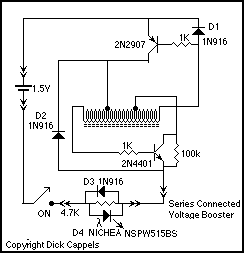
Car Battery Charger
This charger is designed to quickly and efficiently charge most lead-acid batteries. It is an electronics project that is easy to construct, and a circuit diagram is included.
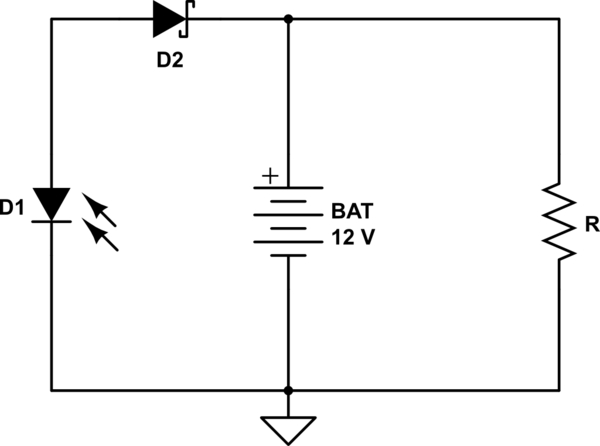
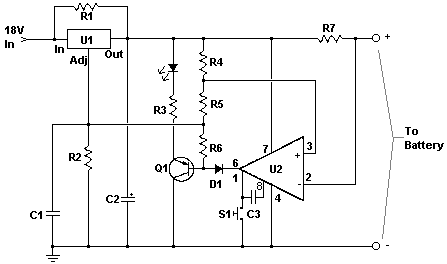
The lead-acid battery charger circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to ensure safe and effective charging. The primary components include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and various protection elements.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging. This lower voltage is then fed into a rectifier, which converts the AC voltage into DC voltage. A common choice for the rectifier is a bridge rectifier configuration, which utilizes four diodes arranged in a bridge formation to efficiently convert the AC input.
After rectification, the DC voltage may require regulation to ensure that the charging voltage does not exceed the battery's specifications. A voltage regulator, such as a linear regulator or a switching regulator, can be employed to maintain a constant output voltage. This is critical to prevent overcharging, which can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate protection features such as fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against overcurrent conditions, as well as diodes to prevent reverse polarity connections. An LED indicator can also be included to signal when the charger is active, providing visual feedback to the user.
The circuit diagram included with the project will illustrate the connections between these components, detailing the input and output terminals, as well as any additional features such as adjustment potentiometers for fine-tuning the output voltage. This project is suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike, offering a practical solution for charging lead-acid batteries efficiently and safely.This charger will quickly and easily charge most any lead acid battery. Electronics project, easy to build, with circuit diagram included.. 🔗 External reference
The lead-acid battery charger circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to ensure safe and effective charging. The primary components include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and various protection elements.
The transformer steps down the AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging. This lower voltage is then fed into a rectifier, which converts the AC voltage into DC voltage. A common choice for the rectifier is a bridge rectifier configuration, which utilizes four diodes arranged in a bridge formation to efficiently convert the AC input.
After rectification, the DC voltage may require regulation to ensure that the charging voltage does not exceed the battery's specifications. A voltage regulator, such as a linear regulator or a switching regulator, can be employed to maintain a constant output voltage. This is critical to prevent overcharging, which can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate protection features such as fuses or circuit breakers to safeguard against overcurrent conditions, as well as diodes to prevent reverse polarity connections. An LED indicator can also be included to signal when the charger is active, providing visual feedback to the user.
The circuit diagram included with the project will illustrate the connections between these components, detailing the input and output terminals, as well as any additional features such as adjustment potentiometers for fine-tuning the output voltage. This project is suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike, offering a practical solution for charging lead-acid batteries efficiently and safely.This charger will quickly and easily charge most any lead acid battery. Electronics project, easy to build, with circuit diagram included.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713