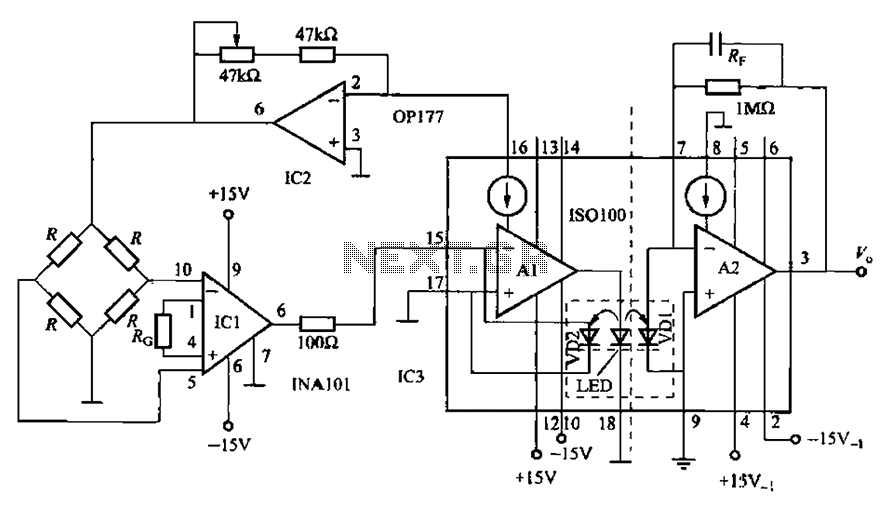
Crystal-controlled signal source
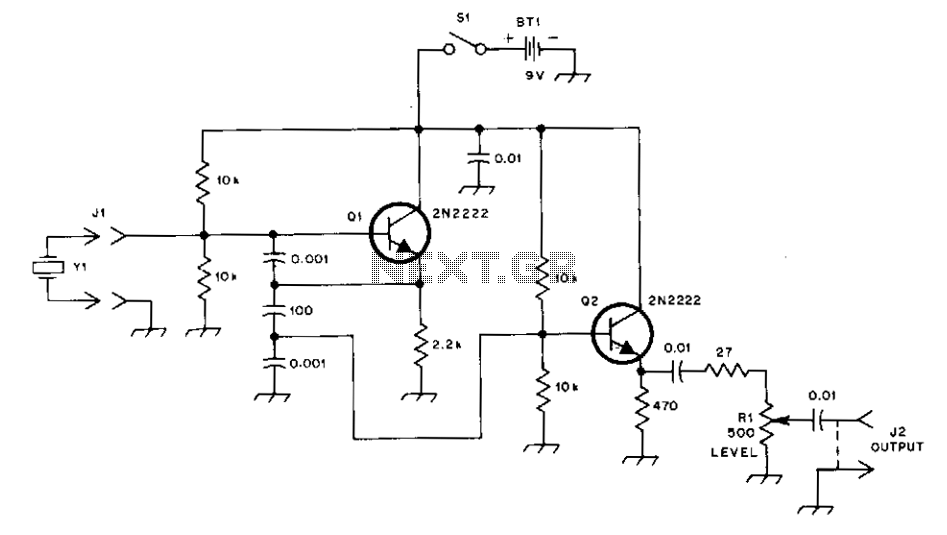
This general-purpose signal source is highly effective for signal-tracing applications. The output level is adjustable, exceeding 1 Vrms into a 50 Ω load. It is compatible with nearly any crystal in the 1 to 15 MHz frequency range. Q1 operates as a Colpitts oscillator, with the output taken from the emitter. A capacitive voltage divider, positioned across the 2.2 Ω emitter resistor, reduces the voltage supplied to the buffer amplifier, Q2. The buffer and emitter follower configuration provides the low input impedance required to drive 50 Ω loads.
The described circuit serves as a versatile signal source, ideal for various applications in electronics testing and development, particularly in signal tracing. The Colpitts oscillator configuration is notable for its stability and ease of tuning, making it suitable for generating sine wave signals at desired frequencies within the specified range. The oscillator's frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate capacitors and inductors in the feedback network, allowing for fine-tuning to specific application needs.
The output stage employs a buffer amplifier, which is crucial for isolating the oscillator from the load. This isolation prevents loading effects that could alter the oscillator's performance. The use of an emitter follower configuration ensures that the output signal maintains the same voltage level while providing the necessary current drive capability.
The capacitive voltage divider serves a dual purpose: it attenuates the output voltage to a suitable level for the buffer amplifier while also maintaining the integrity of the signal. This is particularly important when interfacing with sensitive measurement equipment or when driving loads that require precise voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective approach to generating stable and adjustable signal outputs, catering to the requirements of signal tracing and other related applications in electronic engineering. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures reliable operation across the specified frequency range, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians.This general purpose signal source serves very well in signal-tracing applications. The output level is variable to more than 1 Vrms into a 50 O load. Almost any crystal in the 1 to 15 MHz range can be used. Ql forms a Colpitis oscillator with the output taken from the emitter. A capacitive voltage divider (across the 2.2 emitter resistor) reduces the voltage applied to the buffer amplifier, Q2. The buffer and emitter follower, provides the low input impedance necessary to drive 50 O loads. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a versatile signal source, ideal for various applications in electronics testing and development, particularly in signal tracing. The Colpitts oscillator configuration is notable for its stability and ease of tuning, making it suitable for generating sine wave signals at desired frequencies within the specified range. The oscillator's frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate capacitors and inductors in the feedback network, allowing for fine-tuning to specific application needs.
The output stage employs a buffer amplifier, which is crucial for isolating the oscillator from the load. This isolation prevents loading effects that could alter the oscillator's performance. The use of an emitter follower configuration ensures that the output signal maintains the same voltage level while providing the necessary current drive capability.
The capacitive voltage divider serves a dual purpose: it attenuates the output voltage to a suitable level for the buffer amplifier while also maintaining the integrity of the signal. This is particularly important when interfacing with sensitive measurement equipment or when driving loads that require precise voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies an effective approach to generating stable and adjustable signal outputs, catering to the requirements of signal tracing and other related applications in electronic engineering. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures reliable operation across the specified frequency range, making it a valuable tool for engineers and technicians.This general purpose signal source serves very well in signal-tracing applications. The output level is variable to more than 1 Vrms into a 50 O load. Almost any crystal in the 1 to 15 MHz range can be used. Ql forms a Colpitis oscillator with the output taken from the emitter. A capacitive voltage divider (across the 2.2 emitter resistor) reduces the voltage applied to the buffer amplifier, Q2. The buffer and emitter follower, provides the low input impedance necessary to drive 50 O loads. 🔗 External reference