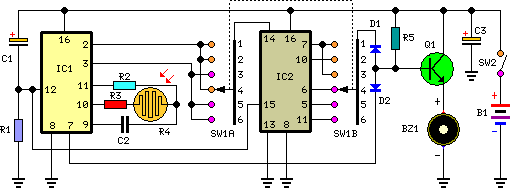
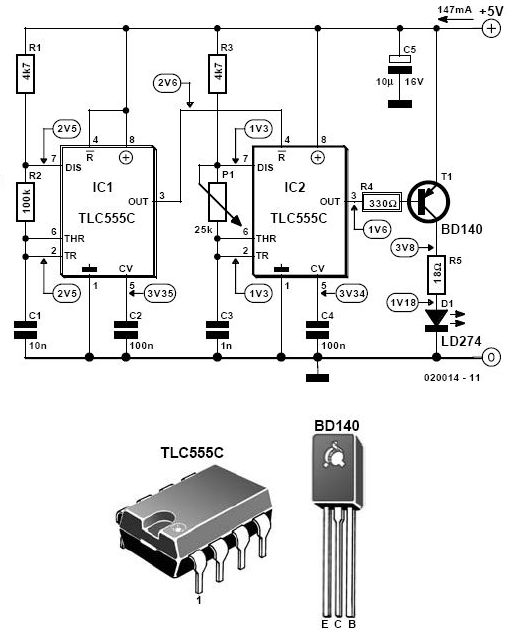
Car Battery And Alternator Monitor Circuit
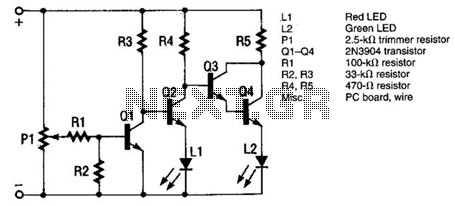
The monitor functions as a basic voltage comparator, utilizing a car battery as its power source. The input voltage to the comparator is adjusted using potentiometer PI. This adjustment ensures that the green LED L2 illuminates when the alternator is functioning correctly, while the red LED L1 lights up when the alternator is not operational. The circuit operates as follows: When the alternator is functioning properly, the battery voltage is higher, and PI is adjusted so that transistor Q1 remains off, which in turn keeps transistor Q2 off. As a result, transistors Q3 and Q4 are fully on, allowing current to flow to green LED L2. Conversely, if the battery voltage drops (indicating the alternator is inoperative), transistor Q1 turns off, which allows transistor Q2 to turn on completely, thus supplying current to red LED L1 to signal a fault. When Q2 is activated, it causes transistors Q3 and Q4 to cease conduction.
The voltage comparator circuit is designed to monitor the operational status of a car's alternator by comparing the battery voltage against a predefined reference voltage set by the potentiometer PI. The circuit comprises several key components: a voltage comparator, transistors, and indicator LEDs. The voltage comparator continuously assesses the battery voltage level. When the alternator is functioning correctly, the voltage exceeds the reference set by PI, keeping Q1 off. This condition prevents Q2 from conducting, which allows Q3 and Q4 to remain active, thereby powering the green LED L2 to indicate normal operation.
In the event of an alternator failure, the battery voltage drops below the reference level. This change causes Q1 to turn off, which in turn enables Q2 to conduct fully. As Q2 becomes active, it interrupts the conduction of Q3 and Q4, resulting in the green LED L2 turning off and the red LED L1 illuminating to indicate a fault condition.
The circuit's design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, allowing for straightforward troubleshooting in automotive applications. The use of LEDs as visual indicators provides immediate feedback to the user regarding the alternator's operational status. The incorporation of a potentiometer for voltage adjustment allows for calibration, ensuring that the system can accommodate variations in battery voltage due to environmental factors or battery health.
Overall, this voltage comparator circuit is a practical solution for monitoring alternator performance, providing clear visual signals that can assist in the maintenance and diagnosis of automotive electrical systems. The monitor is a simple voltage comparator in which a car battery serves as the battery for operation. The input voltage to the comparator is set by adjustment potentiometer PI, which must be adjusted so that the green LED L2 is on when the alternator is operating properly and red LED1 is on when the alternator is inoperative.The circuit operates as follows: When the alternator operates properly, the battery voltage is higher and PI is set so that transistor Ql causes Q2 to be off.
That results in Q3 and Q4 being fully on, thus applying current to green LED L2. If the battery voltage is lowered (alternator inoperative), transistor Ql is turned off. That allows transistor Q2 to turn fully on, applying current to red LED LI, indicating trouble. Once Q2 is on, it causes Q3 and Q4 to go out of conduction. 🔗 External reference
The voltage comparator circuit is designed to monitor the operational status of a car's alternator by comparing the battery voltage against a predefined reference voltage set by the potentiometer PI. The circuit comprises several key components: a voltage comparator, transistors, and indicator LEDs. The voltage comparator continuously assesses the battery voltage level. When the alternator is functioning correctly, the voltage exceeds the reference set by PI, keeping Q1 off. This condition prevents Q2 from conducting, which allows Q3 and Q4 to remain active, thereby powering the green LED L2 to indicate normal operation.
In the event of an alternator failure, the battery voltage drops below the reference level. This change causes Q1 to turn off, which in turn enables Q2 to conduct fully. As Q2 becomes active, it interrupts the conduction of Q3 and Q4, resulting in the green LED L2 turning off and the red LED L1 illuminating to indicate a fault condition.
The circuit's design emphasizes simplicity and effectiveness, allowing for straightforward troubleshooting in automotive applications. The use of LEDs as visual indicators provides immediate feedback to the user regarding the alternator's operational status. The incorporation of a potentiometer for voltage adjustment allows for calibration, ensuring that the system can accommodate variations in battery voltage due to environmental factors or battery health.
Overall, this voltage comparator circuit is a practical solution for monitoring alternator performance, providing clear visual signals that can assist in the maintenance and diagnosis of automotive electrical systems. The monitor is a simple voltage comparator in which a car battery serves as the battery for operation. The input voltage to the comparator is set by adjustment potentiometer PI, which must be adjusted so that the green LED L2 is on when the alternator is operating properly and red LED1 is on when the alternator is inoperative.The circuit operates as follows: When the alternator operates properly, the battery voltage is higher and PI is set so that transistor Ql causes Q2 to be off.
That results in Q3 and Q4 being fully on, thus applying current to green LED L2. If the battery voltage is lowered (alternator inoperative), transistor Ql is turned off. That allows transistor Q2 to turn fully on, applying current to red LED LI, indicating trouble. Once Q2 is on, it causes Q3 and Q4 to go out of conduction. 🔗 External reference