Simple Lead-Acid Battery Charger Circuit
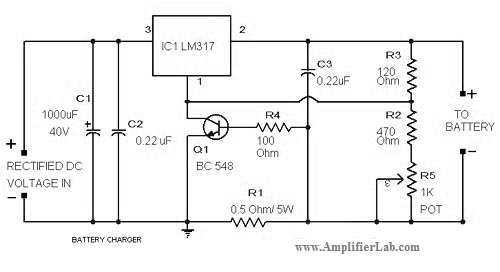
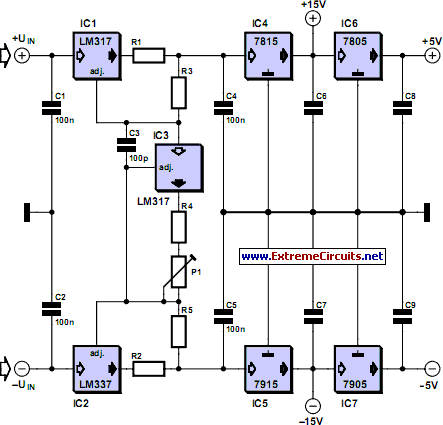
The circuit diagram of a lead-acid battery charger is presented here. The main component of this circuit is the IC LM317.
The lead-acid battery charger circuit utilizing the LM317 voltage regulator is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries while providing adjustable output voltage and current regulation. The LM317 is a popular adjustable three-terminal voltage regulator that can output a voltage range from 1.25V to 37V, making it suitable for charging various types of lead-acid batteries.
In this circuit, the input voltage is typically higher than the desired output voltage, often sourced from an AC to DC converter or a rectified power supply. The LM317 requires a minimum input-to-output voltage differential to function effectively, which is generally around 3V. Thus, if charging a 12V battery, the input voltage should be at least 15V.
The configuration of the LM317 in this application involves two resistors, R1 and R2, which set the output voltage according to the formula: Vout = Vref (1 + R2/R1) + Iadj * R2. Here, Vref is approximately 1.25V. By selecting appropriate resistor values, the output voltage can be tailored to match the nominal voltage of the battery being charged.
To ensure safe charging, a current limiting feature is often integrated into the circuit. This can be accomplished by including a sense resistor in series with the load, which allows the circuit to monitor the charging current. If the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the LM317 will reduce the output voltage, thus preventing overcharging and extending the lifespan of the battery.
Additionally, it is advisable to include a heat sink on the LM317, as it may dissipate significant heat during operation, especially when charging at higher currents. Capacitors are also recommended at the input and output of the LM317 to stabilize the voltage and filter out any noise.
Overall, the lead-acid battery charger circuit using the LM317 is a versatile and effective solution for charging batteries safely and efficiently, with adjustable output parameters to accommodate various battery specifications.The circuit diagram of lead acid battery charger has been described here. The core part of this circuit is the IC LM 317. 🔗 External reference
The lead-acid battery charger circuit utilizing the LM317 voltage regulator is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries while providing adjustable output voltage and current regulation. The LM317 is a popular adjustable three-terminal voltage regulator that can output a voltage range from 1.25V to 37V, making it suitable for charging various types of lead-acid batteries.
In this circuit, the input voltage is typically higher than the desired output voltage, often sourced from an AC to DC converter or a rectified power supply. The LM317 requires a minimum input-to-output voltage differential to function effectively, which is generally around 3V. Thus, if charging a 12V battery, the input voltage should be at least 15V.
The configuration of the LM317 in this application involves two resistors, R1 and R2, which set the output voltage according to the formula: Vout = Vref (1 + R2/R1) + Iadj * R2. Here, Vref is approximately 1.25V. By selecting appropriate resistor values, the output voltage can be tailored to match the nominal voltage of the battery being charged.
To ensure safe charging, a current limiting feature is often integrated into the circuit. This can be accomplished by including a sense resistor in series with the load, which allows the circuit to monitor the charging current. If the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the LM317 will reduce the output voltage, thus preventing overcharging and extending the lifespan of the battery.
Additionally, it is advisable to include a heat sink on the LM317, as it may dissipate significant heat during operation, especially when charging at higher currents. Capacitors are also recommended at the input and output of the LM317 to stabilize the voltage and filter out any noise.
Overall, the lead-acid battery charger circuit using the LM317 is a versatile and effective solution for charging batteries safely and efficiently, with adjustable output parameters to accommodate various battery specifications.The circuit diagram of lead acid battery charger has been described here. The core part of this circuit is the IC LM 317. 🔗 External reference