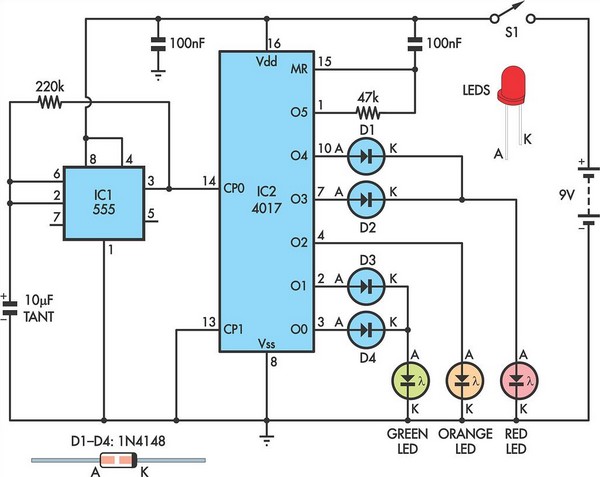
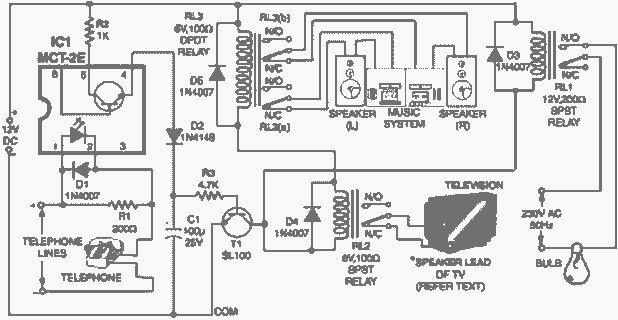
Based LT3756 buck - boost mode drive circuit diagram
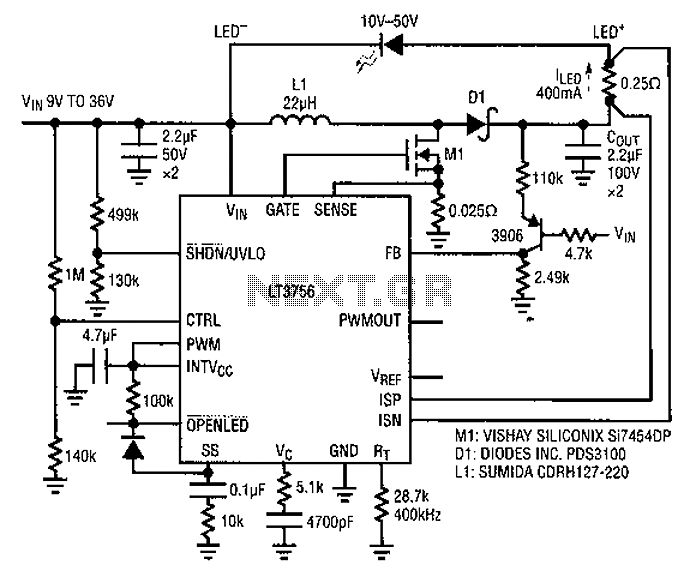
Common LED driver requirements include a wide and overlapping range of LED string voltages and input voltages. Many designers prefer to use an LED driver circuit that accommodates various battery power sources and multiple LED strings. This universal configuration may compromise some efficiency, component costs, and board space, but it simplifies design and reduces time to market. A buck-boost mode driver using a single inductor is illustrated in Figure 1. This driver accepts input voltages from 9V to 36V and is designed to supply 400mA of current to drive LED strings with voltages ranging from 10V to 50V. The inductor current corresponds to the input current and the LED string currents; the peak inductor current is equal to the peak switch current. When the input voltage drops below 9V, the CTRL analog dimming feature reduces the LED current accordingly, thus controlling the inductor current. The UVL0 functional circuit turns off the LED when the input voltage falls below 6V. Components COUT, D1, and MI are rated to withstand up to 95V.
The described LED driver circuit operates in a buck-boost configuration, allowing it to efficiently regulate output voltage over a wide input voltage range. The design utilizes a single inductor to minimize component count, which is beneficial for reducing board space and overall system complexity. The input voltage range of 9V to 36V ensures compatibility with various power sources, including batteries of different chemistries and configurations.
The driver is capable of providing a constant output current of 400mA, which is suitable for powering LED strings with a forward voltage of 10V to 50V. This flexibility allows the driver to be used in diverse applications, from simple indicator lights to more complex lighting systems.
