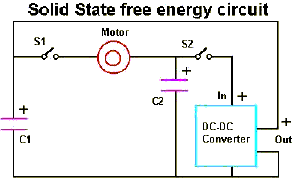
BASIC DIGITAL THERMOMETER KELVIN SCALE WITH ZERO ADJUST
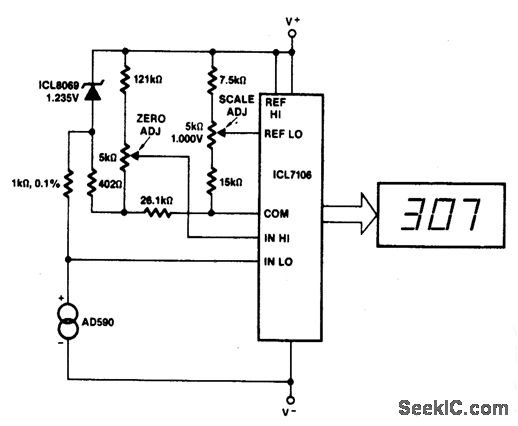
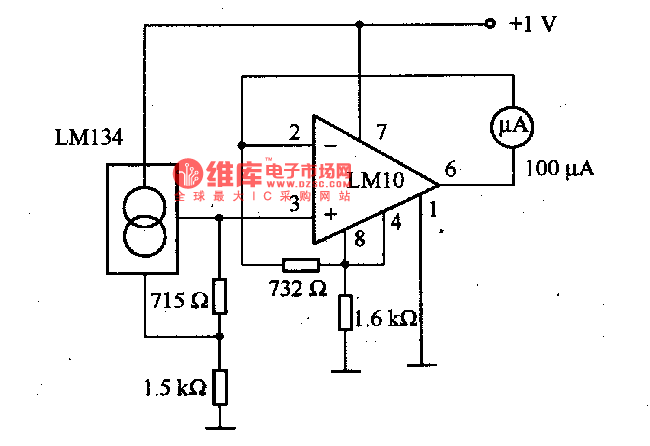
This circuit allows for zero adjustment as well as slope adjustment. The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 K pots trim any offset at 218 °K (-55 °F) and set the scale factor.
The described circuit employs the ICL8069, an integrated circuit designed for precision signal processing, particularly in applications requiring accurate temperature measurements. The zero adjustment feature is crucial for calibrating the output to a reference point, ensuring that the readings reflect true values. The slope adjustment, on the other hand, allows for fine-tuning the gain of the circuit, which is essential for maintaining linearity across the operational range.
The inclusion of 5 K potentiometers provides flexibility in trimming both the offset and the scale factor. This is particularly important in temperature measurement applications, where even minor deviations can lead to significant errors. The adjustment pots enable the user to calibrate the circuit at a specific temperature point, in this case, 218 °K (-55 °F), which is typically a critical temperature for certain sensor applications.
The circuit's design ensures that the input signal remains within the common-mode range of the ICL8069, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the signal processing. This is particularly important in environments where noise and interference may affect the readings. By bringing the input within the common-mode range, the circuit enhances the reliability and accuracy of the measurements.
Overall, this circuit is well-suited for applications in precision temperature sensing, providing the necessary adjustments to ensure accurate and reliable performance in various operating conditions. The careful selection of components and the design of the circuit contribute to its effectiveness in achieving high-precision measurements.This circuit allows zero adjustment as well as slope adjustment. The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 K pots trim any offset at 218 °K (-55 ƒ), and set scale factor. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs the ICL8069, an integrated circuit designed for precision signal processing, particularly in applications requiring accurate temperature measurements. The zero adjustment feature is crucial for calibrating the output to a reference point, ensuring that the readings reflect true values. The slope adjustment, on the other hand, allows for fine-tuning the gain of the circuit, which is essential for maintaining linearity across the operational range.
The inclusion of 5 K potentiometers provides flexibility in trimming both the offset and the scale factor. This is particularly important in temperature measurement applications, where even minor deviations can lead to significant errors. The adjustment pots enable the user to calibrate the circuit at a specific temperature point, in this case, 218 °K (-55 °F), which is typically a critical temperature for certain sensor applications.
The circuit's design ensures that the input signal remains within the common-mode range of the ICL8069, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the signal processing. This is particularly important in environments where noise and interference may affect the readings. By bringing the input within the common-mode range, the circuit enhances the reliability and accuracy of the measurements.
Overall, this circuit is well-suited for applications in precision temperature sensing, providing the necessary adjustments to ensure accurate and reliable performance in various operating conditions. The careful selection of components and the design of the circuit contribute to its effectiveness in achieving high-precision measurements.This circuit allows zero adjustment as well as slope adjustment. The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 K pots trim any offset at 218 °K (-55 ƒ), and set scale factor. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713