a voltage divider that helps in controlling the base current of the transistor. The transistor acts as a switch that can be used to control additional circuitry, such as a relay or an opto-coupler, to disconnect the signal path to the speakers when excessive noise is detected.
The power supply for the circuit can be provided by a bridge rectifier (B1), which can be either a B250C1000 or a configuration of four 1N4003 diodes. This ensures that the circuit operates efficiently with a stable DC voltage, which is essential for the reliable functioning of the LED and the transistor.
In terms of operation, the user can experiment with different values of P1 to adjust the sensitivity of the noise detection. A linear potentiometer of 100 kOhm has been chosen, but variations may yield different performance characteristics. If additional isolation or control is desired, the circuit can be modified to include an opto-coupler for signal switching or a relay to physically disconnect the speakers from the audio path, thus preventing any potential damage.
Overall, this circuit design serves as an effective means of safeguarding audio equipment from noise-induced damage while providing a simple yet functional user interface for monitoring audio levels.This indicator can be used, or see if your speakers can be damaged by the noise power. With P1 you can set the limit to which D1 LED lights. The pot is 100k here, you can even experiment with other values. If you are a logical port on the switch or LED is an opto coupler would use it so you can switch the signal between the preamp and power amp would fall off. Or that the signal to the speakers using a relay would be removed. Parts List R1 = 680 ? R2 = 1.2 kOhm P1 = 100 kOhm linear B1 = B250C1000 or 4 x 1N4003 D1 = LED T1 = 2N3904 🔗 External reference
The circuit described functions as a noise indicator for audio systems, specifically designed to monitor and prevent potential damage to speakers caused by excessive noise power levels. The key component of this circuit is the adjustable potentiometer P1, which allows the user to set a specific threshold for noise detection. When the noise level exceeds this threshold, the LED indicator D1 is activated, providing a visual cue to the user.
The circuit includes two resistors, R1 and R2, which serve to set up the biasing conditions for the transistor T1 (2N3904). Resistor R1 is specified as 680 ohms, and R2 is 1.2 kOhm, which together form a voltage divider that helps in controlling the base current of the transistor. The transistor acts as a switch that can be used to control additional circuitry, such as a relay or an opto-coupler, to disconnect the signal path to the speakers when excessive noise is detected.
The power supply for the circuit can be provided by a bridge rectifier (B1), which can be either a B250C1000 or a configuration of four 1N4003 diodes. This ensures that the circuit operates efficiently with a stable DC voltage, which is essential for the reliable functioning of the LED and the transistor.
In terms of operation, the user can experiment with different values of P1 to adjust the sensitivity of the noise detection. A linear potentiometer of 100 kOhm has been chosen, but variations may yield different performance characteristics. If additional isolation or control is desired, the circuit can be modified to include an opto-coupler for signal switching or a relay to physically disconnect the speakers from the audio path, thus preventing any potential damage.
Overall, this circuit design serves as an effective means of safeguarding audio equipment from noise-induced damage while providing a simple yet functional user interface for monitoring audio levels.This indicator can be used, or see if your speakers can be damaged by the noise power. With P1 you can set the limit to which D1 LED lights. The pot is 100k here, you can even experiment with other values. If you are a logical port on the switch or LED is an opto coupler would use it so you can switch the signal between the preamp and power amp would fall off. Or that the signal to the speakers using a relay would be removed. Parts List R1 = 680 ? R2 = 1.2 kOhm P1 = 100 kOhm linear B1 = B250C1000 or 4 x 1N4003 D1 = LED T1 = 2N3904 🔗 External reference