Car maintenance thyristor voltage regulator
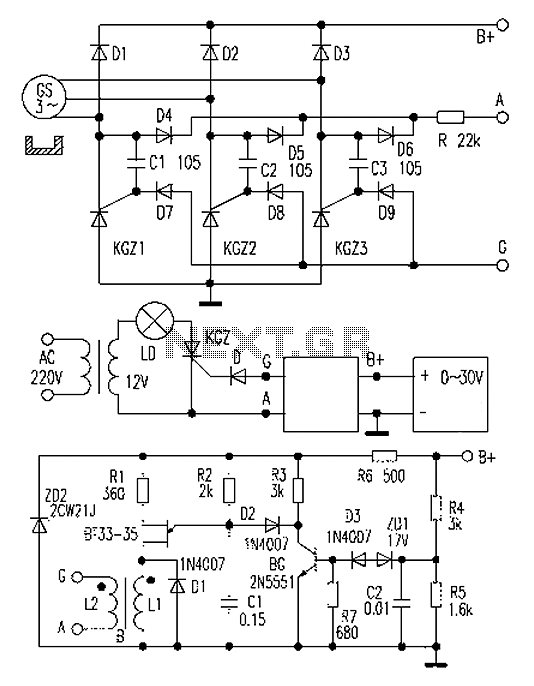
An automobile permanent magnet alternator can fail, causing headlights to suddenly brighten and then go out while driving at night. The issue may stem from a damaged voltage regulator, leading to voltage spikes. This generator, a JFYJ2102 type (28V/36A) AC permanent magnet generator, is designed for higher power and improved efficiency. The aircraft trigger regulator circuit board has been lost, and the generator wiring diagram is provided. The circuit features a three-phase bridge rectifier with semi-controlled thyristors, where G represents the trigger pole for the three thyristors. Simultaneously, diodes D7, D8, and D9 serve as extreme isolation diodes for the three SCRs KGZ1, KGZ2, and KGZ3. Capacitors C1, C2, and C3 are used to prevent false triggering of the thyristors and to protect against high voltage pulses. Diodes D4, D5, and D6 act as isolation diodes to prevent short circuits in the generator's three-phase winding, ensuring proper triggering of the thyristors. The synchronous detection control circuit and transistor relaxation oscillator circuit, composed of a single-junction transistor BT, manage the operation. When power is applied, the oscillator is powered through a current limiting resistor R6 and a zener diode ZD2, charging capacitor C1. The voltage across C1 triggers the discharge through the isolation transformer, and the cycle continues. The output pulse is synchronized with the pulsating power from the three-phase rectifier. When the voltage exceeds 28V, ZD1 conducts, stopping the oscillator and preventing SCR triggering. Below 28V, the oscillator resumes operation, allowing the SCR to conduct and power the output. The circuit is designed to maintain the output voltage at or below 28V. If the trigger current is insufficient, resistance R can be adjusted. The circuit components include metal film resistors rated at 1/2W, a magnetic transformer core, and enameled wire for the windings. When testing the circuit, if the output voltage exceeds 28V, the LD light bulb extinguishes, and it lights up again when below this threshold. The regulator circuit board should be sealed with silicone rubber for protection. This regulator has shown good performance and can be used for similar generators. For a 14V generator, adjustments to component values are necessary, including R, ZD1, R6, and ZD2.
The JFYJ2102 type AC permanent magnet generator operates by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy using permanent magnets. The generator's output is three-phase AC, which is then rectified using a three-phase bridge rectifier composed of thyristors. The thyristors are controlled through a triggering mechanism that ensures they conduct at the appropriate times, allowing for efficient power conversion and regulation.
The voltage regulation process is critical for maintaining a stable output voltage, particularly in automotive applications where fluctuations can affect performance and safety. The use of zener diodes in the circuit provides a voltage reference, ensuring that the system responds correctly to changes in load and input conditions. The isolation diodes prevent backfeeding into the generator, which could lead to damage or malfunction.
The design of the circuit includes careful consideration of component ratings and specifications to ensure reliability and longevity. The use of metal film resistors and appropriate transformer materials minimizes losses and enhances the overall efficiency of the system. The winding ratios of the isolation transformer are chosen to optimize the trigger pulse characteristics, ensuring that the thyristors are activated at the right moments.
In practical applications, the installation of the regulator circuit board should be performed with attention to environmental factors, such as moisture and dust, which can compromise the integrity of the components. Sealing the board with silicone rubber provides a protective barrier, extending the lifespan of the regulator in automotive environments.
