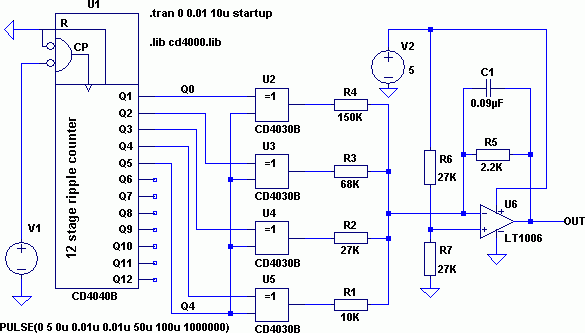
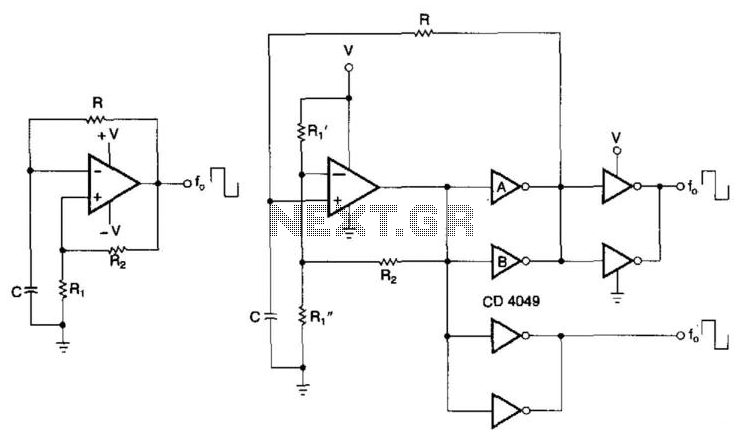
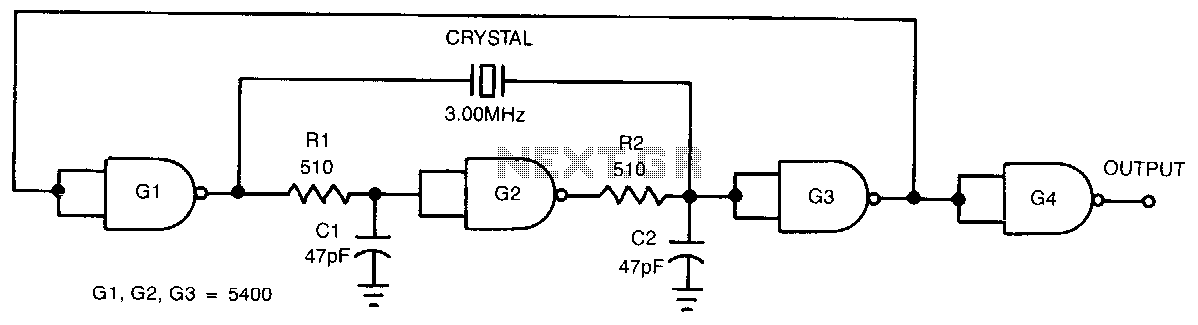
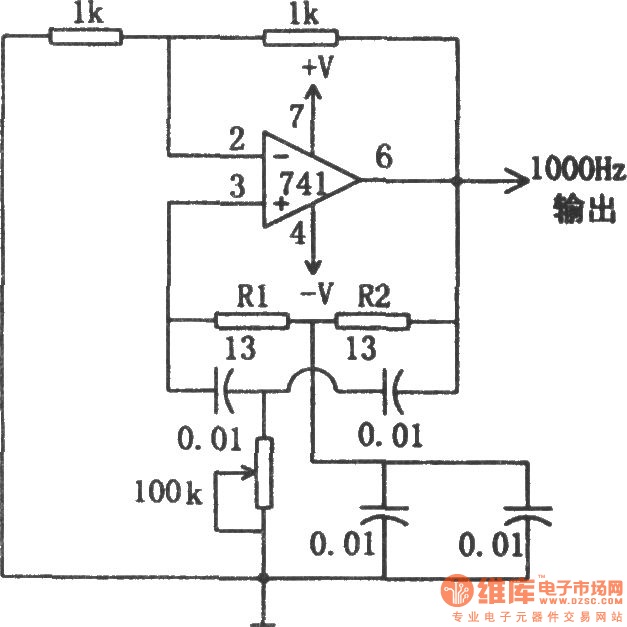
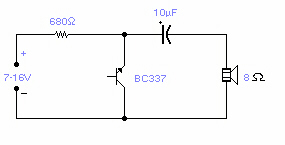
colpitts oscillator
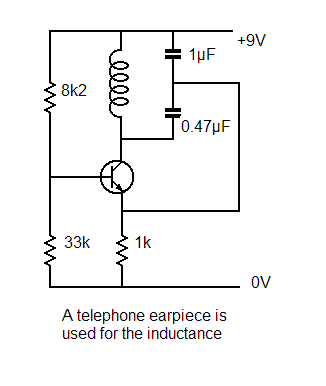
The intent is to utilize the inductance of a standard telephone earpiece as the inductor (L) in a Colpitts oscillator, thereby removing the necessity for a separate amplifier or buffer.
The Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a combination of inductance and capacitance to generate oscillations. In this configuration, the inductance of the telephone earpiece serves as the primary reactive component. The key to the Colpitts oscillator's functionality is its feedback network, which typically consists of two capacitors arranged in series and a single inductor.
In this design, the inductance of the earpiece, which is typically in the range of a few hundred microhenries, can be effectively integrated into the oscillator circuit. The earpiece's inductive properties allow it to resonate at a specific frequency determined by the values of the capacitors and the inductance. The chosen capacitors should be selected to create a suitable resonant frequency, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L \cdot C_{eq}}} \]
where \( C_{eq} \) is the equivalent capacitance of the two capacitors in the feedback network.
To implement this design, the circuit will require a power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current for operation. The output of the Colpitts oscillator can be taken from the junction of the capacitors, which will provide a sinusoidal output signal. This output can be directly used in applications where amplification is not critical, effectively eliminating the need for a separate amplifier or buffer stage.
The use of a telephone earpiece in this application not only serves to simplify the circuit but also reduces component count and potentially lowers the overall cost. However, careful consideration must be given to the earpiece's inductance and its impact on the oscillator's performance, including stability and frequency drift. Additionally, the quality factor (Q) of the inductor will influence the oscillator's output signal amplitude and spectral purity, which are critical parameters in many electronic applications.
In summary, integrating the inductance of a telephone earpiece into a Colpitts oscillator circuit offers a novel approach to oscillator design, streamlining the process by removing the need for additional amplification components while maintaining the essential characteristics of the oscillator.I thought I would try to use a standard telephone earpiece`s inductance as the L of a Colpitts oscillator, and in so doing eliminate the need for a separate amplifer/buffer. 🔗 External reference
The Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a combination of inductance and capacitance to generate oscillations. In this configuration, the inductance of the telephone earpiece serves as the primary reactive component. The key to the Colpitts oscillator's functionality is its feedback network, which typically consists of two capacitors arranged in series and a single inductor.
In this design, the inductance of the earpiece, which is typically in the range of a few hundred microhenries, can be effectively integrated into the oscillator circuit. The earpiece's inductive properties allow it to resonate at a specific frequency determined by the values of the capacitors and the inductance. The chosen capacitors should be selected to create a suitable resonant frequency, which can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L \cdot C_{eq}}} \]
where \( C_{eq} \) is the equivalent capacitance of the two capacitors in the feedback network.
To implement this design, the circuit will require a power supply to provide the necessary voltage and current for operation. The output of the Colpitts oscillator can be taken from the junction of the capacitors, which will provide a sinusoidal output signal. This output can be directly used in applications where amplification is not critical, effectively eliminating the need for a separate amplifier or buffer stage.
The use of a telephone earpiece in this application not only serves to simplify the circuit but also reduces component count and potentially lowers the overall cost. However, careful consideration must be given to the earpiece's inductance and its impact on the oscillator's performance, including stability and frequency drift. Additionally, the quality factor (Q) of the inductor will influence the oscillator's output signal amplitude and spectral purity, which are critical parameters in many electronic applications.
In summary, integrating the inductance of a telephone earpiece into a Colpitts oscillator circuit offers a novel approach to oscillator design, streamlining the process by removing the need for additional amplification components while maintaining the essential characteristics of the oscillator.I thought I would try to use a standard telephone earpiece`s inductance as the L of a Colpitts oscillator, and in so doing eliminate the need for a separate amplifer/buffer. 🔗 External reference