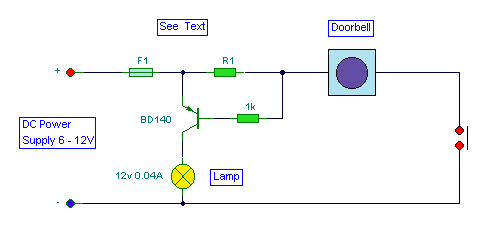
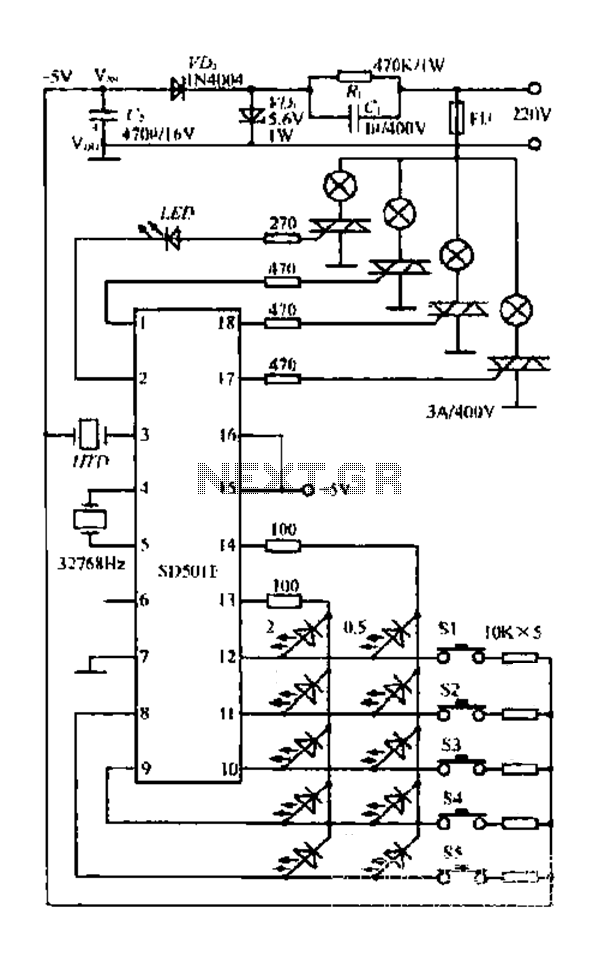
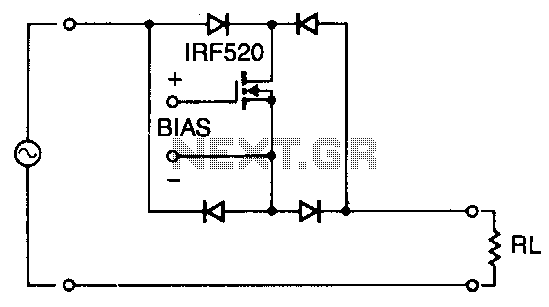
Audio remote control switch schematic
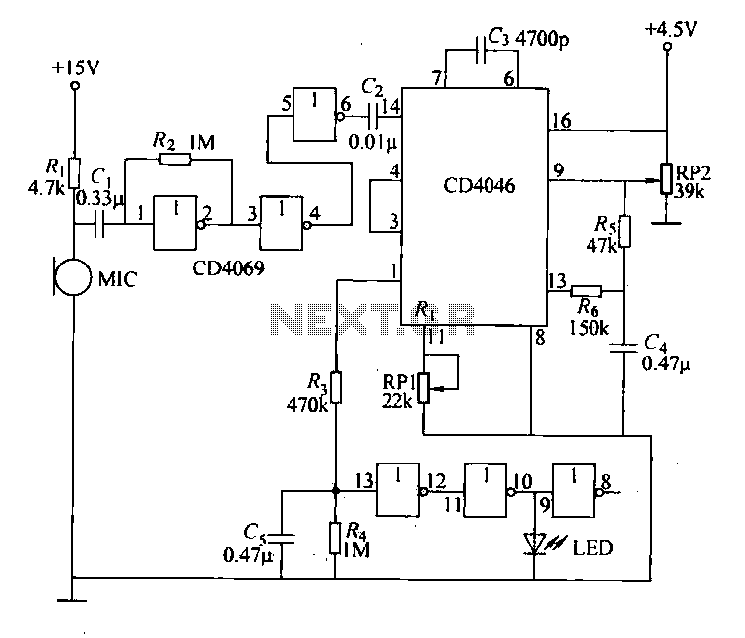
Each issue produces a specific frequency of sound, and the audio remote control will switch states based on these frequencies. The circuit is designed to detect other frequencies emitted by environmental sounds with strong anti-interference capabilities. The circuit operates on the following principles: 1) Phase Locked Loop (PLL) circuit principle: The CD4046 PLL circuit consists of a phase comparator, a low-pass filter, and a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase comparator compares the external sound signal with an internal pulse signal of a center frequency. When both frequencies match, the output from the first comparator reaches a high potential. If the frequencies do not match, the circuit enters an unlock state. To address this issue, the phase-locked loop circuit uses feedback voltage from the phase comparator output to adjust the frequency of the internal oscillator, aligning it with the external signal frequency. The range within which the circuit can lock onto the input signal frequency is known as the frequency capture range. The pin configuration for CD4046 is depicted in Figure 18-43a, while the pin diagram for the CD4069 hex inverter is shown in Figure 18-43b. The circuit includes signal input (PH11), comparison signal input (PHlZ), VCO control terminal (VC01), inhibit terminal (INH), internal zener negative terminal (Z), demodulated output terminal (DEMo), external resistor terminals (R2, Rz), external capacitor terminals (G, G), phase comparator outputs (PH01, PH02), and the output of the phase comparator (PH03). When the circuit is locked, the output is high; when it loses lock, the output is low. The VCO output terminal is indicated as VCOo. 2) Principle analysis: The circuit can detect whistle sounds as a transmission signal for remote control. It receives signals through a microphone (BM) and adjusts the receiving frequency to respond only to specific whistle sounds. The circuit is finely tuned for maximum sensitivity and control distance. Experienced users may also adjust the circuit by blowing into it. The receiving circuit is shown in Figure 18-43c. The hex inverter circuit is built using the CD4069 and CD4060, which includes a hex serial counter/divider and other components, forming an audio amplifier circuit, PLL circuit, and switch output circuit. The audio amplifier amplifies the microphone signal, and the amplified external sound signal is fed into the PLL circuit. The PLL features an internal voltage-controlled oscillator that operates at a set frequency. When the PLL circuit receives the external audio signal, it locks onto the signal whenever the VCO operating frequency matches the incoming audio signal. As a result, the voltage output of the circuit transitions from low to high, changing the status of the control switch circuit.
