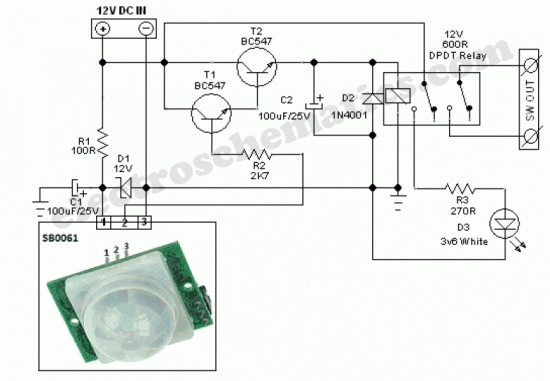
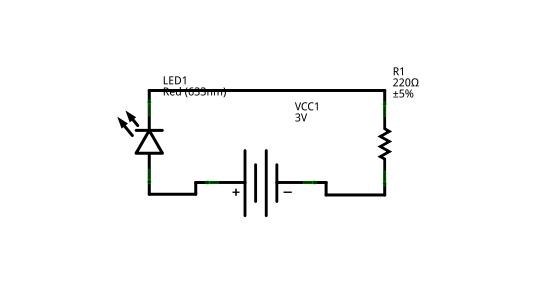
Circuit Diagram Of Slave Flash Light Control
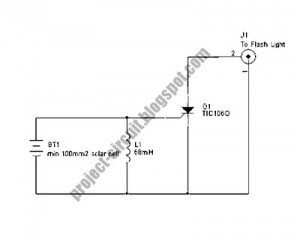
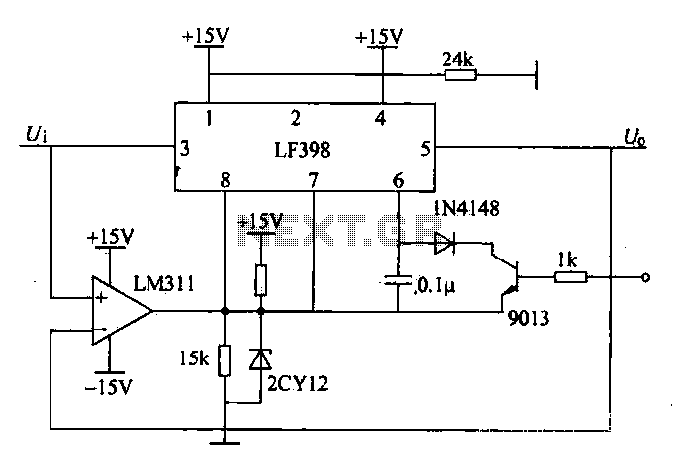
The following circuit illustrates a Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features include a 68mH inductor that provides an automatic trigger for the secondary flash light.
The Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is designed to manage the operation of a secondary flash light in conjunction with a primary flash unit. This circuit typically operates on the principle of inductive coupling, where the 68mH inductor plays a crucial role in energy transfer and triggering the secondary flash light.
In this circuit, the primary flash light acts as the main source of illumination, which, when activated, induces a current in the 68mH inductor. This induced current serves to automatically trigger the secondary flash light, allowing it to illuminate shortly after the primary flash. The timing of the secondary flash can be adjusted by modifying the characteristics of the inductor and associated components, such as capacitors and resistors, which may be included in the circuit for timing control.
The design may also incorporate additional features such as a diode for rectification, ensuring that the current flows in the correct direction and protecting against potential back EMF generated by the inductor. A transistor may be used as a switch to control the activation of the secondary flash light based on the signal received from the inductor.
Overall, this Slave Flash Light Control Circuit provides a reliable method for synchronizing multiple flash lights, enhancing photographic applications or emergency lighting systems where additional illumination is required.The following circuit shows about Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features: 68mH Inductor, give auto trigger for secondary flash light, . 🔗 External reference
The Slave Flash Light Control Circuit is designed to manage the operation of a secondary flash light in conjunction with a primary flash unit. This circuit typically operates on the principle of inductive coupling, where the 68mH inductor plays a crucial role in energy transfer and triggering the secondary flash light.
In this circuit, the primary flash light acts as the main source of illumination, which, when activated, induces a current in the 68mH inductor. This induced current serves to automatically trigger the secondary flash light, allowing it to illuminate shortly after the primary flash. The timing of the secondary flash can be adjusted by modifying the characteristics of the inductor and associated components, such as capacitors and resistors, which may be included in the circuit for timing control.
The design may also incorporate additional features such as a diode for rectification, ensuring that the current flows in the correct direction and protecting against potential back EMF generated by the inductor. A transistor may be used as a switch to control the activation of the secondary flash light based on the signal received from the inductor.
Overall, this Slave Flash Light Control Circuit provides a reliable method for synchronizing multiple flash lights, enhancing photographic applications or emergency lighting systems where additional illumination is required.The following circuit shows about Slave Flash Light Control Circuit Diagram. Features: 68mH Inductor, give auto trigger for secondary flash light, . 🔗 External reference