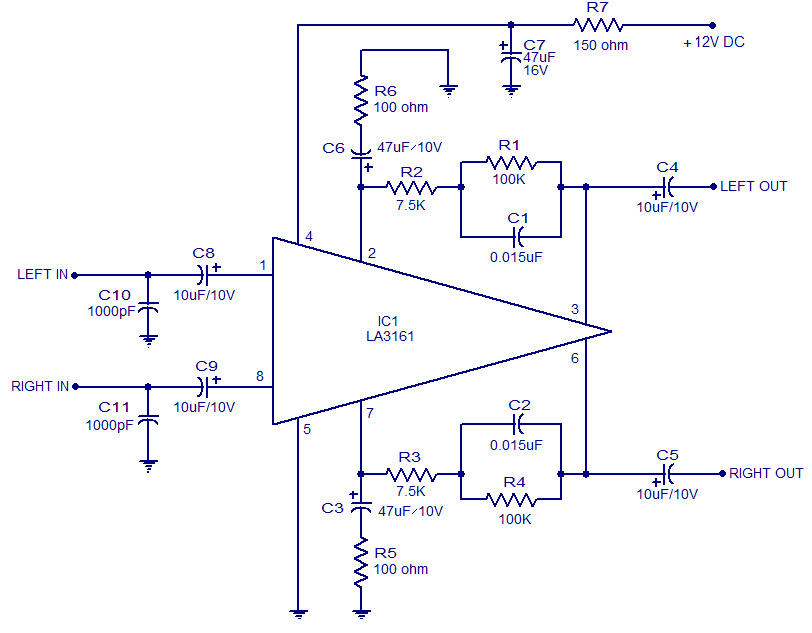
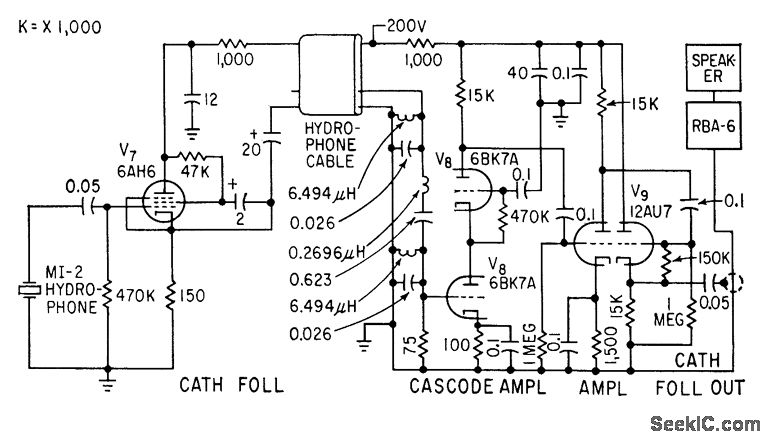
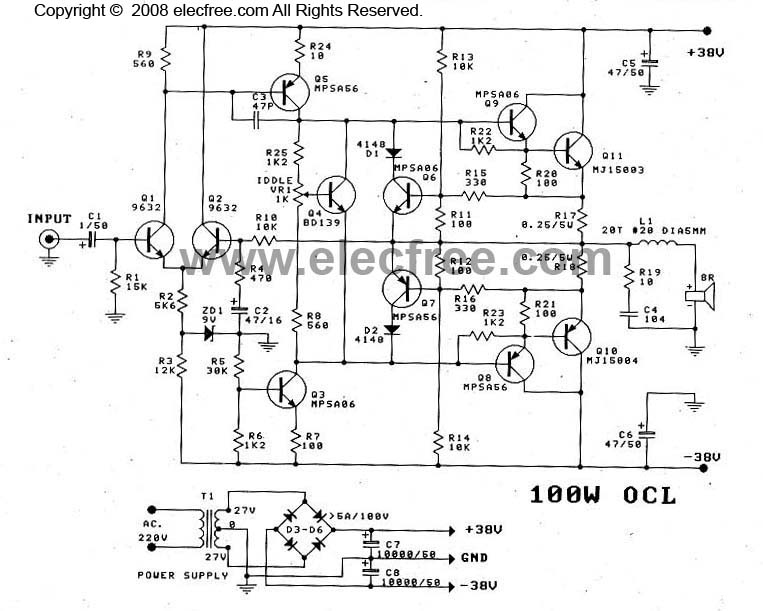
Micropower Single-Supply Instrumentation Amplifier
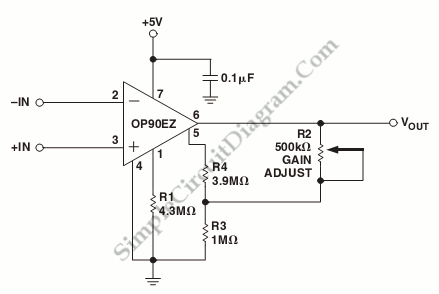
A schematic diagram of a micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is presented. This circuit requires only 15µA of current and can provide over...
The micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is designed for applications where low power consumption is critical. The amplifier operates with a supply voltage typically ranging from 1.8V to 5V, making it suitable for battery-operated devices.
The core of the circuit typically includes three operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide high input impedance, excellent common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), and differential signal amplification. The first two op-amps serve as input stages, allowing the circuit to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any common-mode signals. The third op-amp is used for further amplification and to set the gain of the circuit, which is adjustable through external resistors.
To achieve such low power consumption, the op-amps used in this circuit are specifically designed for micropower applications. They feature low bias currents and low offset voltages, which are crucial for maintaining accuracy in low-power scenarios. The circuit also employs techniques such as biasing and feedback to minimize power usage while maintaining performance.
The output of the instrumentation amplifier provides a differential signal that can be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or further processing stages. The low current requirement of 15µA allows this circuit to be integrated into portable devices, sensor applications, and other low-power systems where efficiency is paramount.
In summary, this micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is an effective solution for low-power applications, providing high accuracy and performance while consuming minimal current.A schematic diagram of a micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is shown below. This circuit only need 15µA of current and can give over.. 🔗 External reference
The micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is designed for applications where low power consumption is critical. The amplifier operates with a supply voltage typically ranging from 1.8V to 5V, making it suitable for battery-operated devices.
The core of the circuit typically includes three operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to provide high input impedance, excellent common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), and differential signal amplification. The first two op-amps serve as input stages, allowing the circuit to amplify the difference between two input signals while rejecting any common-mode signals. The third op-amp is used for further amplification and to set the gain of the circuit, which is adjustable through external resistors.
To achieve such low power consumption, the op-amps used in this circuit are specifically designed for micropower applications. They feature low bias currents and low offset voltages, which are crucial for maintaining accuracy in low-power scenarios. The circuit also employs techniques such as biasing and feedback to minimize power usage while maintaining performance.
The output of the instrumentation amplifier provides a differential signal that can be fed into an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or further processing stages. The low current requirement of 15µA allows this circuit to be integrated into portable devices, sensor applications, and other low-power systems where efficiency is paramount.
In summary, this micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is an effective solution for low-power applications, providing high accuracy and performance while consuming minimal current.A schematic diagram of a micropower single-supply instrumentation amplifier circuit is shown below. This circuit only need 15µA of current and can give over.. 🔗 External reference