The audio remote control system described utilizes a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) circuit to achieve precise frequency detection and switching capabilities. The CD4046 PLL chip serves as the core of this system, integrating essential components such as a phase comparator, low-pass filter, and voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase comparator plays a critical role in comparing the frequency of incoming audio signals with a reference frequency generated internally. This comparison enables the system to maintain synchronization between the detected sound and the internal oscillator, thereby facilitating accurate control operations.
The circuit's robustness against environmental interference is a significant advantage, as it can filter out unwanted noise and respond only to specific frequencies, such as those produced by a whistle. The design incorporates feedback mechanisms that adjust the oscillator's frequency, ensuring that it remains locked onto the desired signal even in the presence of competing sounds.
In practical applications, the microphone (BM) captures the audio signals, which are then amplified and processed by the PLL circuit. The output from the PLL circuit is used to control a switch, enabling or disabling connected devices based on the detected audio frequency. The system's effectiveness can be enhanced through careful tuning of the receiving circuit, allowing for optimal sensitivity and range. This feature makes the audio remote control suitable for various applications, including remote activation of devices in environments where traditional remote controls may be ineffective.
Overall, the combination of the CD4046 PLL circuit, audio amplification, and precise frequency detection creates a reliable and efficient audio remote control system capable of functioning effectively in diverse conditions.Each issue a specific frequency of sound, audio remote control will switch changes state, the circuit for other frequencies emitted by the environment sound with strong anti-in terference ability. (1) circuit principle 1) phase locked loop circuit principle: CD4046 PLL circuit includes a phase comparator, a low-pass filter and a voltage controlled oscillator section 3 group into. The phase comparator function is outside the sound signal with the center frequency of the internal pulse signal frequency comparison + when the same frequency, the output from the first O feet high potential; whether it is internal or external sound signal oscillation signal whose frequency It will have to unlock like state.
In order to solve this. Problem, phase-locked loop circuit through the filter of the phase comparator output voltage feedback voltage to the oscillator to change the frequency of the internal oscillator pulses, so that the frequency of the external signal is the same; that starting from the unlock state to the final Lou set of allowed state of the input signal frequency range is called the frequency capture range. CD4046 pin shown in Figure 18-43a. CD4069 hex inverter pin diagram shown in Figure 18-43b. Fig. 1 PH11 signal input; PHlZ the comparison signal input terminal {VC01 for the VCO control terminal; INH to prohibit the end; Z is the internal zener negative terminal} DEMo demodulated output terminal; R2, Rz is external resistor end; G, G for the external capacitor end; PH01, PH02 for the phase comparator - Guo ln} PH03 output of the phase output terminal, when the lockup high, low loss of lock when almost; vCOo as a voltage controlled oscillator output terminal 2) principle analysis: circuit can whistle sound as a transmission signal, the remote control.
