Color sensor amplifier circuit
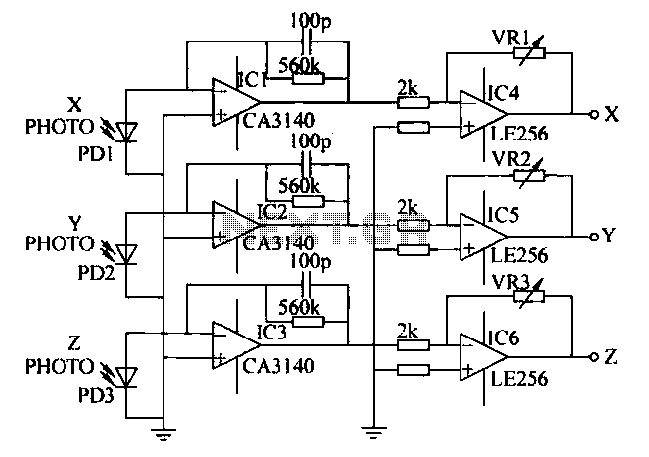
A semiconductor color sensor is designed to identify the color of an object using three photodiodes (PD1, PD2, PD3) and three corresponding color filters (X-PHOTO, Y-PHOTO, Z-PHOTO). Each photodiode is paired with a specific color filter: red (R), green (G), and blue (B). The sensor captures light reflected from an object, which is then separated into three distinct color components. Following this, the color signals are amplified through operational amplifiers, with subsequent processing logic determining the output based on the combination of colors detected. The amplification circuit for the color sensor is illustrated in Figure 7-23, showcasing the X, Y, and Z output colors. This circuit has practical applications in color vision technology.
The semiconductor color sensor operates by utilizing three photodiodes, each equipped with a specific color filter to detect the primary colors of light. The photodiodes PD1, PD2, and PD3 are responsible for capturing light reflected from an object, enabling the sensor to identify its color. The filters, labeled X-PHOTO, Y-PHOTO, and Z-PHOTO, correspond to the red, green, and blue wavelengths, respectively.
When light reflects off an object, it passes through the filters and reaches the photodiodes. Each photodiode generates a current proportional to the intensity of the light filtered through it. The output from each photodiode is a voltage signal that corresponds to the intensity of the red, green, or blue light detected.
These signals are then sent to operational amplifiers, which amplify the weak signals to a more usable level. The amplified signals are processed by a logic circuit that interprets the color data. The logic circuit analyzes the combination of amplified signals to determine the overall color of the object.
The amplification circuit, as depicted in Figure 7-23, includes configurations for the X, Y, and Z outputs, allowing for the effective representation of the color data. This circuit is instrumental in applications requiring color detection and analysis, such as in automated sorting systems, color matching in manufacturing processes, and advanced imaging systems that rely on accurate color representation. The reliability and precision of the semiconductor color sensor make it a valuable component in various technological applications where color identification is critical.Semiconductor color sensor having an identification of the object color capacity by three photodiodes PD1, PD2, PD3 and three color filters X-PHOTO, Y-PHOTO and Z-PHOTO constitution. Respectively mounted on each of the photo diode red (R), green (G), blue (B) color filters, from the reflected object light decomposed into three colors. After the color signal op amps after enlarging processing, processing logic depending on the combination of the color obtained after the actual output. Figure 7-23 is a color sensor s amplification circuit, the X, Y, Z output colors. The practical application of color vision based on the circuit.
The semiconductor color sensor operates by utilizing three photodiodes, each equipped with a specific color filter to detect the primary colors of light. The photodiodes PD1, PD2, and PD3 are responsible for capturing light reflected from an object, enabling the sensor to identify its color. The filters, labeled X-PHOTO, Y-PHOTO, and Z-PHOTO, correspond to the red, green, and blue wavelengths, respectively.
When light reflects off an object, it passes through the filters and reaches the photodiodes. Each photodiode generates a current proportional to the intensity of the light filtered through it. The output from each photodiode is a voltage signal that corresponds to the intensity of the red, green, or blue light detected.
These signals are then sent to operational amplifiers, which amplify the weak signals to a more usable level. The amplified signals are processed by a logic circuit that interprets the color data. The logic circuit analyzes the combination of amplified signals to determine the overall color of the object.
The amplification circuit, as depicted in Figure 7-23, includes configurations for the X, Y, and Z outputs, allowing for the effective representation of the color data. This circuit is instrumental in applications requiring color detection and analysis, such as in automated sorting systems, color matching in manufacturing processes, and advanced imaging systems that rely on accurate color representation. The reliability and precision of the semiconductor color sensor make it a valuable component in various technological applications where color identification is critical.Semiconductor color sensor having an identification of the object color capacity by three photodiodes PD1, PD2, PD3 and three color filters X-PHOTO, Y-PHOTO and Z-PHOTO constitution. Respectively mounted on each of the photo diode red (R), green (G), blue (B) color filters, from the reflected object light decomposed into three colors. After the color signal op amps after enlarging processing, processing logic depending on the combination of the color obtained after the actual output. Figure 7-23 is a color sensor s amplification circuit, the X, Y, Z output colors. The practical application of color vision based on the circuit.