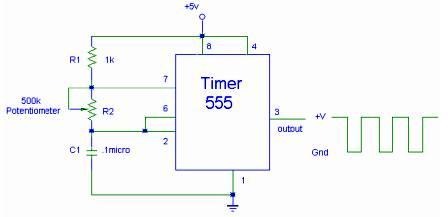
1kHz sine wave oscillator(741)
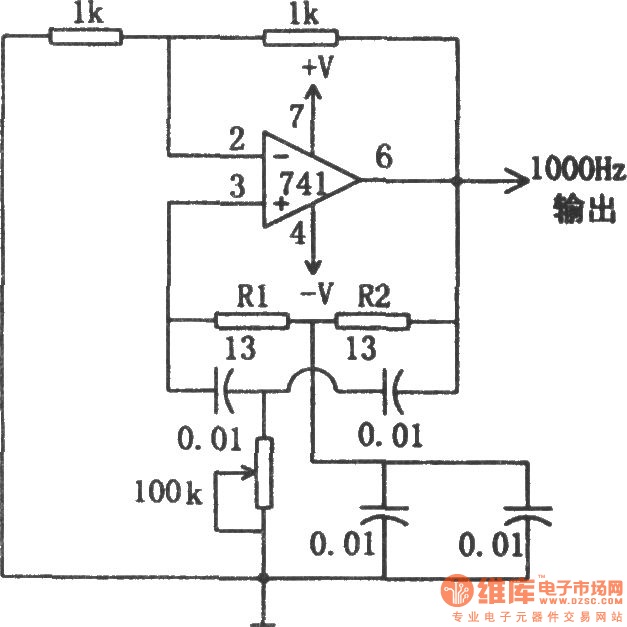
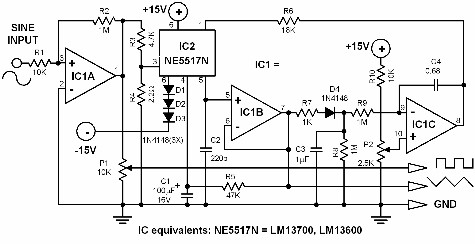
The circuit illustrated in the diagram is a 1 kHz sine wave oscillator circuit. Based on a double-T circuit configuration, it utilizes a standard 741 operational amplifier to generate a 1000 Hz sine wave output. The circuit begins oscillation when a 100 kΩ potentiometer is adjusted, with the oscillation frequency being determined by resistors R1 and R2, which typically have specific values.
The described circuit employs a double-T oscillator topology, which is renowned for its simplicity and effectiveness in producing sine wave outputs. The heart of the circuit is the 741 operational amplifier, a widely used component in analog applications due to its versatility and availability. In this configuration, the operational amplifier is set up to provide necessary gain and feedback, which are crucial for sustaining oscillations.
The oscillation starts when the 100 kΩ potentiometer is adjusted, allowing fine-tuning of the circuit's threshold for initiating oscillation. The resistors R1 and R2 play a pivotal role in determining the frequency of oscillation. Their values, typically chosen for a 1 kHz output, must be carefully calculated to ensure that the circuit resonates at the desired frequency. The relationship between these resistors and the feedback network defines the oscillation frequency, following the formula for a double-T oscillator.
Additionally, the circuit may include capacitors in the feedback loop to stabilize the oscillation and filter any unwanted high-frequency noise. Proper selection of these capacitors is essential to maintain the integrity of the sine wave output. The output of the circuit can be connected to various loads, such as audio applications or signal processing circuits, where a stable sine wave is required.
Overall, this 1 kHz sine wave oscillator circuit exemplifies the fundamental principles of analog signal generation and can serve as a foundational design for more complex applications in electronic engineering.The circuit shown in the chart is 1kHz sine wave oscillator circuit. Basing on the double-T circuit, the circuit using 741ordinary operational amplifier to produce 1000Hz sine wave output. Adjusting 100k? potentiometer will make circuit start oscillation, the oscillation frequency is determined by R1 and R2, and under normal circumstances, the value of two..
🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a double-T oscillator topology, which is renowned for its simplicity and effectiveness in producing sine wave outputs. The heart of the circuit is the 741 operational amplifier, a widely used component in analog applications due to its versatility and availability. In this configuration, the operational amplifier is set up to provide necessary gain and feedback, which are crucial for sustaining oscillations.
The oscillation starts when the 100 kΩ potentiometer is adjusted, allowing fine-tuning of the circuit's threshold for initiating oscillation. The resistors R1 and R2 play a pivotal role in determining the frequency of oscillation. Their values, typically chosen for a 1 kHz output, must be carefully calculated to ensure that the circuit resonates at the desired frequency. The relationship between these resistors and the feedback network defines the oscillation frequency, following the formula for a double-T oscillator.
Additionally, the circuit may include capacitors in the feedback loop to stabilize the oscillation and filter any unwanted high-frequency noise. Proper selection of these capacitors is essential to maintain the integrity of the sine wave output. The output of the circuit can be connected to various loads, such as audio applications or signal processing circuits, where a stable sine wave is required.
Overall, this 1 kHz sine wave oscillator circuit exemplifies the fundamental principles of analog signal generation and can serve as a foundational design for more complex applications in electronic engineering.The circuit shown in the chart is 1kHz sine wave oscillator circuit. Basing on the double-T circuit, the circuit using 741ordinary operational amplifier to produce 1000Hz sine wave output. Adjusting 100k? potentiometer will make circuit start oscillation, the oscillation frequency is determined by R1 and R2, and under normal circumstances, the value of two..
🔗 External reference