Received by the microphone BM, adjusting circuit receiving frequency, so that the circuit only respond to a specific whistle sounds. Carefully adjusted so that the circuit the highest sensitivity, control distances. As if the producers have more experience, you can also use the mouth blowing a whistle to adjust the circuit.
Receiving circuit shown in Figure 18-43c. Hex inverter circuit by the CD4069 and CD4060 14 in hex serial counter/divider and other components audio amplifier circuit, PLL circuit and a switch output circuit. Audio amplifier sound microphone signal was subjected to amplification. External sound signal after amplification to the input of the PLL circuit. PLL has an internal voltage-controlled oscillator, flat while working on the set operating frequency.
When the external audio signal successor PLL circuit, and every time it receives the VCO operating frequency when the same audio signal, phase locked loop circuit is in a locked state, the voltage output of the circuit changes from low to high, the output of the control switch circuit change switch status.
The audio remote control system described utilizes a Phase Locked Loop (PLL) circuit to achieve precise frequency detection and switching capabilities. The CD4046 PLL chip serves as the core of this system, integrating essential components such as a phase comparator, low-pass filter, and voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). The phase comparator plays a critical role in comparing the frequency of incoming audio signals with a reference frequency generated internally. This comparison enables the system to maintain synchronization between the detected sound and the internal oscillator, thereby facilitating accurate control operations.
The circuit's robustness against environmental interference is a significant advantage, as it can filter out unwanted noise and respond only to specific frequencies, such as those produced by a whistle. The design incorporates feedback mechanisms that adjust the oscillator's frequency, ensuring that it remains locked onto the desired signal even in the presence of competing sounds.
In practical applications, the microphone (BM) captures the audio signals, which are then amplified and processed by the PLL circuit. The output from the PLL circuit is used to control a switch, enabling or disabling connected devices based on the detected audio frequency. The system's effectiveness can be enhanced through careful tuning of the receiving circuit, allowing for optimal sensitivity and range. This feature makes the audio remote control suitable for various applications, including remote activation of devices in environments where traditional remote controls may be ineffective.
Overall, the combination of the CD4046 PLL circuit, audio amplification, and precise frequency detection creates a reliable and efficient audio remote control system capable of functioning effectively in diverse conditions.Each issue a specific frequency of sound, audio remote control will switch changes state, the circuit for other frequencies emitted by the environment sound with strong anti-in terference ability. (1) circuit principle 1) phase locked loop circuit principle: CD4046 PLL circuit includes a phase comparator, a low-pass filter and a voltage controlled oscillator section 3 group into. The phase comparator function is outside the sound signal with the center frequency of the internal pulse signal frequency comparison + when the same frequency, the output from the first O feet high potential; whether it is internal or external sound signal oscillation signal whose frequency It will have to unlock like state.
In order to solve this. Problem, phase-locked loop circuit through the filter of the phase comparator output voltage feedback voltage to the oscillator to change the frequency of the internal oscillator pulses, so that the frequency of the external signal is the same; that starting from the unlock state to the final Lou set of allowed state of the input signal frequency range is called the frequency capture range. CD4046 pin shown in Figure 18-43a. CD4069 hex inverter pin diagram shown in Figure 18-43b. Fig. 1 PH11 signal input; PHlZ the comparison signal input terminal {VC01 for the VCO control terminal; INH to prohibit the end; Z is the internal zener negative terminal} DEMo demodulated output terminal; R2, Rz is external resistor end; G, G for the external capacitor end; PH01, PH02 for the phase comparator - Guo ln} PH03 output of the phase output terminal, when the lockup high, low loss of lock when almost; vCOo as a voltage controlled oscillator output terminal 2) principle analysis: circuit can whistle sound as a transmission signal, the remote control.
Received by the microphone BM, adjusting circuit receiving frequency, so that the circuit only respond to a specific whistle sounds. Carefully adjusted so that the circuit the highest sensitivity, control distances. As if the producers have more experience, you can also use the mouth blowing a whistle to adjust the circuit.
Receiving circuit shown in Figure 18-43c. Hex inverter circuit by the CD4069 and CD4060 14 in hex serial counter/divider and other components audio amplifier circuit, PLL circuit and a switch output circuit. Audio amplifier sound microphone signal was subjected to amplification. External sound signal after amplification to the input of the PLL circuit. PLL has an internal voltage-controlled oscillator, flat while working on the set operating frequency.
When the external audio signal successor PLL circuit, and every time it receives the VCO operating frequency when the same audio signal, phase locked loop circuit is in a locked state, the voltage output of the circuit changes from low to high, the output of the control switch circuit change switch status.