The inductor plays a critical role in energy transfer within the circuit. The relationship between inductor current and LED string current is crucial; as the inductor charges, it stores energy that is then released to the LED strings. The peak inductor current must be monitored, as it directly influences the peak switch current, which is necessary for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits.
The CTRL pin provides an analog dimming feature, which is particularly useful for applications requiring variable brightness. By adjusting the input voltage, the LED current can be reduced, thereby controlling the brightness of the LEDs. This dimming capability enhances the versatility of the driver in various lighting scenarios.
The under-voltage lockout (UVL0) feature is essential for protecting the LEDs from operating under insufficient voltage conditions. If the input voltage drops below 6V, the circuit automatically turns off the LED output, preventing potential damage to the LEDs and ensuring reliable operation.
The components COUT, D1, and MI are designed to withstand voltages up to 95V, providing an added layer of reliability and safety in the circuit. This high-voltage rating is particularly important in applications where input voltage fluctuations may occur, ensuring that the driver remains functional under varying conditions. Overall, this LED driver design represents a robust solution for a wide range of LED lighting applications, balancing efficiency, cost, and design simplicity.A common LED driver requirements are: The LED string voltage and the input voltage is very wide and overlapping. In fact, some designers prefer to use with a LED driver circuit for a variety of battery power, and a plurality of different LED strings. Such universal configuration needs to sacrifice some efficiency, component costs and board space expense, in exchange for simplicity of design time to market and product. Figure 1 is a buck-boost mode driver using a single inductor. It accepts 9V to 36V input, it is designed to 400mA of current to drive the LED strings 10V ~ 50V. Inductor current is the input current to the LED string currents; peak inductor current is equal to the peak switch current.
In the case of less than 9V input, CTRL analog dimming the LED current will be correspondingly reduced, so that the inductor current under control. UVL0 functional circuit at less than 6VIN off LED. Here, COUT, Dl and MI can withstand up to 95V.
The described LED driver circuit operates in a buck-boost configuration, allowing it to efficiently regulate output voltage over a wide input voltage range. The design utilizes a single inductor to minimize component count, which is beneficial for reducing board space and overall system complexity. The input voltage range of 9V to 36V ensures compatibility with various power sources, including batteries of different chemistries and configurations.
The driver is capable of providing a constant output current of 400mA, which is suitable for powering LED strings with a forward voltage of 10V to 50V. This flexibility allows the driver to be used in diverse applications, from simple indicator lights to more complex lighting systems.
The inductor plays a critical role in energy transfer within the circuit. The relationship between inductor current and LED string current is crucial; as the inductor charges, it stores energy that is then released to the LED strings. The peak inductor current must be monitored, as it directly influences the peak switch current, which is necessary for ensuring that the circuit operates within safe limits.
The CTRL pin provides an analog dimming feature, which is particularly useful for applications requiring variable brightness. By adjusting the input voltage, the LED current can be reduced, thereby controlling the brightness of the LEDs. This dimming capability enhances the versatility of the driver in various lighting scenarios.
The under-voltage lockout (UVL0) feature is essential for protecting the LEDs from operating under insufficient voltage conditions. If the input voltage drops below 6V, the circuit automatically turns off the LED output, preventing potential damage to the LEDs and ensuring reliable operation.
The components COUT, D1, and MI are designed to withstand voltages up to 95V, providing an added layer of reliability and safety in the circuit. This high-voltage rating is particularly important in applications where input voltage fluctuations may occur, ensuring that the driver remains functional under varying conditions. Overall, this LED driver design represents a robust solution for a wide range of LED lighting applications, balancing efficiency, cost, and design simplicity.A common LED driver requirements are: The LED string voltage and the input voltage is very wide and overlapping. In fact, some designers prefer to use with a LED driver circuit for a variety of battery power, and a plurality of different LED strings. Such universal configuration needs to sacrifice some efficiency, component costs and board space expense, in exchange for simplicity of design time to market and product. Figure 1 is a buck-boost mode driver using a single inductor. It accepts 9V to 36V input, it is designed to 400mA of current to drive the LED strings 10V ~ 50V. Inductor current is the input current to the LED string currents; peak inductor current is equal to the peak switch current.
In the case of less than 9V input, CTRL analog dimming the LED current will be correspondingly reduced, so that the inductor current under control. UVL0 functional circuit at less than 6VIN off LED. Here, COUT, Dl and MI can withstand up to 95V.