Overall, the design and implementation of the JFYJ2102 generator and its associated voltage regulator circuit exemplify advanced engineering principles in power electronics, focusing on reliability, efficiency, and adaptability to various operational conditions.An automobile permanent magnet alternator failure, the phenomenon of cars at night driving, headlights suddenly increase in brightness, then goes out. Analyzing the generator v oltage regulator may be damaged, resulting in the voltage rise due. This generator has no part excitation coil can not use a conventional voltage regulator substitution. This machine is JFYJ2102 type (28V/36A) AC permanent magnet generator, higher power, better use. Aircraft trigger regulator circuit board has been lost, as shown by the actual mapping generator wiring diagram in Fig.
The circuit is a three-phase bridge rectifier semi-controlled thyristor surge line, G for the three-way thyristor trigger pole, and at the same time is triggered, D7, D8, D9, respectively, for the three SCR KGZ1, KGZ2, KGZ3 trigger extreme isolation diode, C1, C2, C3 is to prevent interference with pulse thyristor three false triggering while protecting three pole SCR trigger, the breakdown will not be too high and high voltage pulse, play a protective role; D4, D5, D6 of isolation diode to prevent the three SCR cathode is directly connected, and the resulting three-phase winding of the generator is short-circuited in order to give the three thyristor cathode electrode is applied to the trigger and the trigger pulse. Synchronous detection control circuit and transistor relaxation oscillator circuit consists of BG this single-junction transistor BT composition than the composition.
When the B + on the termination power, through the current limiting resistor R6 and zener diode ZD2 to the oscillator power supply via a resistor R2 to the capacitor C1 is charged, when the voltage rises across the single-junction transistor G1 peak voltage of BT, BTs e, b1 extremely conductive, capacitor C1 by BT of e, the primary L1 b1 pole isolation transformer to discharge. When the voltage of C1 drops to the valley point BT, BTs e, b1 extremely restore blocked. Then began the second capacitor C1 charge/discharge, so the cycle. After the start-up circuit, through the isolation transformer B L2 of the output pulse, the G, A is added to the end of the SCR triggered thyristor pole leaving.
Since the power from the three-phase rectifier pulsating power, so the output pulse in synchronization with the pulsating power thyristor can be synchronized trigger. When the B + terminal voltage reaches or ZD1 breakdown conduction, BG base potential rises above 28V, BG conduction, the collector potential decreases, the diode D2 is turned on, so that a short circuit across C1, the oscillator to stop, SCR not the trigger signal, the zero crossing is blocked.
When the voltage is below 28V, ZD1 breakdown is not, BG group is extremely low potential, BG off, its collector is high potential, D2 off, oscillator, SCR is triggered by conduction, the rectifier output current outward powered by. So again and again, always the rectifier output voltage of the generator does not exceed 28V. If the trigger current is too small, it can be appropriate to reduce the resistance R in Figure 1. Selection of all the circuit resistance metal film resistors 1/2W A, B selected magnetic tank or cross-sectional area of 0.5 to 0.8c©O S25mm radio transformer core with S0.23 ~ S0.25mm enameled wire, L1 about 100T, L2 around 200T.
Power LD light bulbs, power supply with adjustable output voltage rises when output is 28V, the lamp LD suddenly extinguished; when the voltage is set lower than 28V, the lamp can be lit again LD, otherwise, it should change the value ZD1, R4s. Then trigger the regulator circuit board connected to the corresponding connection generator mounted to the car test run, if stable, to the board with silicone rubber seal to prevent water and dust.
This triggers the regulator by the actual use of good results, this method can be a similar type of generator maintenance; if it is 14V generator can change values of R, ZD1, so just ZD1 is turned on when the 14V far; at the same time to R6 100, ZD2 to 10V zener diode. Car repair thyristor circuit diagram of the voltage regulator shown in FIG.
The JFYJ2102 type AC permanent magnet generator operates by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy using permanent magnets. The generator's output is three-phase AC, which is then rectified using a three-phase bridge rectifier composed of thyristors. The thyristors are controlled through a triggering mechanism that ensures they conduct at the appropriate times, allowing for efficient power conversion and regulation.
The voltage regulation process is critical for maintaining a stable output voltage, particularly in automotive applications where fluctuations can affect performance and safety. The use of zener diodes in the circuit provides a voltage reference, ensuring that the system responds correctly to changes in load and input conditions. The isolation diodes prevent backfeeding into the generator, which could lead to damage or malfunction.
