Cable TV amplifier Using 2 Transistor
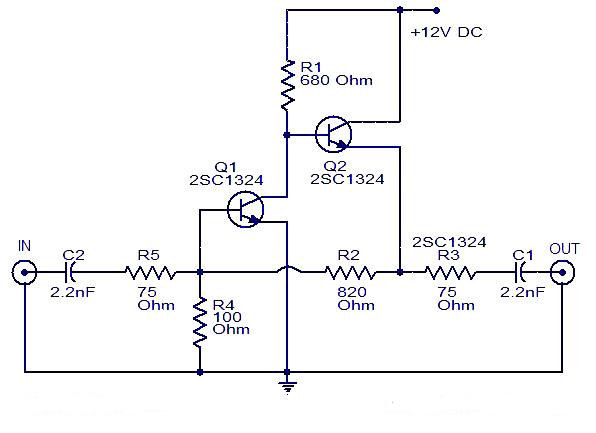
This is a cable TV amplifier utilizing two transistors. The amplifier circuit is designed for cable TV systems using 75 Ohm coaxial cables and operates effectively up to 150 MHz. Transistor T1 is responsible for amplification, providing an expected gain of up to 20 dB. T2 is configured as an emitter follower to provide current gain.
The cable TV amplifier circuit consists of two main components, T1 and T2, both of which are crucial for enhancing the signal strength of the incoming cable TV signal. The first transistor, T1, is configured in a common emitter mode, which allows it to amplify the voltage of the signal. The expected gain of 20 dB indicates that the output signal will be significantly stronger than the input, making it suitable for compensating for signal losses that may occur over long coaxial cable runs.
T2, the second transistor, is configured as an emitter follower. This configuration is important as it provides a high input impedance and a low output impedance, effectively isolating the previous stage from the load. This helps to ensure that the amplification provided by T1 is not adversely affected by the subsequent stages of the circuit or by the load connected to the output. The emitter follower configuration also maintains the voltage level while allowing for a higher current output, which is beneficial for driving loads such as television receivers or further amplification stages.
The circuit is designed to operate within the frequency range of up to 150 MHz, making it suitable for most standard cable TV signals. The use of 75 Ohm coaxial cables is standard in cable television systems, and the amplifier is optimized for this impedance to ensure maximum power transfer and minimal signal reflection.
Overall, this cable TV amplifier circuit is a practical solution for enhancing signal strength in cable television systems, ensuring clear and reliable reception across a range of frequencies. Proper implementation of the circuit with appropriate power supply and layout considerations will maximize performance and reliability.This is cable TV amplifier using 2 transistors. This amplifier circuit is for cable TV systems using Ohm coaxial cables and works fine up to 150MHz. Transistor T1 performs of amplification. Up to 20dB gain expected from the circuit. T2 is wired as an emitter follower current gain. 🔗 External reference
The cable TV amplifier circuit consists of two main components, T1 and T2, both of which are crucial for enhancing the signal strength of the incoming cable TV signal. The first transistor, T1, is configured in a common emitter mode, which allows it to amplify the voltage of the signal. The expected gain of 20 dB indicates that the output signal will be significantly stronger than the input, making it suitable for compensating for signal losses that may occur over long coaxial cable runs.
T2, the second transistor, is configured as an emitter follower. This configuration is important as it provides a high input impedance and a low output impedance, effectively isolating the previous stage from the load. This helps to ensure that the amplification provided by T1 is not adversely affected by the subsequent stages of the circuit or by the load connected to the output. The emitter follower configuration also maintains the voltage level while allowing for a higher current output, which is beneficial for driving loads such as television receivers or further amplification stages.
The circuit is designed to operate within the frequency range of up to 150 MHz, making it suitable for most standard cable TV signals. The use of 75 Ohm coaxial cables is standard in cable television systems, and the amplifier is optimized for this impedance to ensure maximum power transfer and minimal signal reflection.
Overall, this cable TV amplifier circuit is a practical solution for enhancing signal strength in cable television systems, ensuring clear and reliable reception across a range of frequencies. Proper implementation of the circuit with appropriate power supply and layout considerations will maximize performance and reliability.This is cable TV amplifier using 2 transistors. This amplifier circuit is for cable TV systems using Ohm coaxial cables and works fine up to 150MHz. Transistor T1 performs of amplification. Up to 20dB gain expected from the circuit. T2 is wired as an emitter follower current gain. 🔗 External reference