The design of the circuit includes careful consideration of component ratings and specifications to ensure reliability and longevity. The use of metal film resistors and appropriate transformer materials minimizes losses and enhances the overall efficiency of the system. The winding ratios of the isolation transformer are chosen to optimize the trigger pulse characteristics, ensuring that the thyristors are activated at the right moments.
In practical applications, the installation of the regulator circuit board should be performed with attention to environmental factors, such as moisture and dust, which can compromise the integrity of the components. Sealing the board with silicone rubber provides a protective barrier, extending the lifespan of the regulator in automotive environments.
Overall, the design and implementation of the JFYJ2102 generator and its associated voltage regulator circuit exemplify advanced engineering principles in power electronics, focusing on reliability, efficiency, and adaptability to various operational conditions.An automobile permanent magnet alternator failure, the phenomenon of cars at night driving, headlights suddenly increase in brightness, then goes out. Analyzing the generator v oltage regulator may be damaged, resulting in the voltage rise due. This generator has no part excitation coil can not use a conventional voltage regulator substitution. This machine is JFYJ2102 type (28V/36A) AC permanent magnet generator, higher power, better use. Aircraft trigger regulator circuit board has been lost, as shown by the actual mapping generator wiring diagram in Fig.
The circuit is a three-phase bridge rectifier semi-controlled thyristor surge line, G for the three-way thyristor trigger pole, and at the same time is triggered, D7, D8, D9, respectively, for the three SCR KGZ1, KGZ2, KGZ3 trigger extreme isolation diode, C1, C2, C3 is to prevent interference with pulse thyristor three false triggering while protecting three pole SCR trigger, the breakdown will not be too high and high voltage pulse, play a protective role; D4, D5, D6 of isolation diode to prevent the three SCR cathode is directly connected, and the resulting three-phase winding of the generator is short-circuited in order to give the three thyristor cathode electrode is applied to the trigger and the trigger pulse. Synchronous detection control circuit and transistor relaxation oscillator circuit consists of BG this single-junction transistor BT composition than the composition.
When the B + on the termination power, through the current limiting resistor R6 and zener diode ZD2 to the oscillator power supply via a resistor R2 to the capacitor C1 is charged, when the voltage rises across the single-junction transistor G1 peak voltage of BT, BTs e, b1 extremely conductive, capacitor C1 by BT of e, the primary L1 b1 pole isolation transformer to discharge. When the voltage of C1 drops to the valley point BT, BTs e, b1 extremely restore blocked. Then began the second capacitor C1 charge/discharge, so the cycle. After the start-up circuit, through the isolation transformer B L2 of the output pulse, the G, A is added to the end of the SCR triggered thyristor pole leaving.
Since the power from the three-phase rectifier pulsating power, so the output pulse in synchronization with the pulsating power thyristor can be synchronized trigger. When the B + terminal voltage reaches or ZD1 breakdown conduction, BG base potential rises above 28V, BG conduction, the collector potential decreases, the diode D2 is turned on, so that a short circuit across C1, the oscillator to stop, SCR not the trigger signal, the zero crossing is blocked.
When the voltage is below 28V, ZD1 breakdown is not, BG group is extremely low potential, BG off, its collector is high potential, D2 off, oscillator, SCR is triggered by conduction, the rectifier output current outward powered by. So again and again, always the rectifier output voltage of the generator does not exceed 28V. If the trigger current is too small, it can be appropriate to reduce the resistance R in Figure 1. Selection of all the circuit resistance metal film resistors 1/2W A, B selected magnetic tank or cross-sectional area of 0.5 to 0.8c©O S25mm radio transformer core with S0.23 ~ S0.25mm enameled wire, L1 about 100T, L2 around 200T.
Power LD light bulbs, power supply with adjustable output voltage rises when output is 28V, the lamp LD suddenly extinguished; when the voltage is set lower than 28V, the lamp can be lit again LD, otherwise, it should change the value ZD1, R4s. Then trigger the regulator circuit board connected to the corresponding connection generator mounted to the car test run, if stable, to the board with silicone rubber seal to prevent water and dust.
This triggers the regulator by the actual use of good results, this method can be a similar type of generator maintenance; if it is 14V generator can change values of R, ZD1, so just ZD1 is turned on when the 14V far; at the same time to R6 100, ZD2 to 10V zener diode. Car repair thyristor circuit diagram of the voltage regulator shown in FIG.